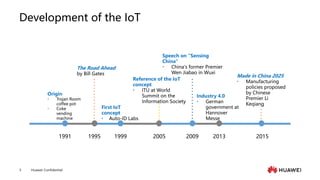
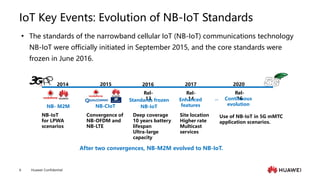
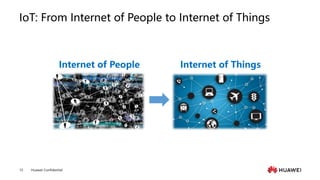
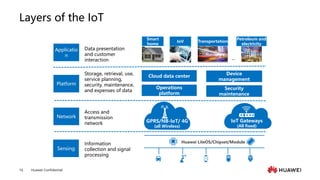
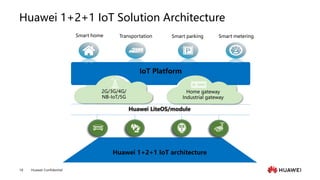
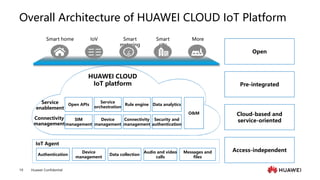
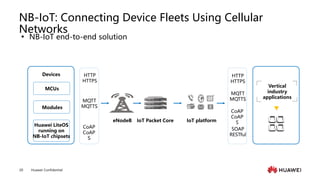
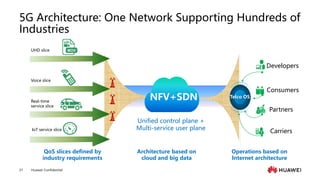
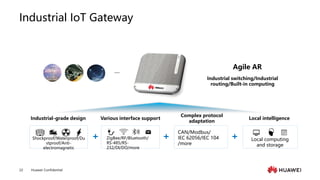
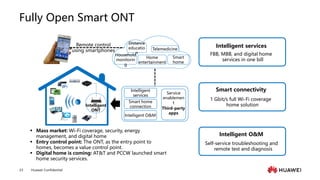
The document provides an overview of the history and development of IoT, including key events and concepts. It discusses the origins of IoT in 1991 with the Trojan Room coffee pot and the development of concepts and standards over time. It also outlines the layers of the IoT architecture including sensing, network, platform and application layers. Finally, it introduces Huawei's 1+2+1 IoT solution architecture and components like NB-IoT, LiteOS, gateways and the IoT platform.













![Huawei Confidential
24
Lightweight, Intelligent Huawei LiteOS
Chip-level application
virtual machine
Delay reduction
Accuracy
improvement
Support for short-distance
and long-distance
protocols
Automatic networking
[KB-level kernel]
[Milliwatt-level
power
consumption]
[Microsecond-level
response]
[Intelligent sensing]
[Intelligent connection]
[Intelligent application]
Shorter time-to-market for devices
Support for connection and device management by
industrial protocol stacks
Support for Huawei and third-party platforms
Supports HiSilicon and third-party chipsets
Security
framework
Open APIs
Connectivity
Sensor
framework
Runtime
engine
Kernel
Intelligence
Lightweight
Huawei
LiteOS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01iotdevelopmenthistoryandoverview-221026100359-b327e861/85/01-IoT-Development-History-and-Overview-pptx-25-320.jpg)


