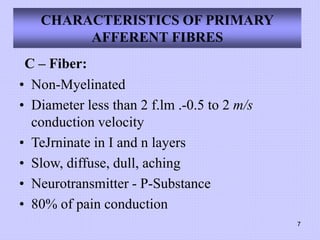
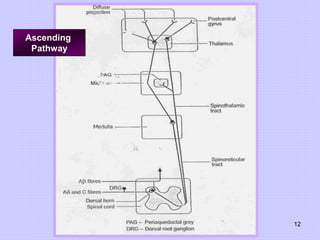
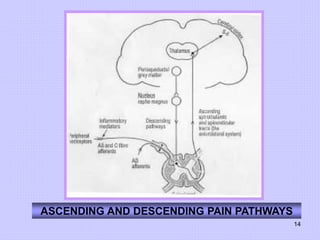
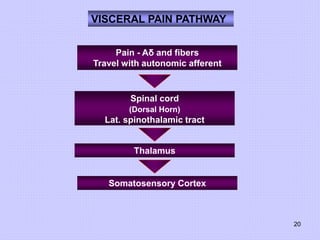
This document discusses pain perception and classification. It describes how pain is categorized into somatic and visceral pain. Somatic pain can be superficial or deep, while visceral pain is sometimes referred to other sites innervated by the same spinal segment. The document also summarizes the characteristics of different types of primary afferent fibers that conduct pain signals, including Aδ fibers and C fibers. Finally, it outlines ascending and descending pain pathways in the central nervous system and various mechanisms of pain modulation.