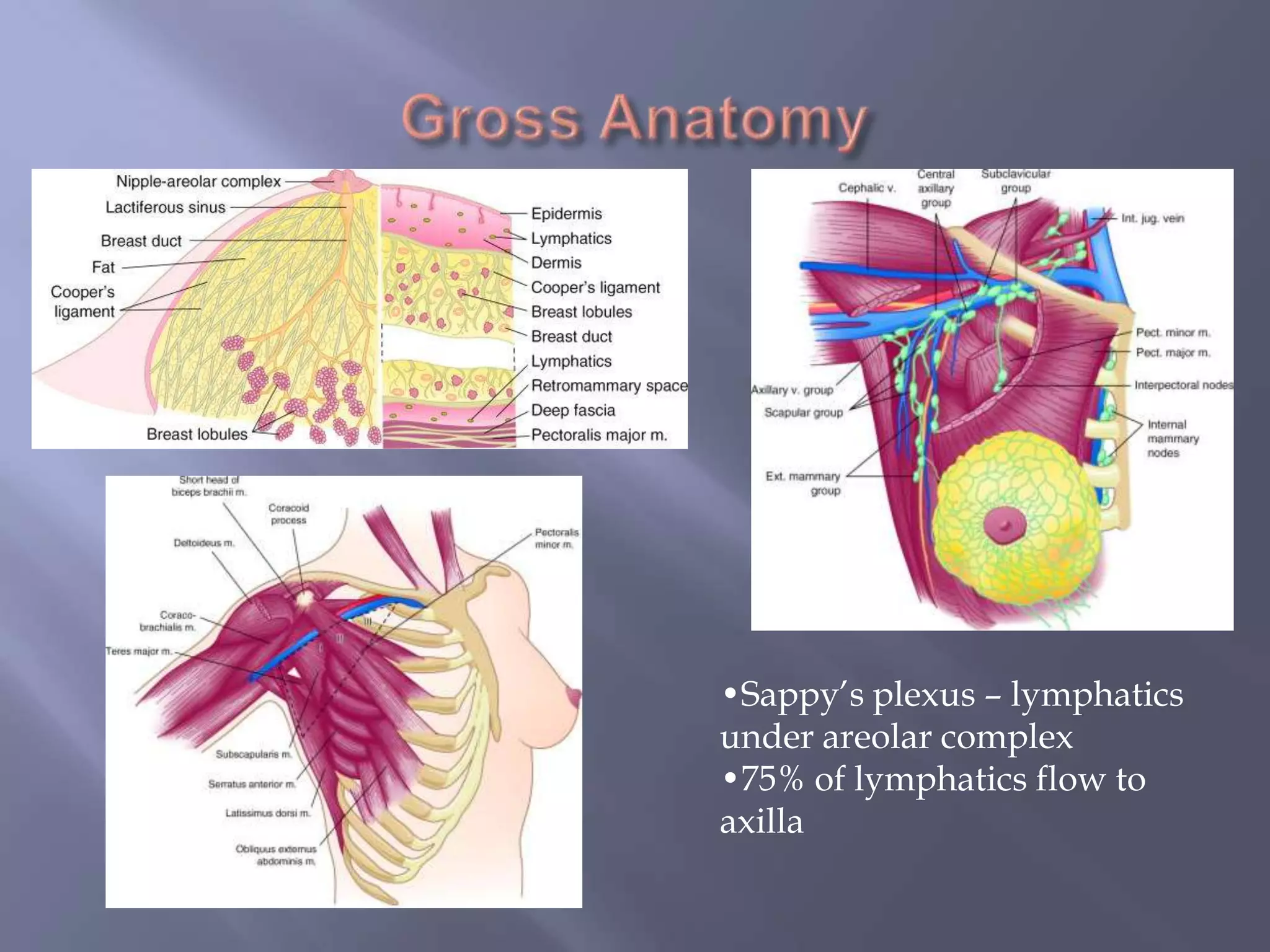
