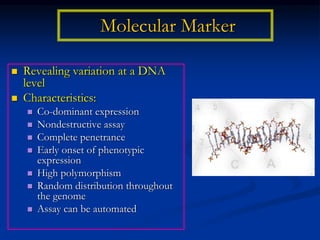
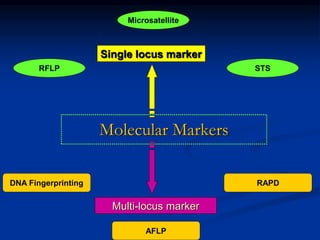
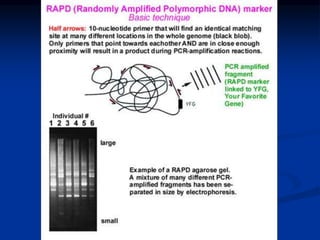
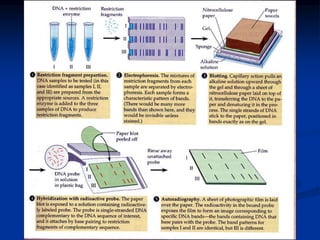
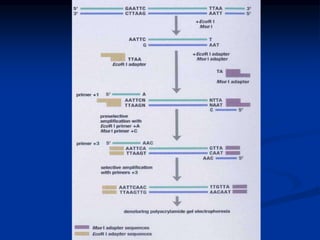
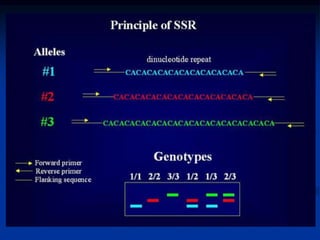
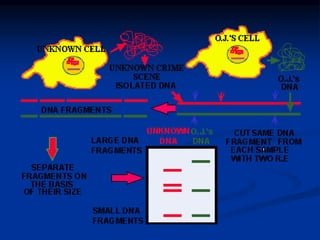
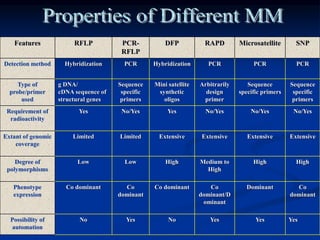
Marker is a piece of DNA associated with a trait. There are four main types of markers: morphological, biochemical, chromosomal, and genetic. Molecular markers reveal DNA level variations and have advantages like being co-dominant, allowing nondestructive assays, and being randomly distributed throughout the genome. Common molecular marker techniques include RAPD, RFLP, AFLP, microsatellites, and SNPs. Molecular markers can be used for applications like gene mapping, disease diagnosis, evolution studies, parentage determination, and marker assisted selection in animal breeding.