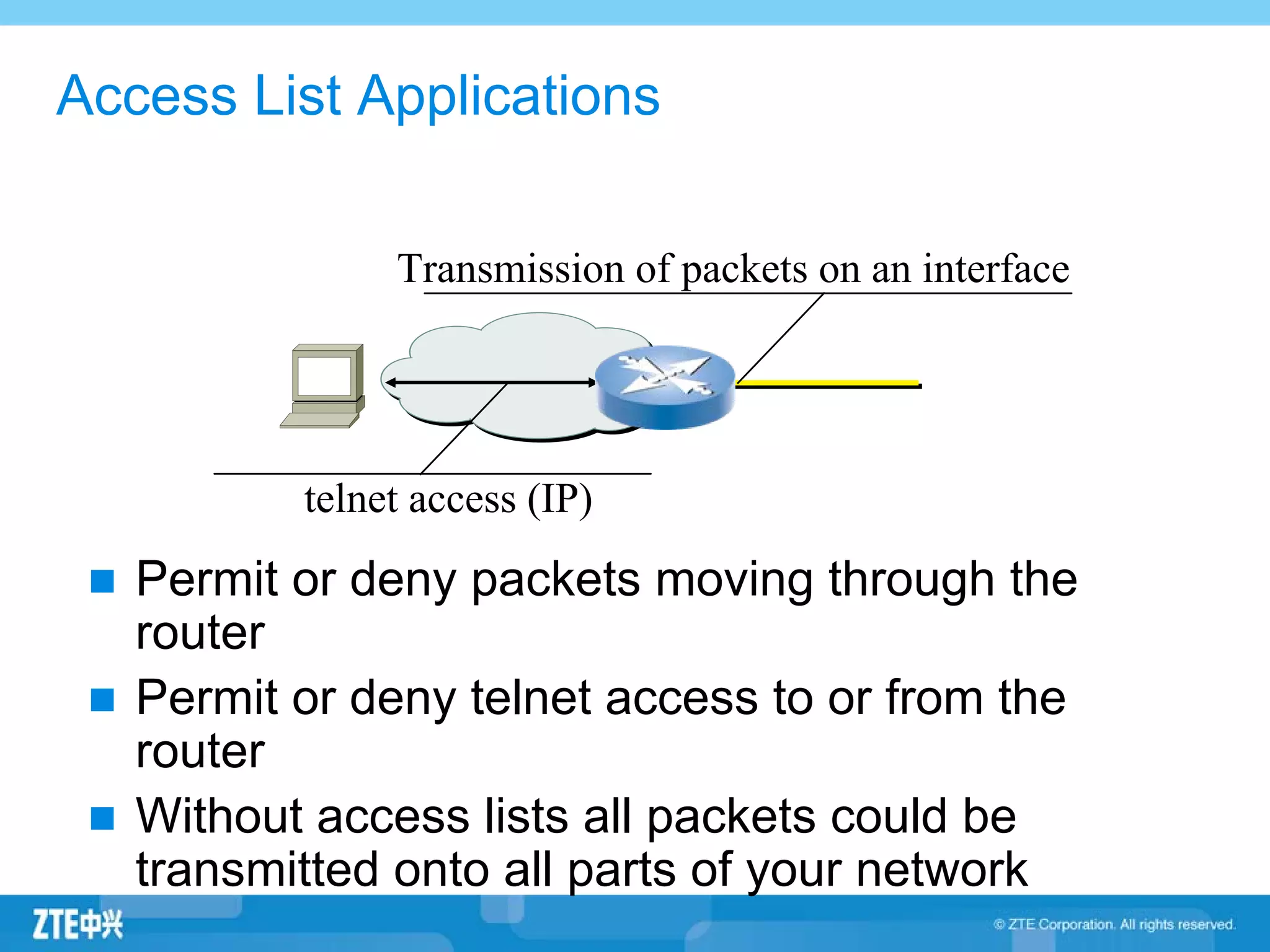
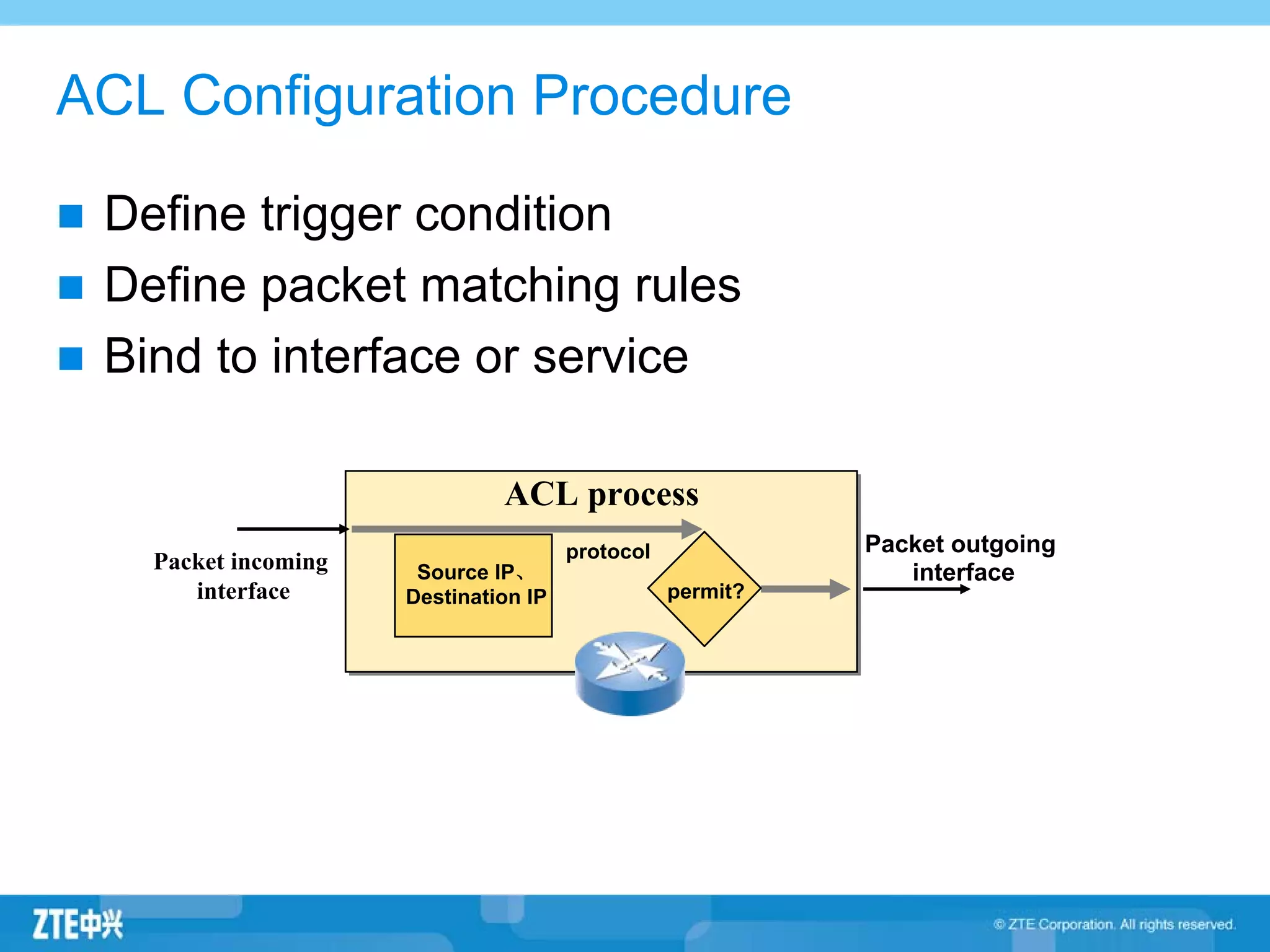
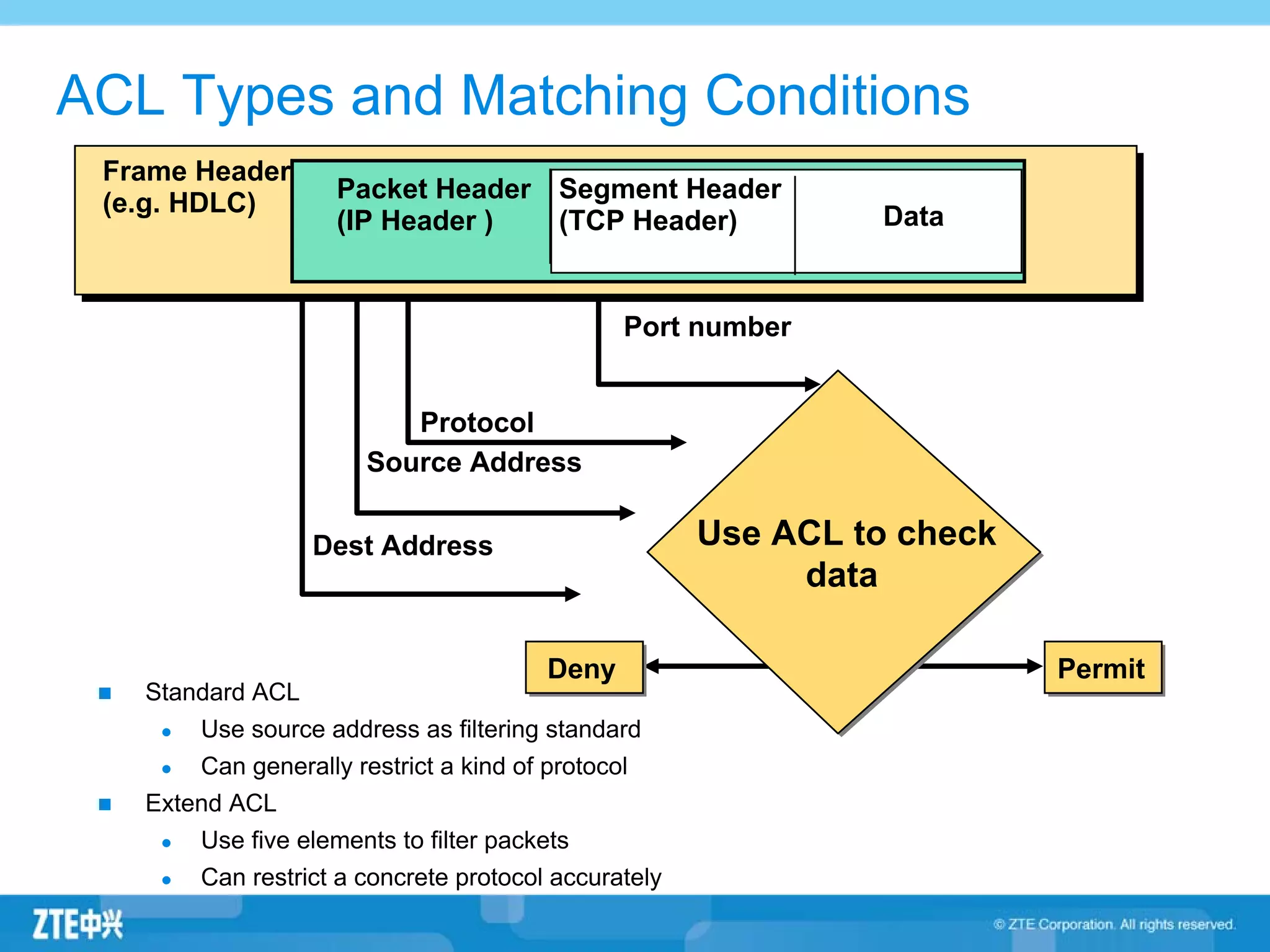