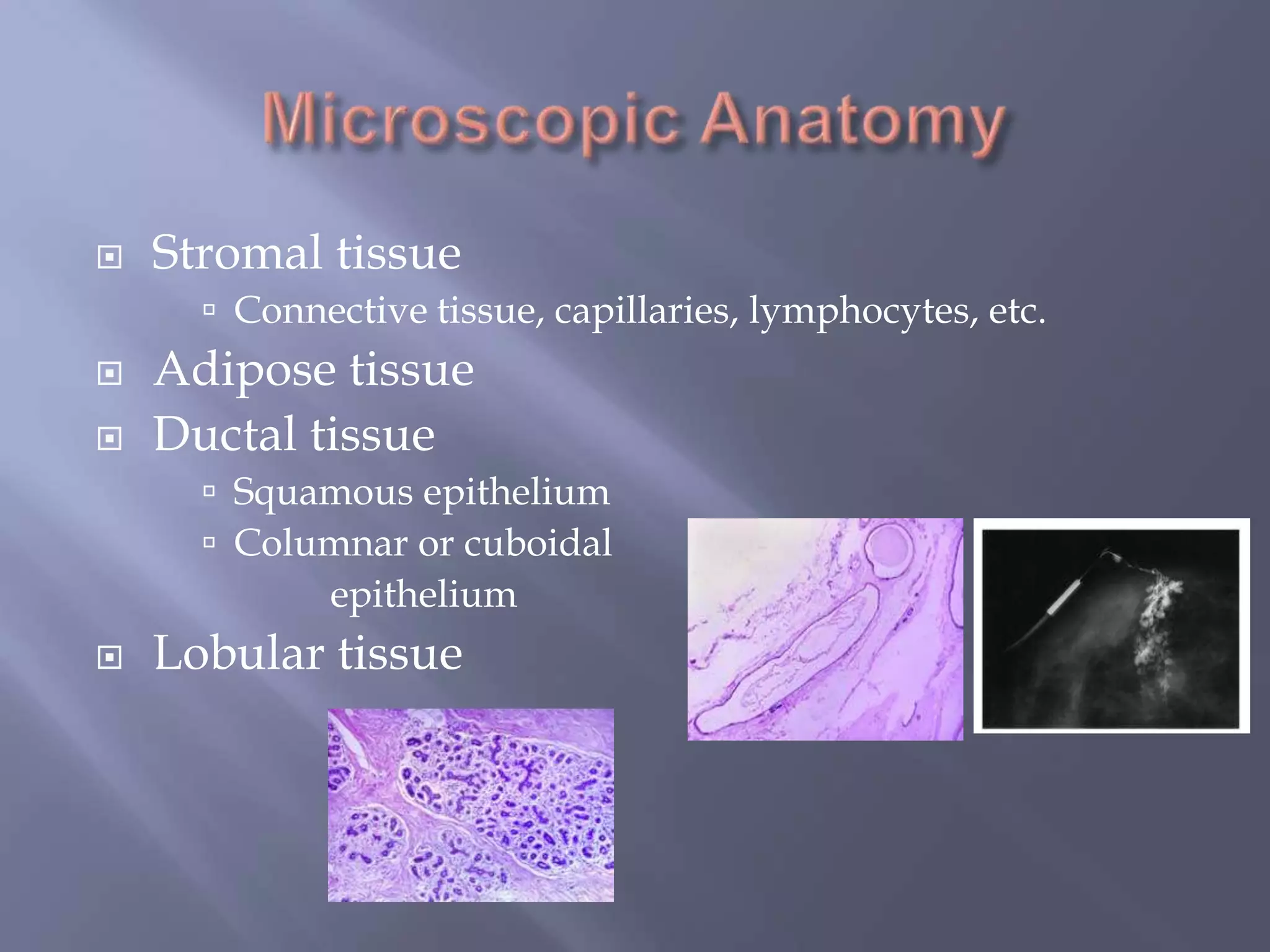
