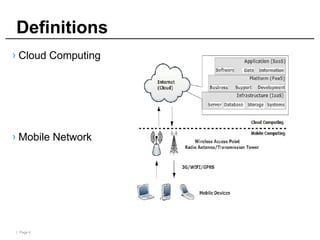
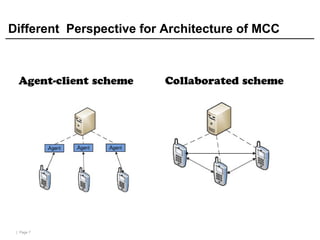
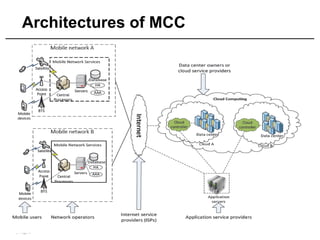
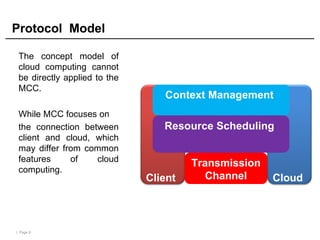
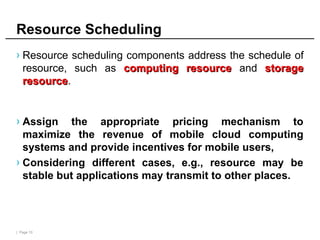
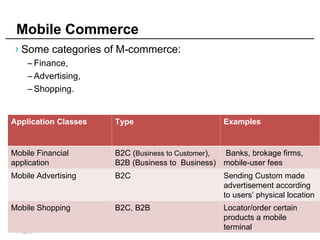
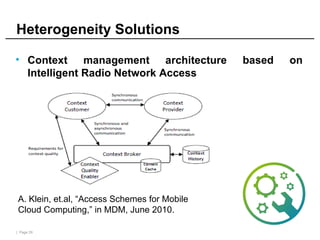
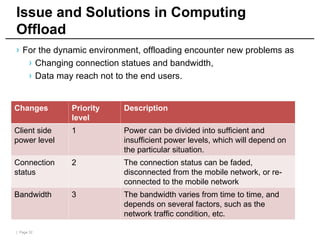
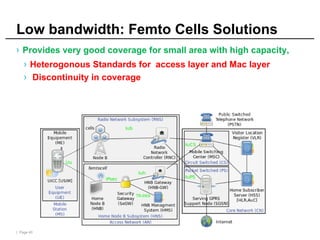
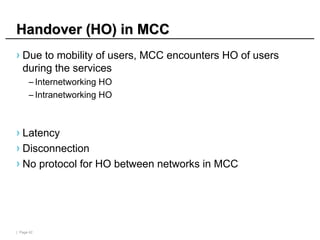
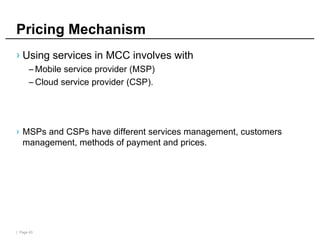
Mobile cloud computing (MCC) refers to an infrastructure where data storage and processing occur outside mobile devices in the cloud. This overcomes limitations of mobile devices like limited storage, processing power and battery life. MCC provides advantages like improved reliability, extended battery life and increased storage and processing capabilities. Key challenges include integrating mobile networks with cloud computing, addressing issues like low bandwidth, heterogeneity and availability. Effective solutions involve offloading computation and data to cloud servers and developing adaptive resource scheduling and context management.

















![| Page 45
References
References
[1] Hoang T. Dinh, etal, “A survey of Mobile Cloud Computing: architecture,
applications, and approaches”, Wireless communications and Mobile Computing
– Wiley, 2012.
[2] M. Satyanarayanan, “Mobile computing: the next decade,” in MCS, June
2010.
[3] Le Guan, etal. “A survey of research on mobile cloud computing”, IEEE/ACIS,
2010.
[4] H. Qui, etal. “Research on mobile cloud computing: review, trend and
perspective”, IEEE 2012.
[5] M. H. Tang, et.al “A dynamic mechanism for handling mobile computing
environmental changes,” in InfoScale, no. 7, pp. 1-9, May 2006.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08mobile-cloud-introduction-221019171335-c8b67d9f/85/08_Mobile-Cloud-Introduction-pdf-45-320.jpg)