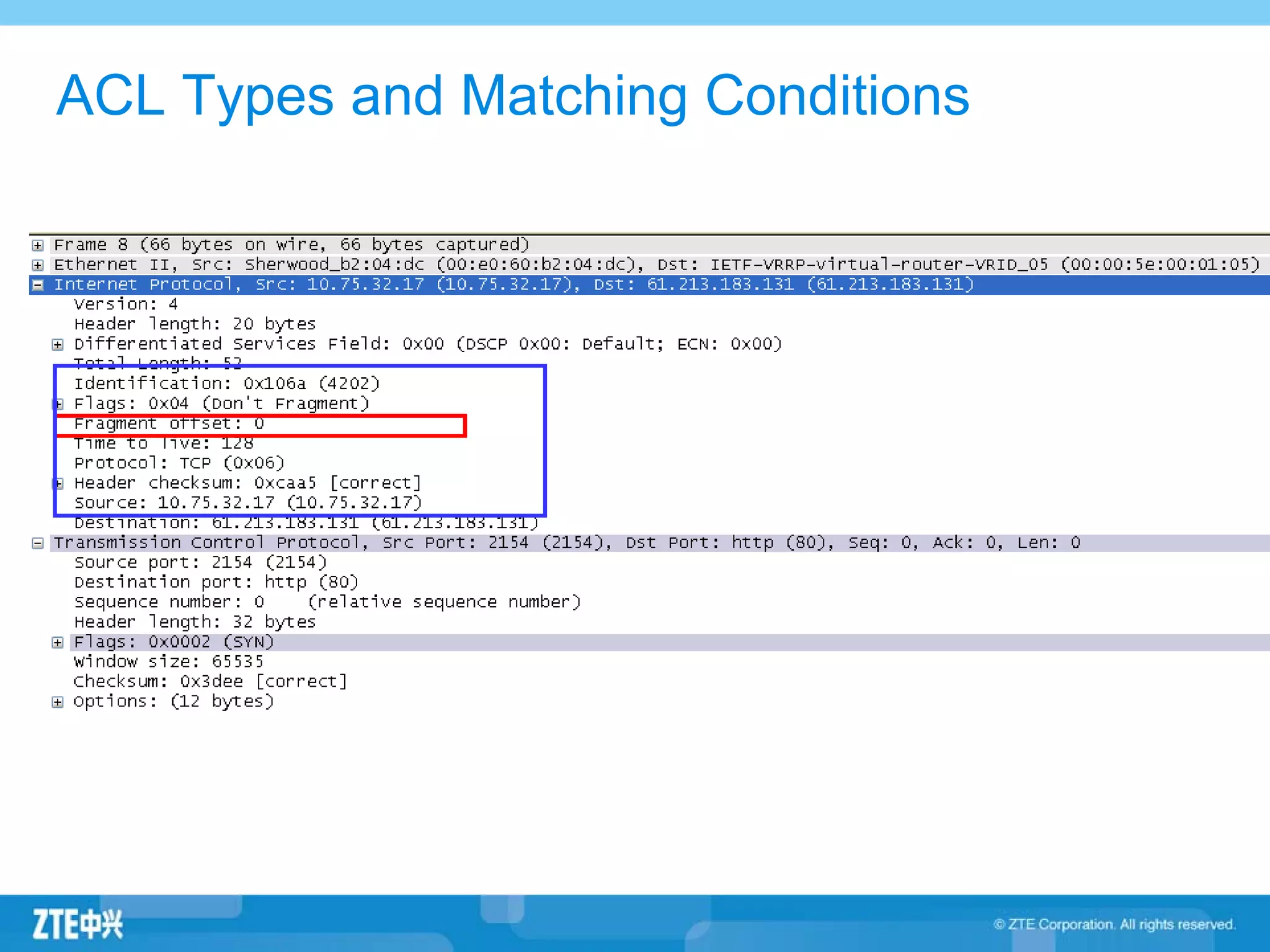
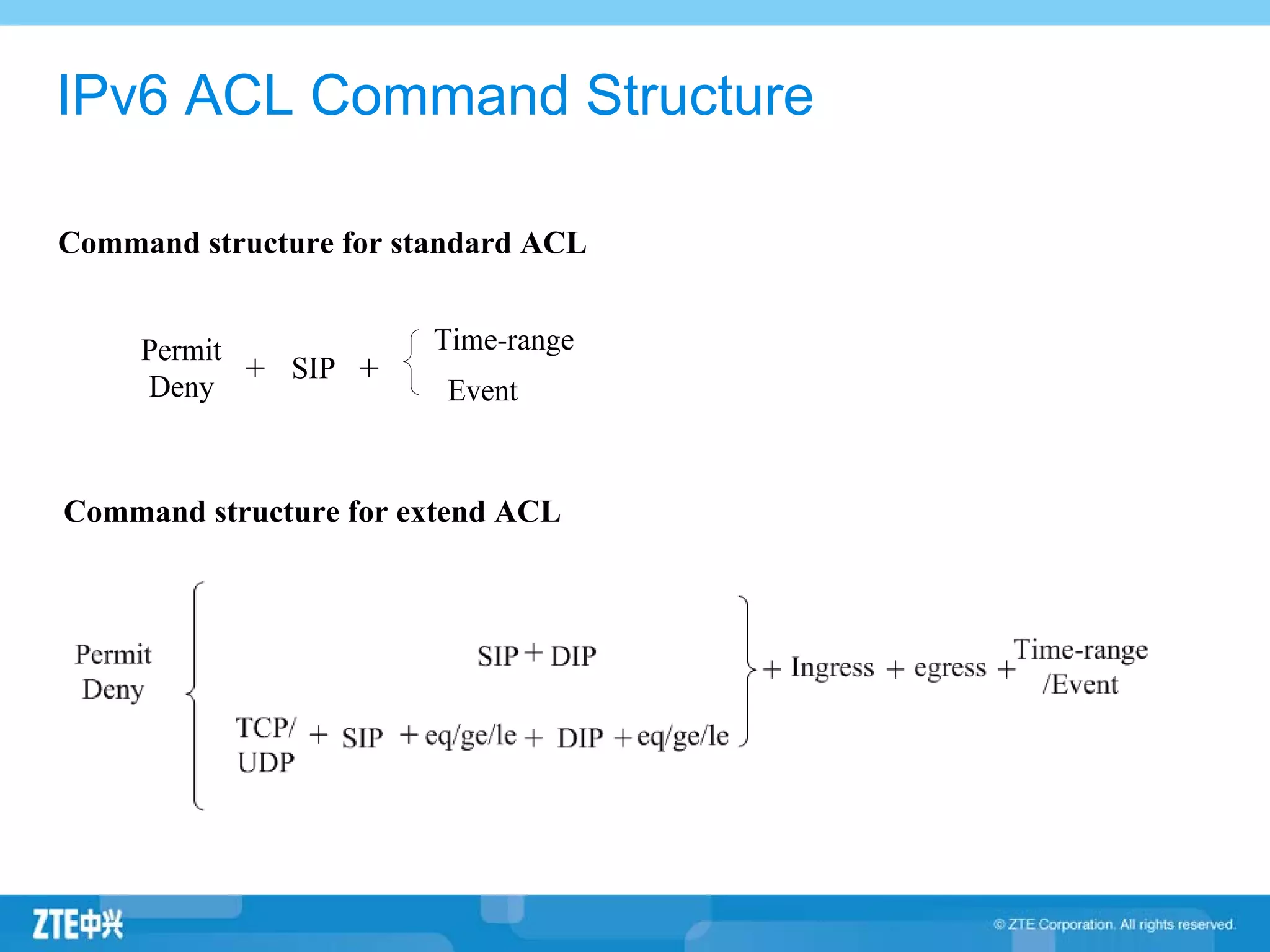
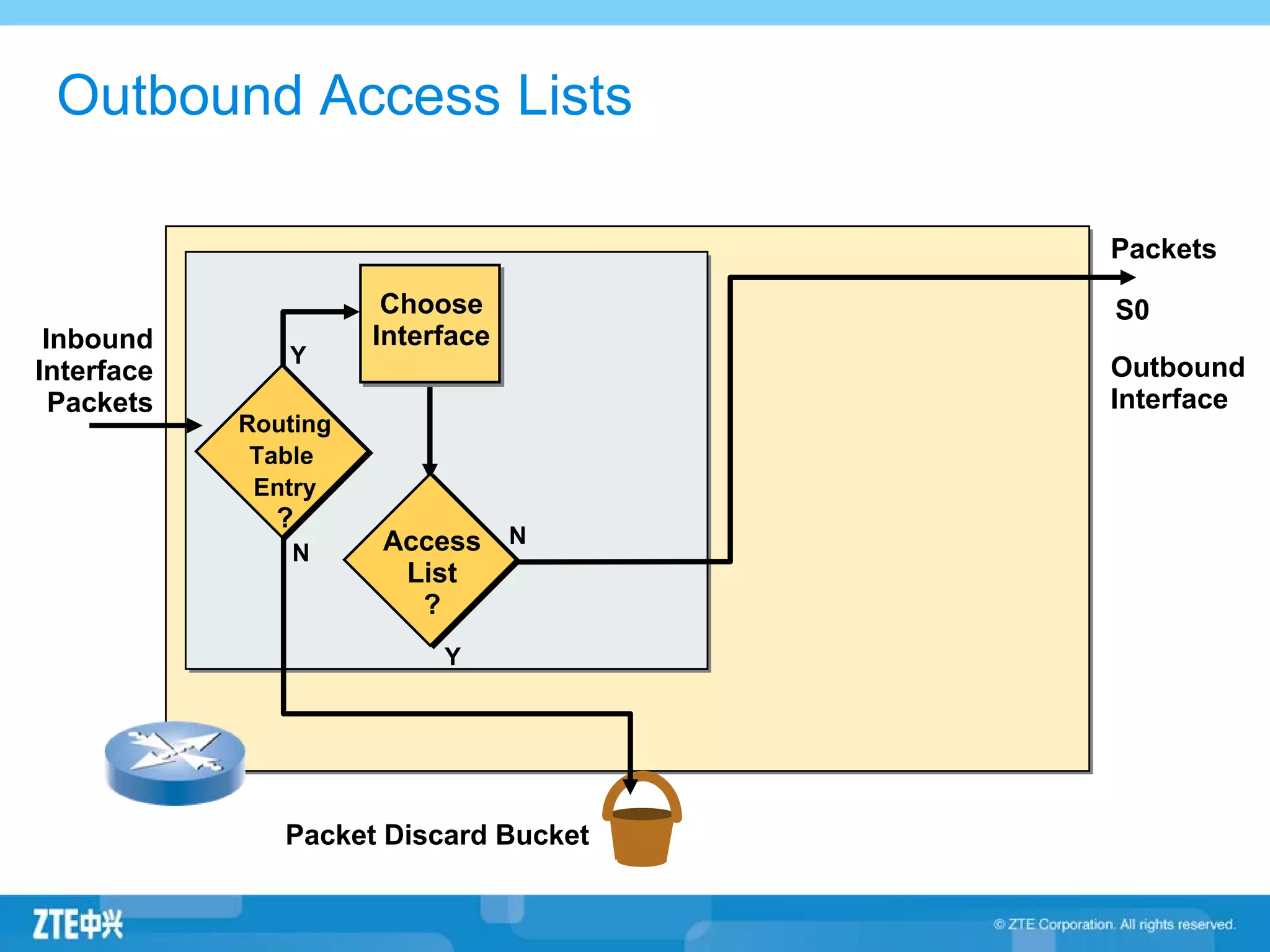