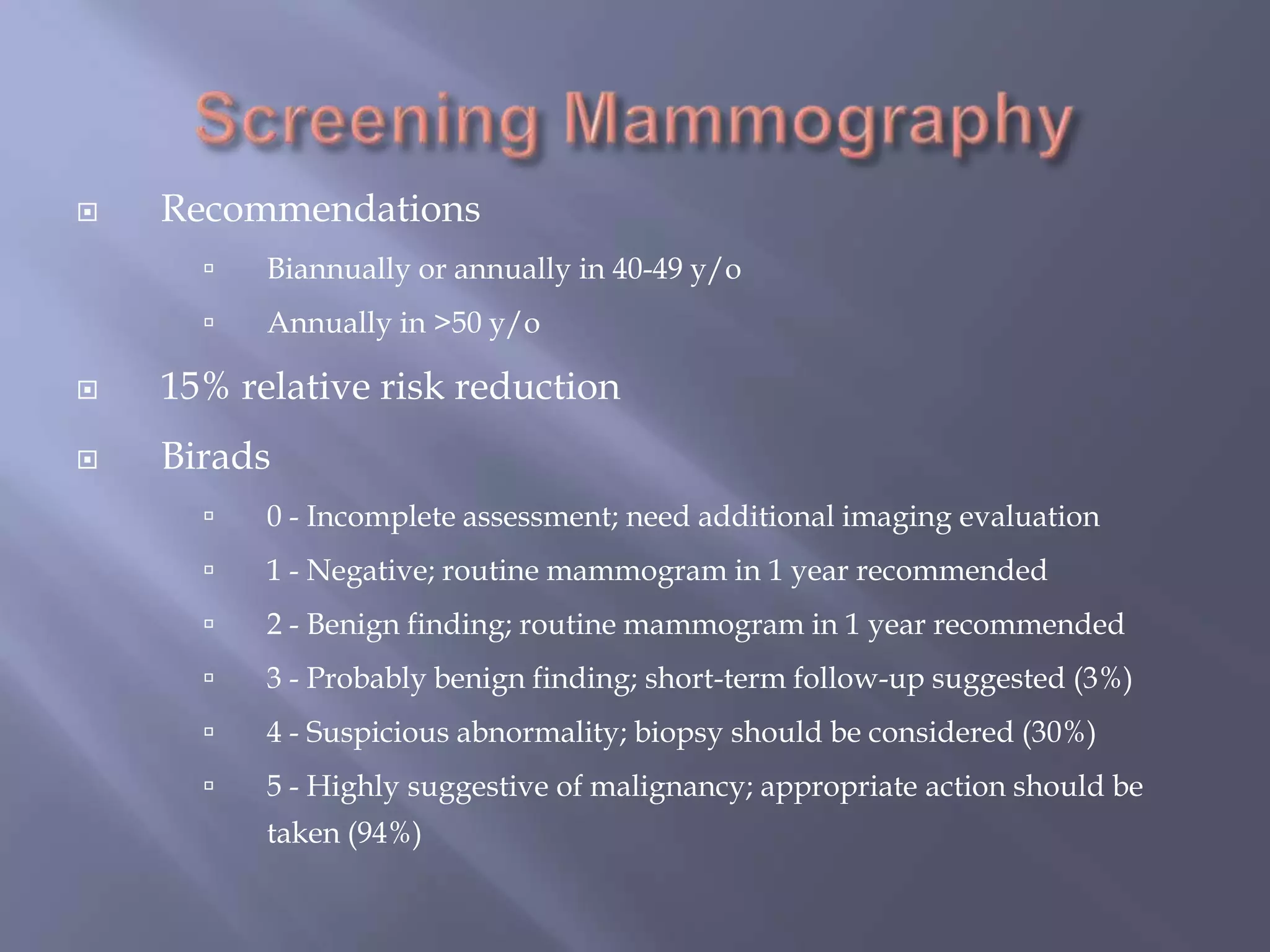
