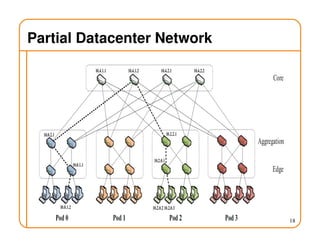
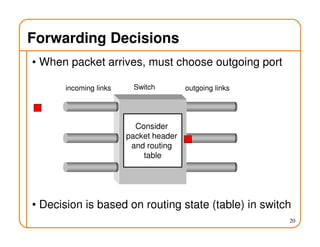
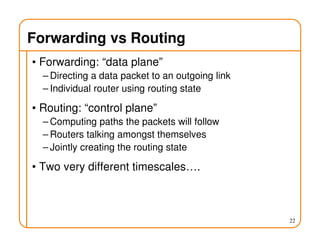
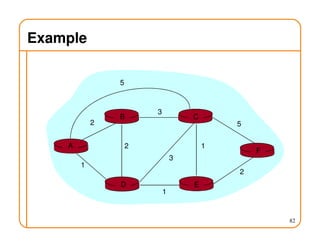
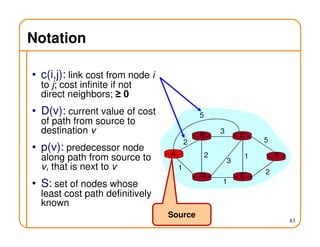
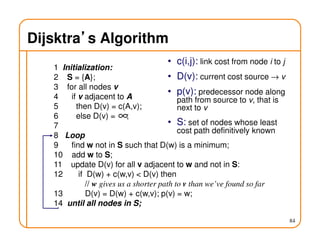
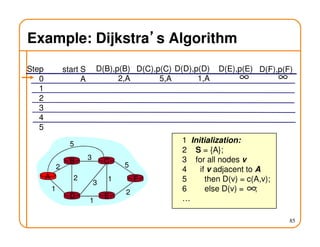
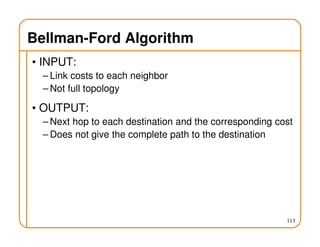
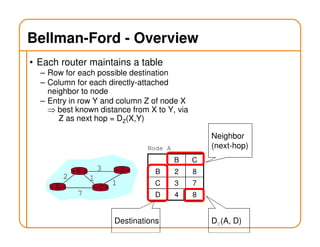
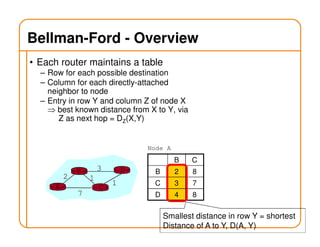
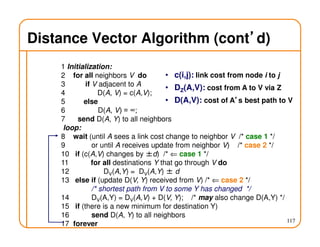
This document provides an overview of routing fundamentals, including:
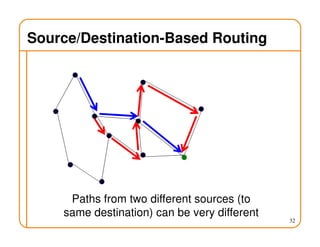
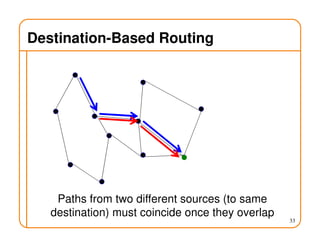
- Routing involves delivering packets from any source to any destination by making forwarding decisions at switches/routers based on routing state.
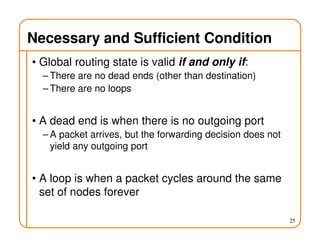
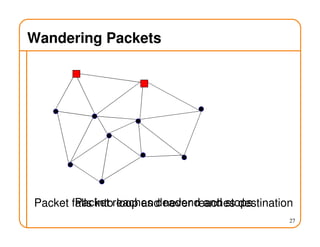
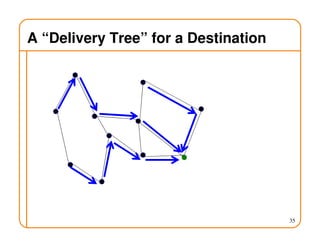
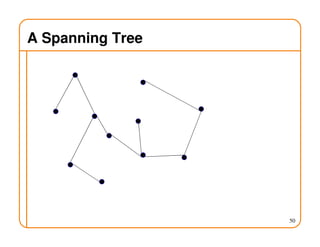
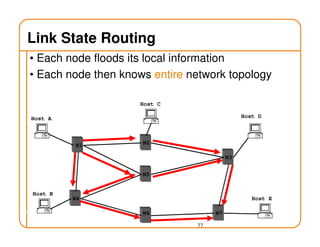
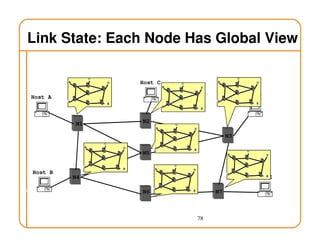
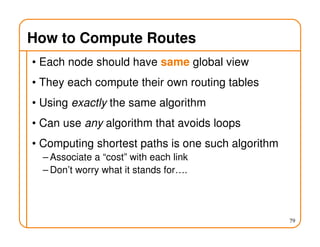
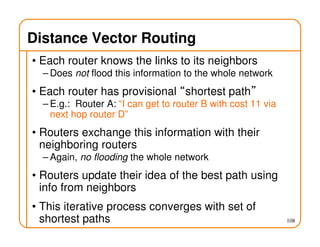
- Routing state can be computed in a distributed manner to avoid loops, such as by minimizing a metric or restricting the network topology to a spanning tree.
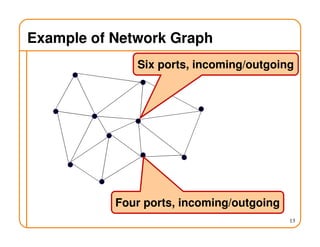
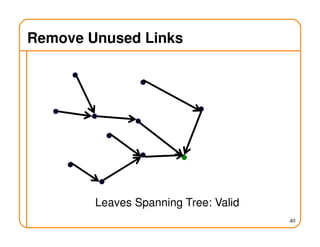
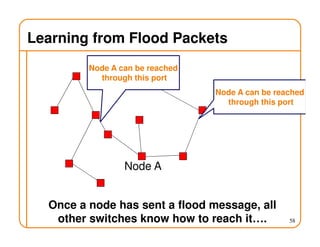
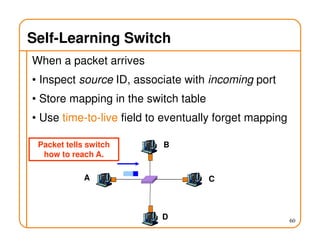
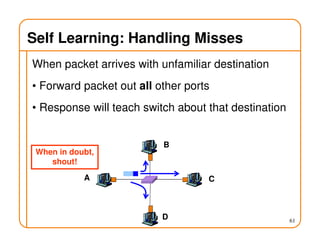
- On a spanning tree, switches can learn routes by observing packet floods without explicitly computing routes, ensuring there is only one path between any two nodes.