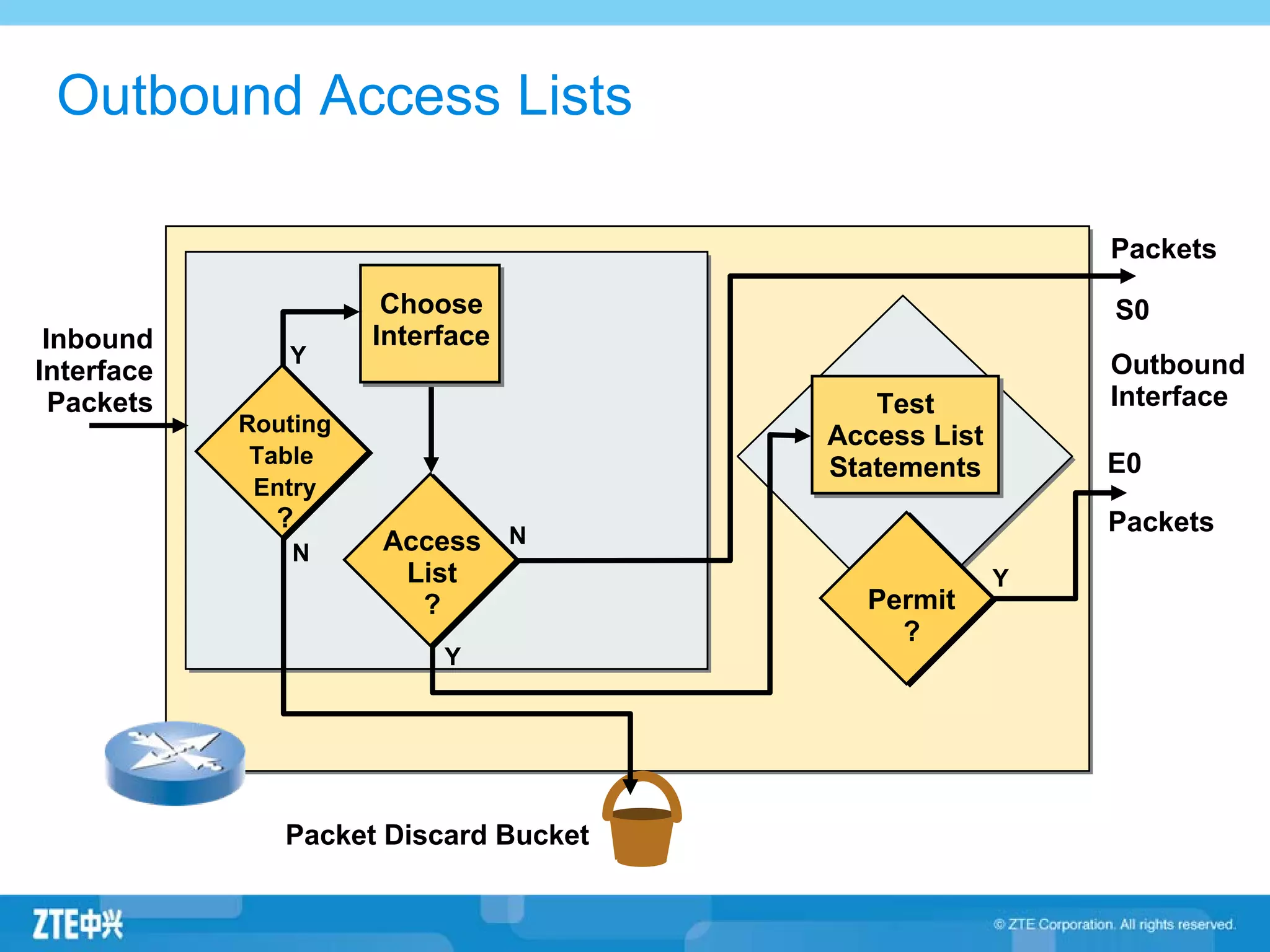
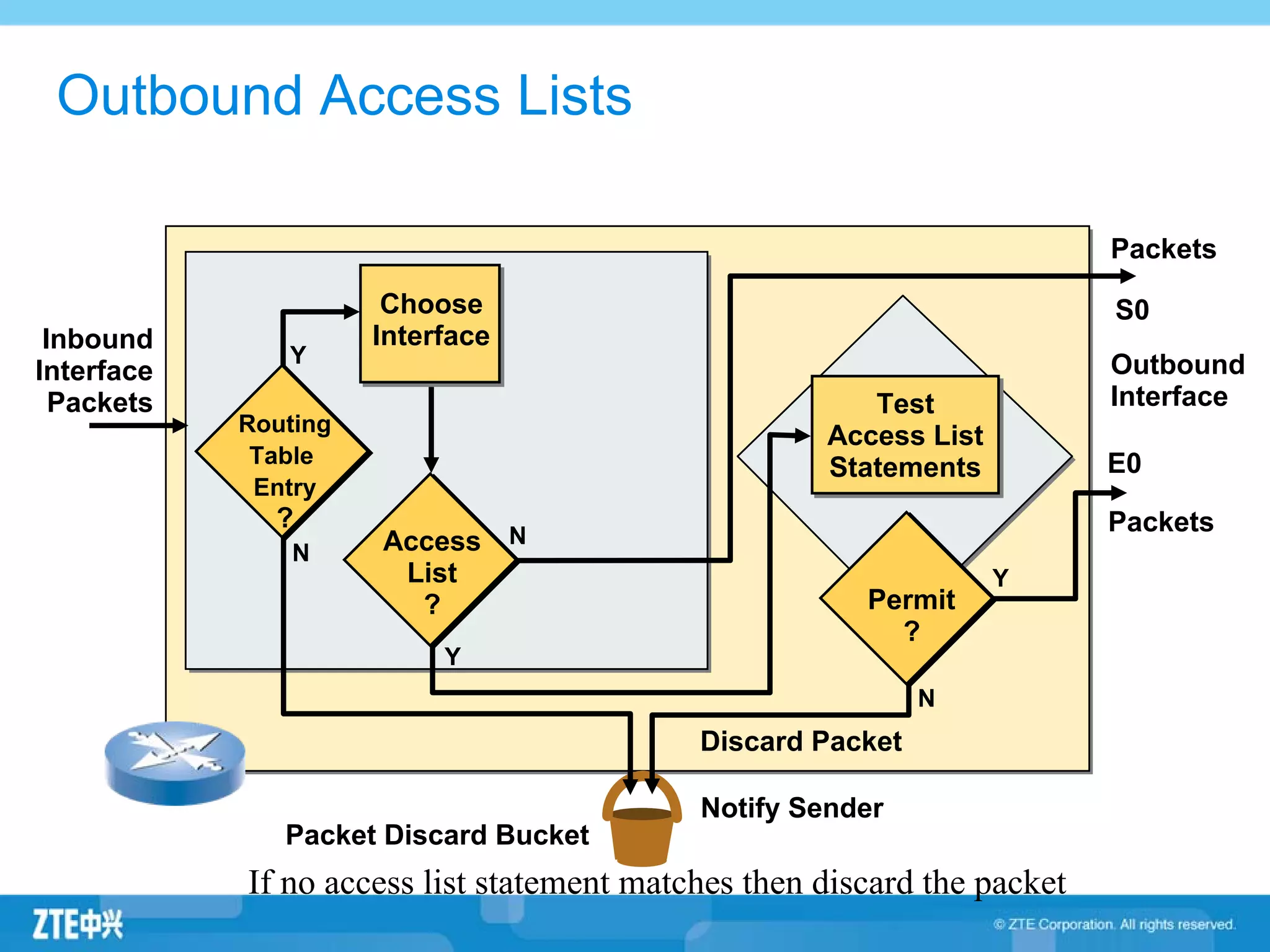
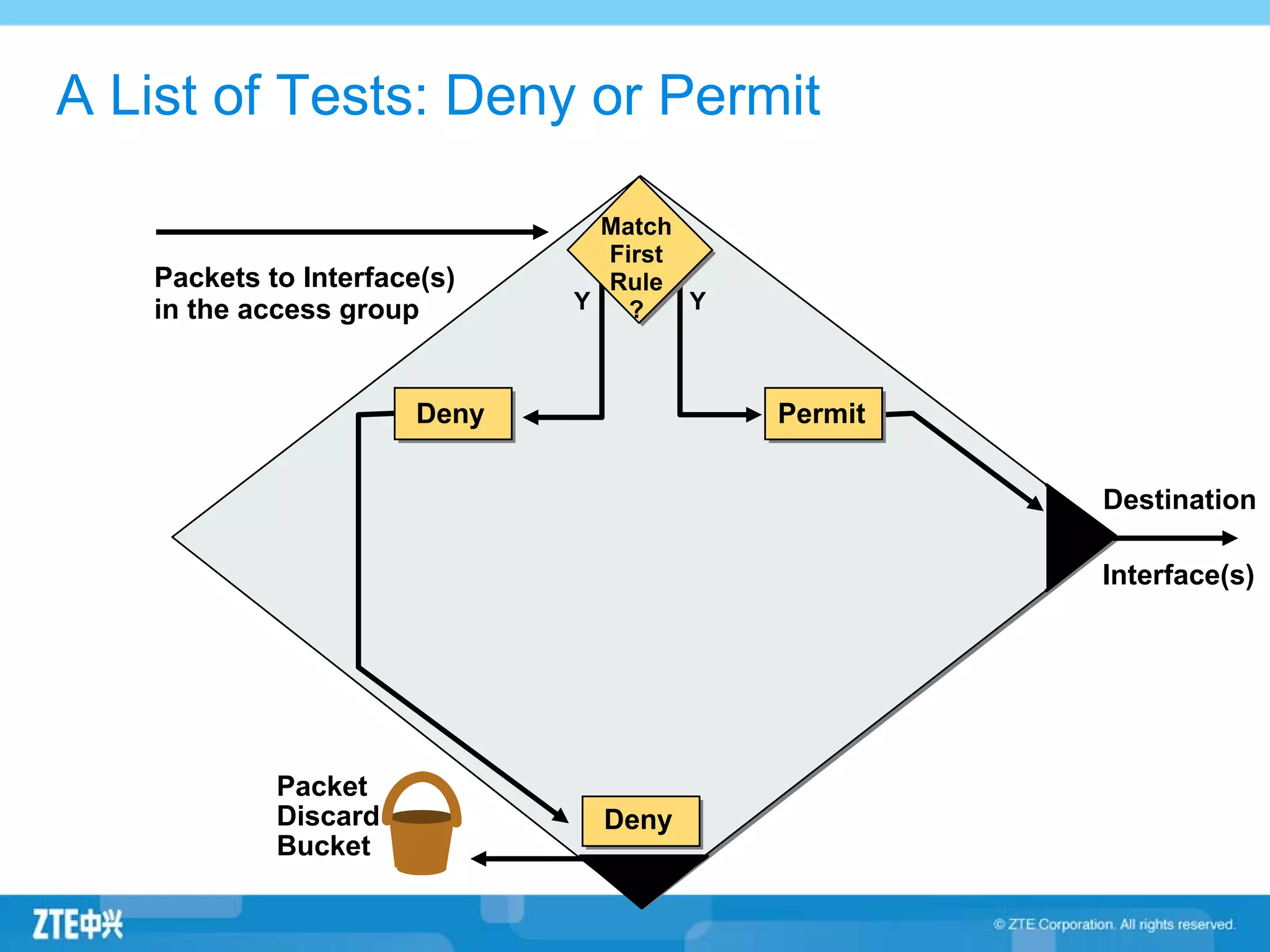
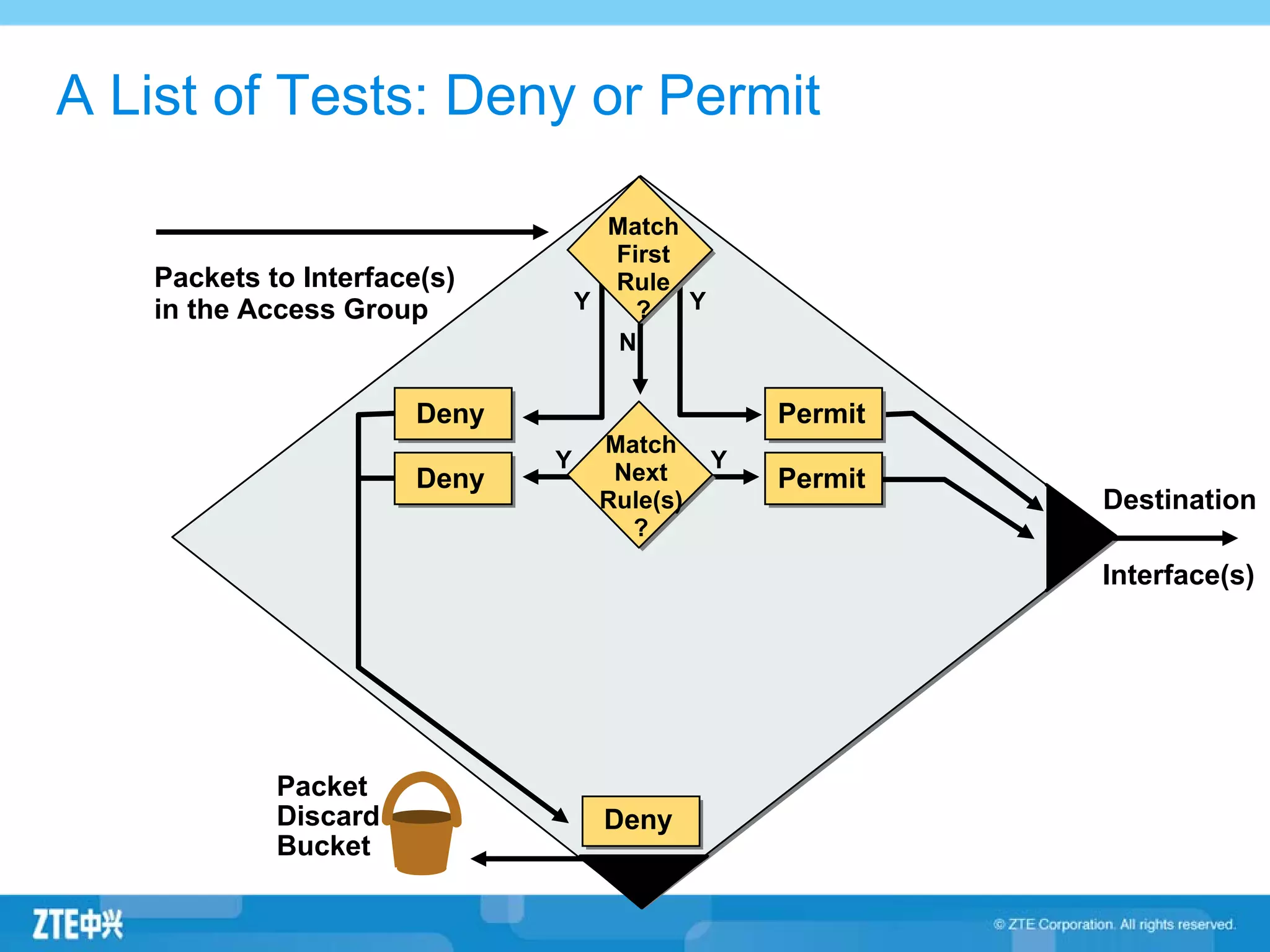
