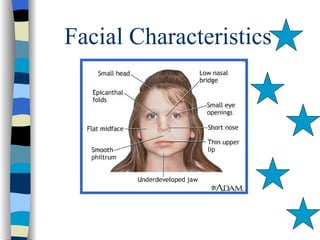
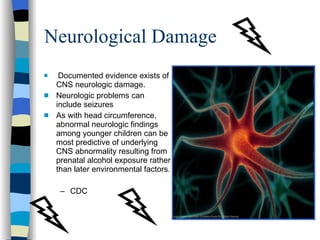
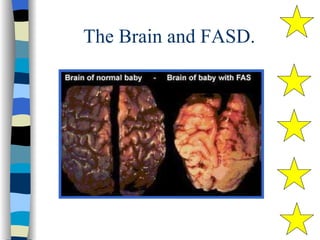
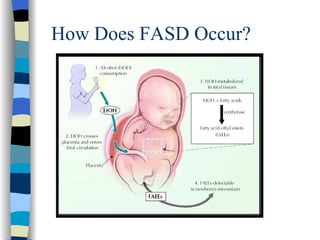
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur in individuals whose mothers drank alcohol during pregnancy, including physical, mental, behavioral, and learning disabilities. FASD is the leading preventable cause of mental retardation and birth defects in the United States, affecting an estimated 1 in 100 live births annually. The document outlines the various effects of prenatal alcohol exposure such as growth deficiency, facial features, neurological damage, structural abnormalities, motor skills delays, cognitive deficits, and attention problems. It emphasizes that FASD is completely preventable by avoiding alcohol during pregnancy.



![Growth Deficiency
s Growth deficiency is ranked as
follows by the "4-Digit
Diagnostic Code:"[1]
s * Severe - Height and weight
at or below the 3rd percentile.
s * Moderate - Either height or
weight at or below the 3rd
percentile, but not both.
s * Mild - Either height or
weight or both between the 3rd
and 10th percentiles.
s * None - Height and weight
both above the 10th percentile.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fasd-090718233647-phpapp01/85/Fetal-Alcohol-Spectrum-Disorder-5-320.jpg)