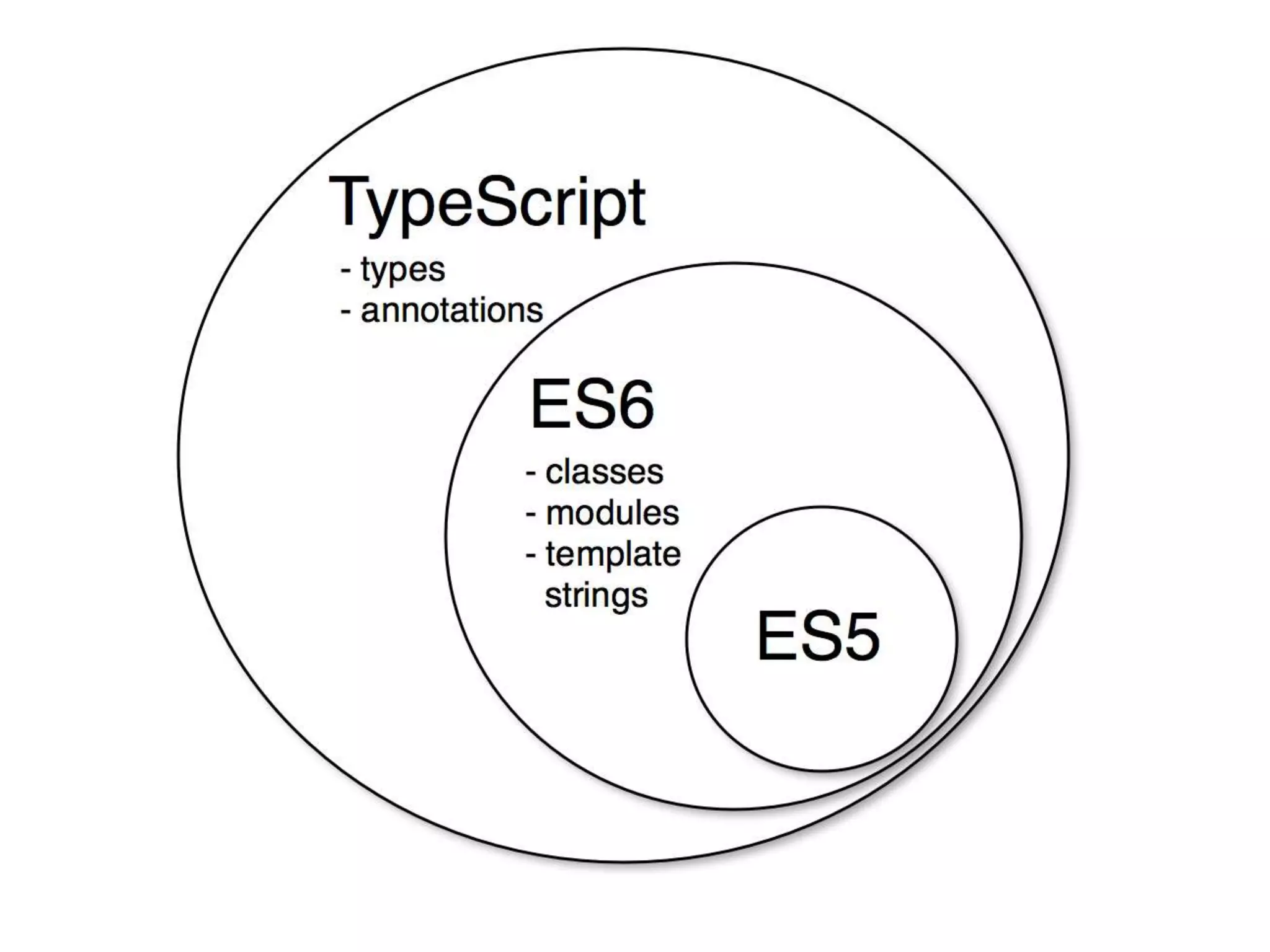
TypeScript is an open-source programming language developed and maintained by Microsoft. It is a strict syntactical superset of JavaScript, and adds static typing and class-based object-oriented programming to the language. Anders Hejlsberg, the chief architect of C# and creator of Delphi and Turbo Pascal, worked on the development of TypeScript. TypeScript can be used to build JavaScript applications for execution on the client-side or server-side (Node.js). Some key features of TypeScript include static typing, support for type definitions of existing JavaScript libraries, and support for object-oriented programming.
































![The for...in loop
for (var val in list)
{
//statements
}
var j:any;
var n:any=“abc"
for(j in n)
{
console.log(n[j])
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002-170929154928/75/002-Introducere-in-type-script-34-2048.jpg)



![Rest Parameters
function addNumbers(...nums:number[])
{
var i;
var sum:number=0;
for(i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
{
sum=sum+nums[i];
}
console.log("sum of the numbers",sum)
}
addNumbers(1,2,3)
addNumbers(10,10,10,10,10)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002-170929154928/75/002-Introducere-in-type-script-38-2048.jpg)

![The Function Constructor
var res=new Function( [arguments] ) { ... }
-------------
var myFunction =
new Function("a", "b", "return a * b");
var x = myFunction(4, 3);
console.log(x);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002-170929154928/75/002-Introducere-in-type-script-40-2048.jpg)
![Lambda Expression
It is an anonymous function expression that
points to a single line of code.
( [param1, parma2,…param n] )=>statement;
-----------------------------
var foo=(x:number)=>10+x
console.log(foo(100)) //outputs 110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002-170929154928/75/002-Introducere-in-type-script-41-2048.jpg)




![TypeScript – Arrays
var alphas:string[];
alphas=["1","2","3","4"]
console.log(alphas[0]);
console.log(alphas[1]);
----------------
var names = new Array("Mary", "Tom", "Jack", "Jill");
for (var i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
console.log(names[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/002-170929154928/75/002-Introducere-in-type-script-46-2048.jpg)