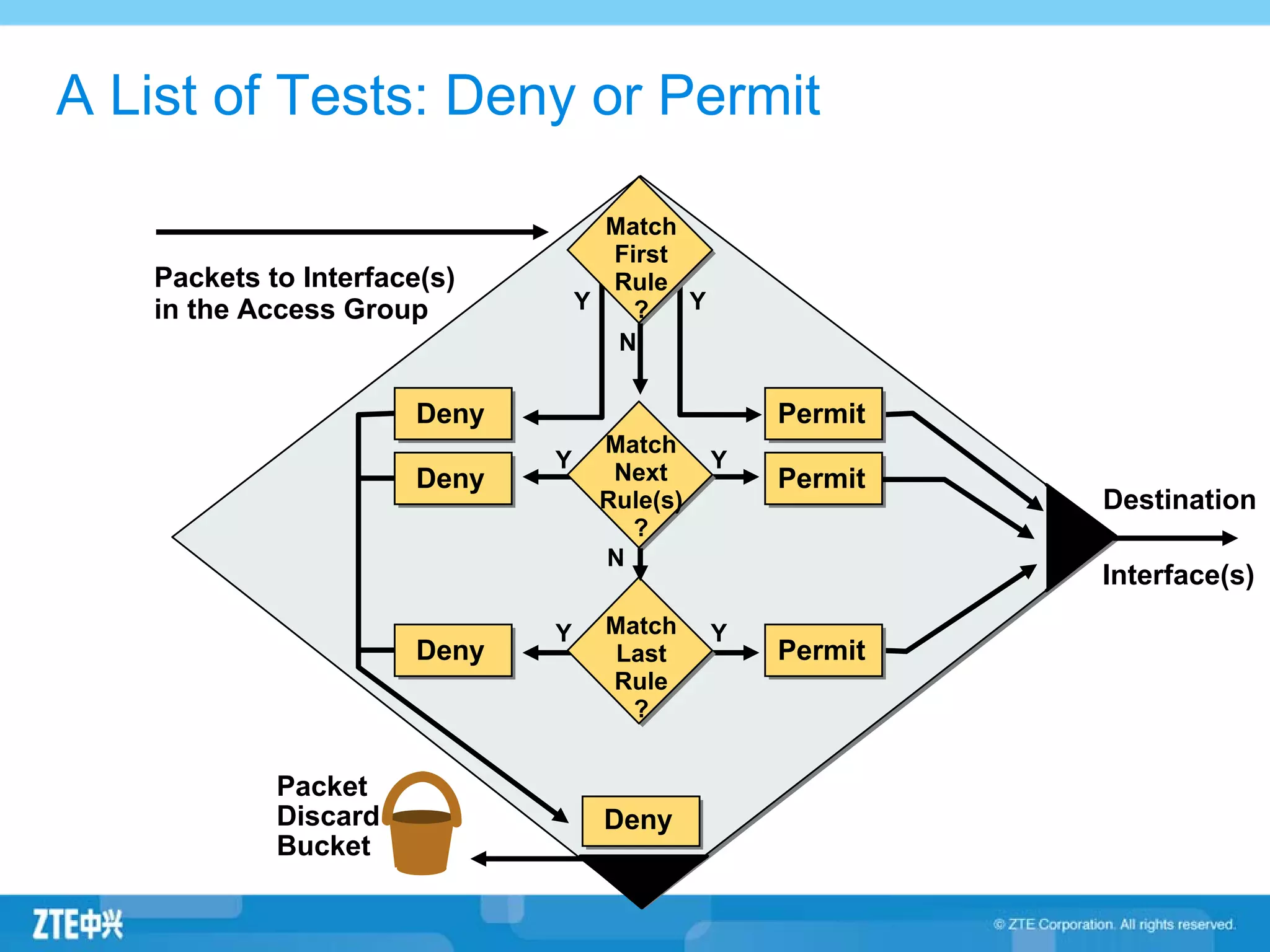
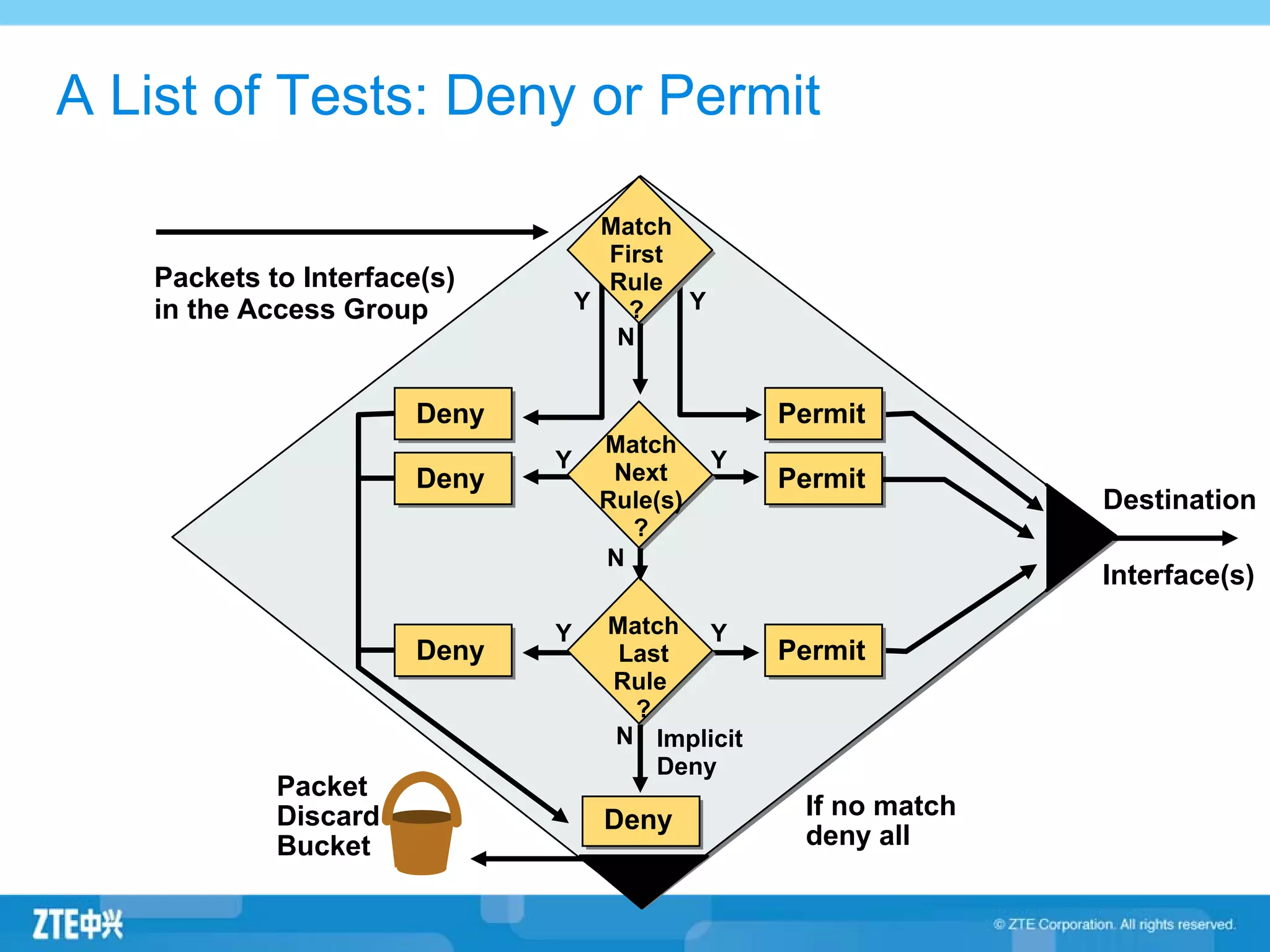
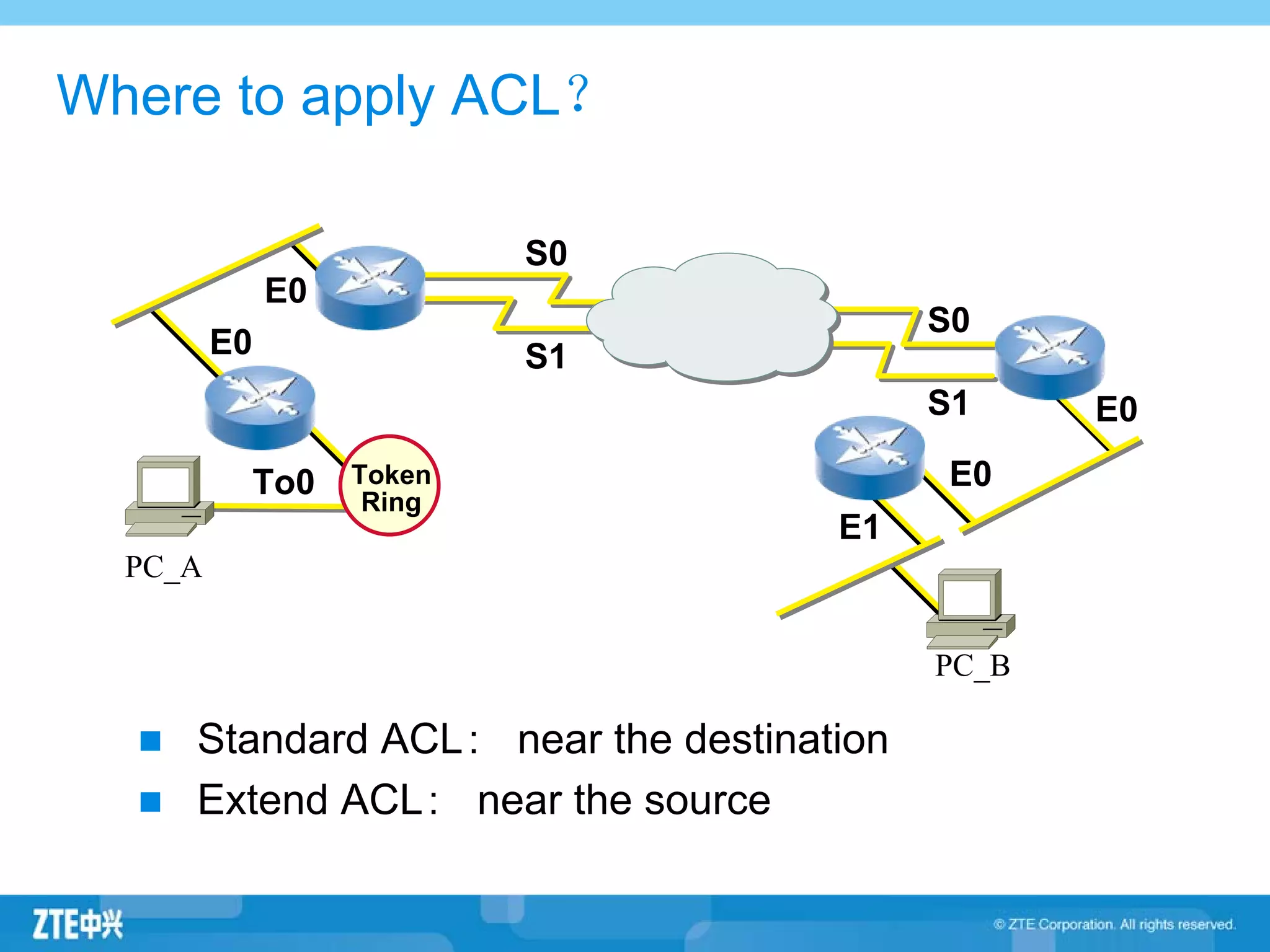
ACLs (access control lists) are used to filter network traffic by permitting or denying packets based on source/destination addresses, protocols, ports, and other packet attributes. There are two main types - standard ACLs filter based on source IP address, while extended ACLs filter on source/destination IP addresses, protocols, ports and other fields. ACL rules are ordered and the first matching rule determines if a packet is permitted or denied. If no rules match, the implicit deny at the end of the ACL is applied.