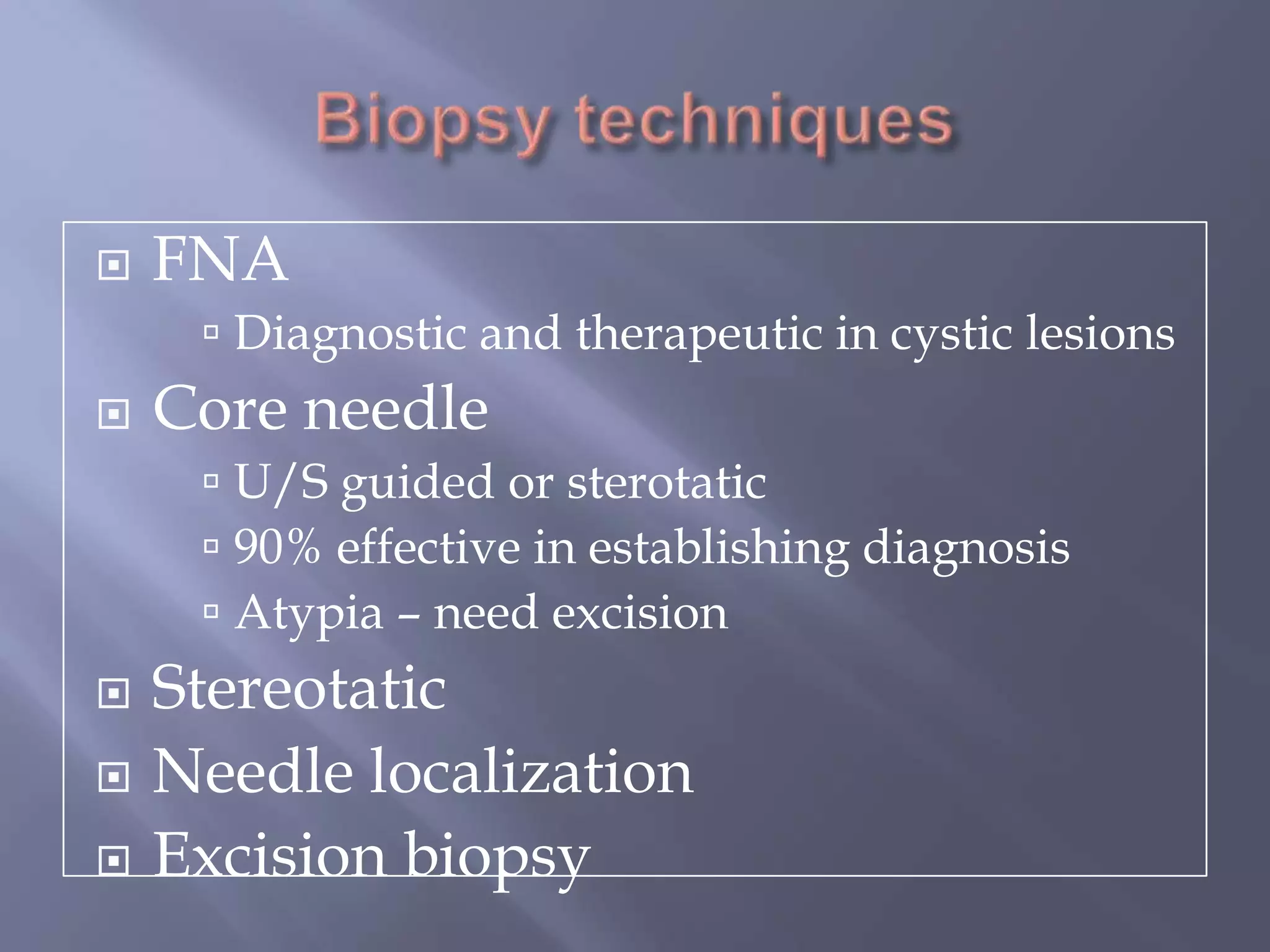
