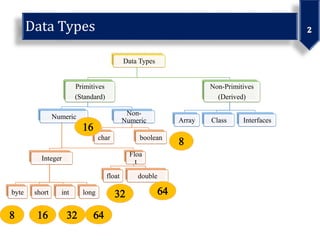
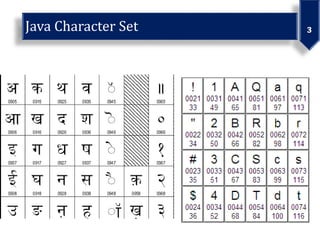
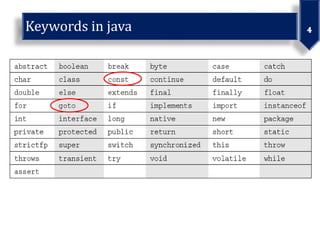
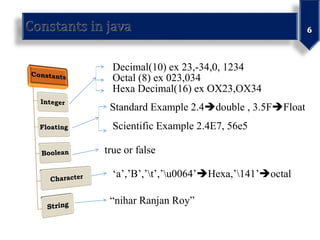
This document discusses various data types in Java including primitives like integers, floats, chars, and booleans as well as non-primitives like arrays, classes, and interfaces. It also covers identifiers, literals, operators, and examples of bitwise operations on positive and negative numbers.








![A frog starts climbing 30 ft well. Each hour frog
climbs 3ft and slips back 2ft. How many hours
does it take to reach top and get out?
[Hint: if Height>30 break;]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02datatypesinjava-230124141004-05a29ff7/85/02_Data-Types-in-java-pdf-19-320.jpg)
![[Hint: sum of cubes of individual digits
give same number.
153=13+53+33=1+125+27=153]
Write a java program to find the
Armstrong number from 100 to 1000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02datatypesinjava-230124141004-05a29ff7/85/02_Data-Types-in-java-pdf-20-320.jpg)