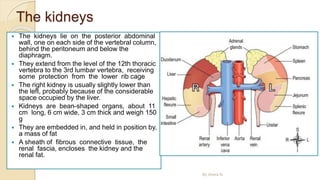
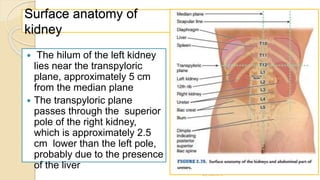
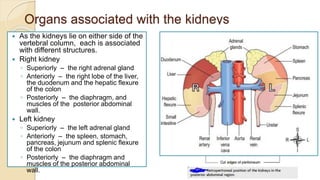
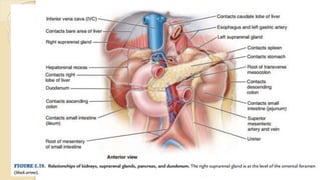
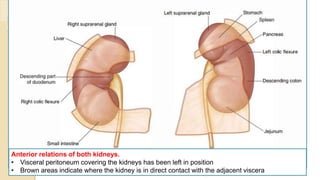
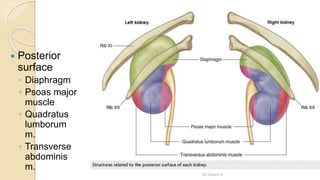
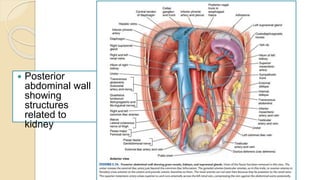
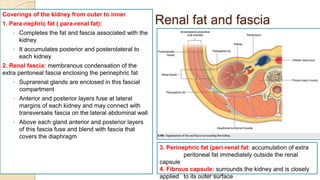
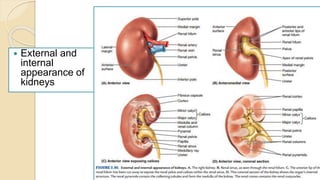
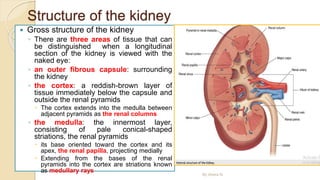
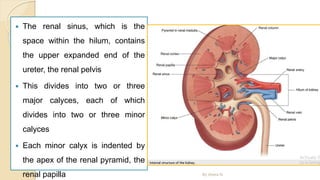
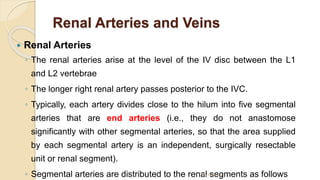
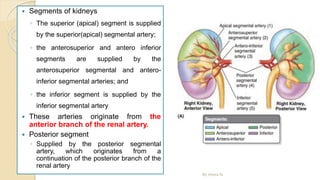
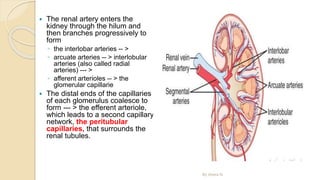
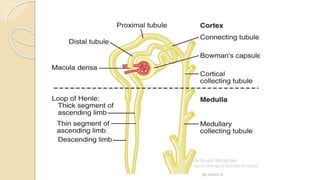
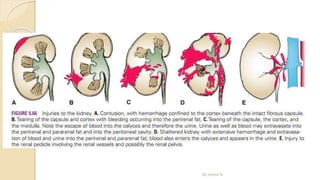
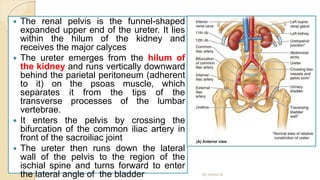
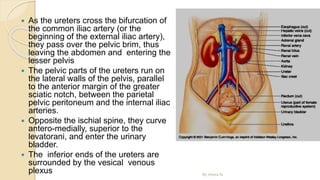
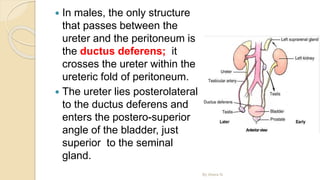
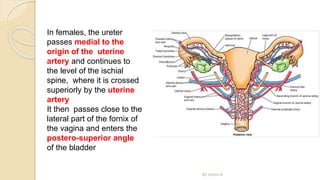
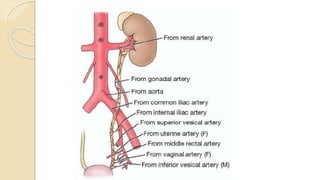
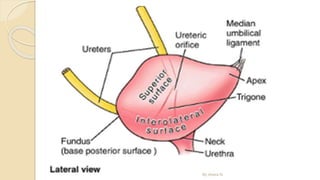
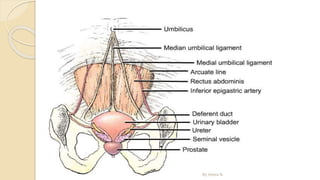
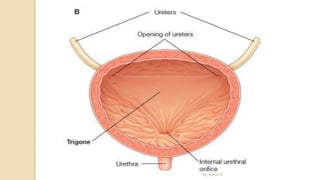
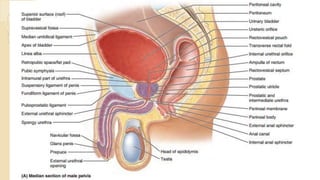
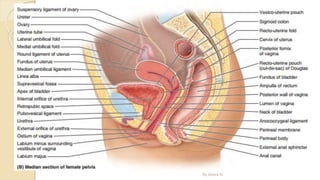
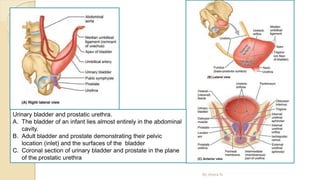
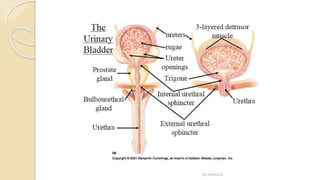
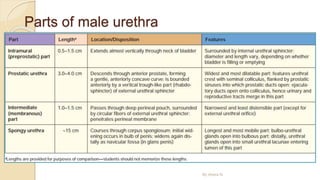
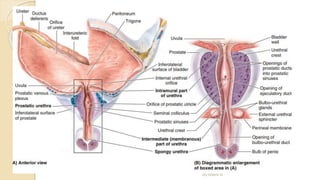
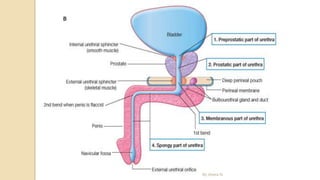
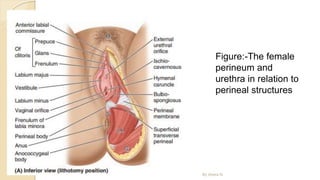
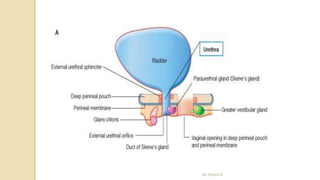
The document provides an overview of the urinary system. It describes the main components which include the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine, which is then transported via the ureters to the bladder. The bladder stores urine until urination, at which point urine exits the body through the urethra. The document also discusses the structures and functions of the kidneys and nephrons in more detail.