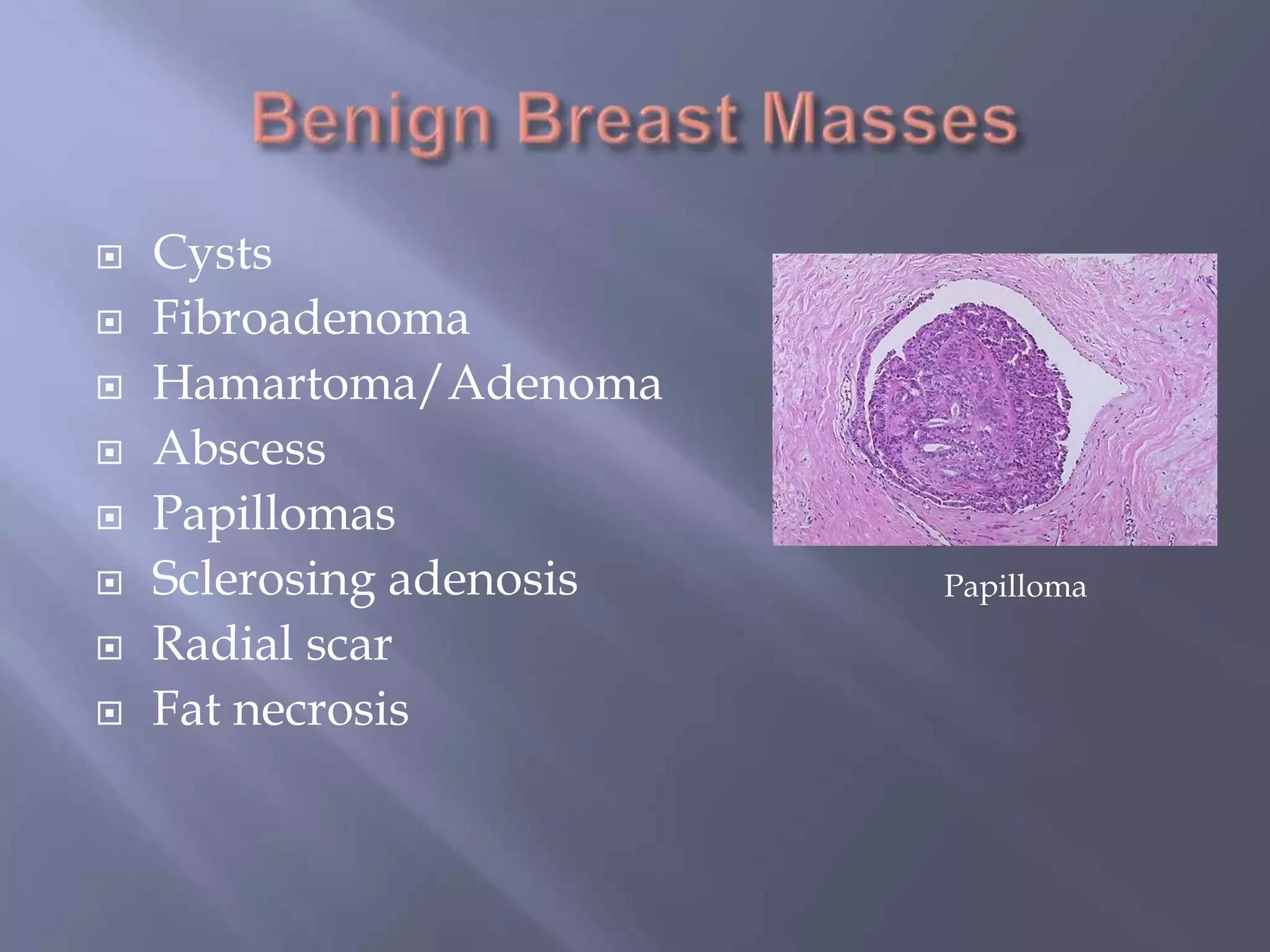
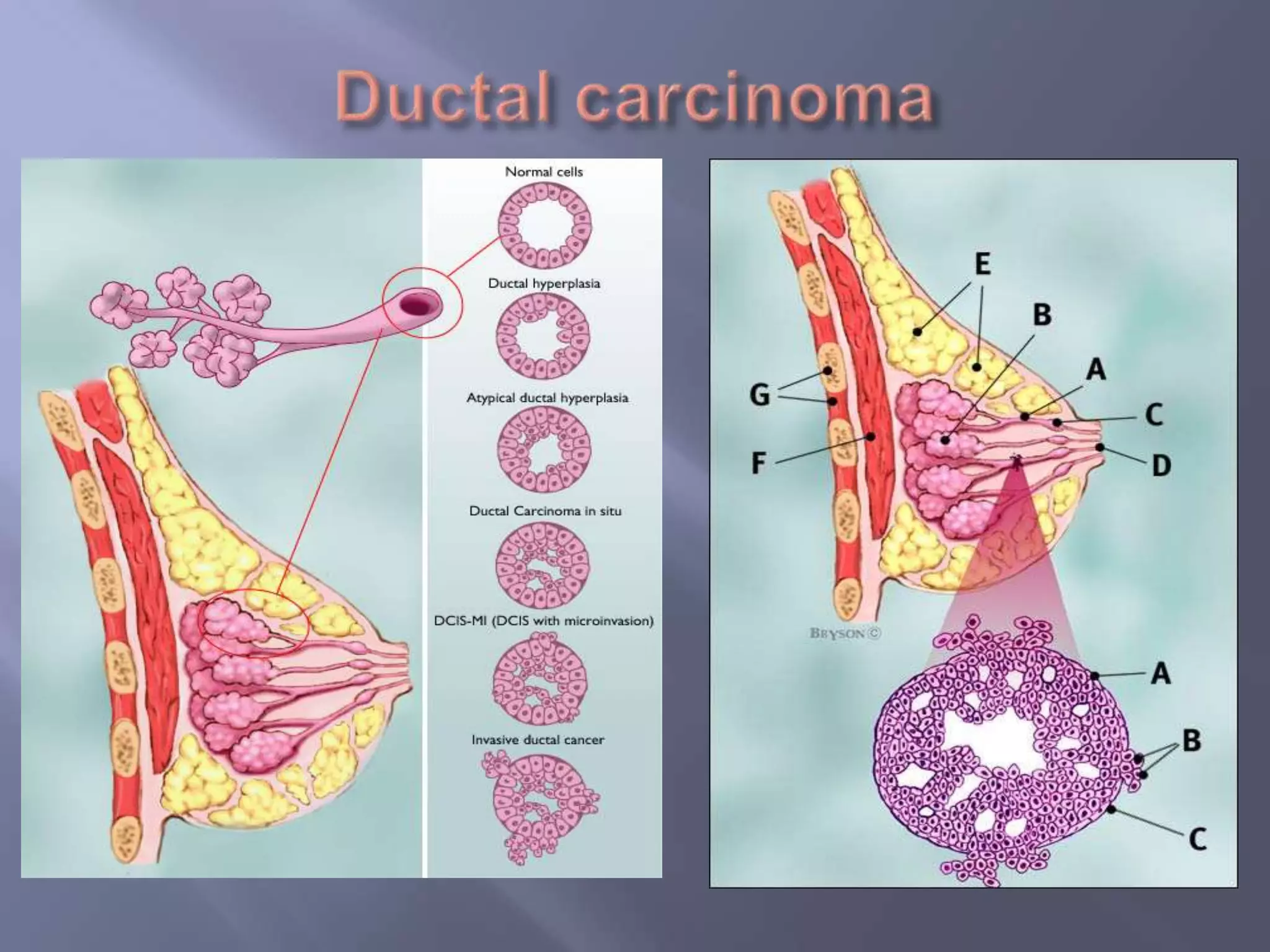
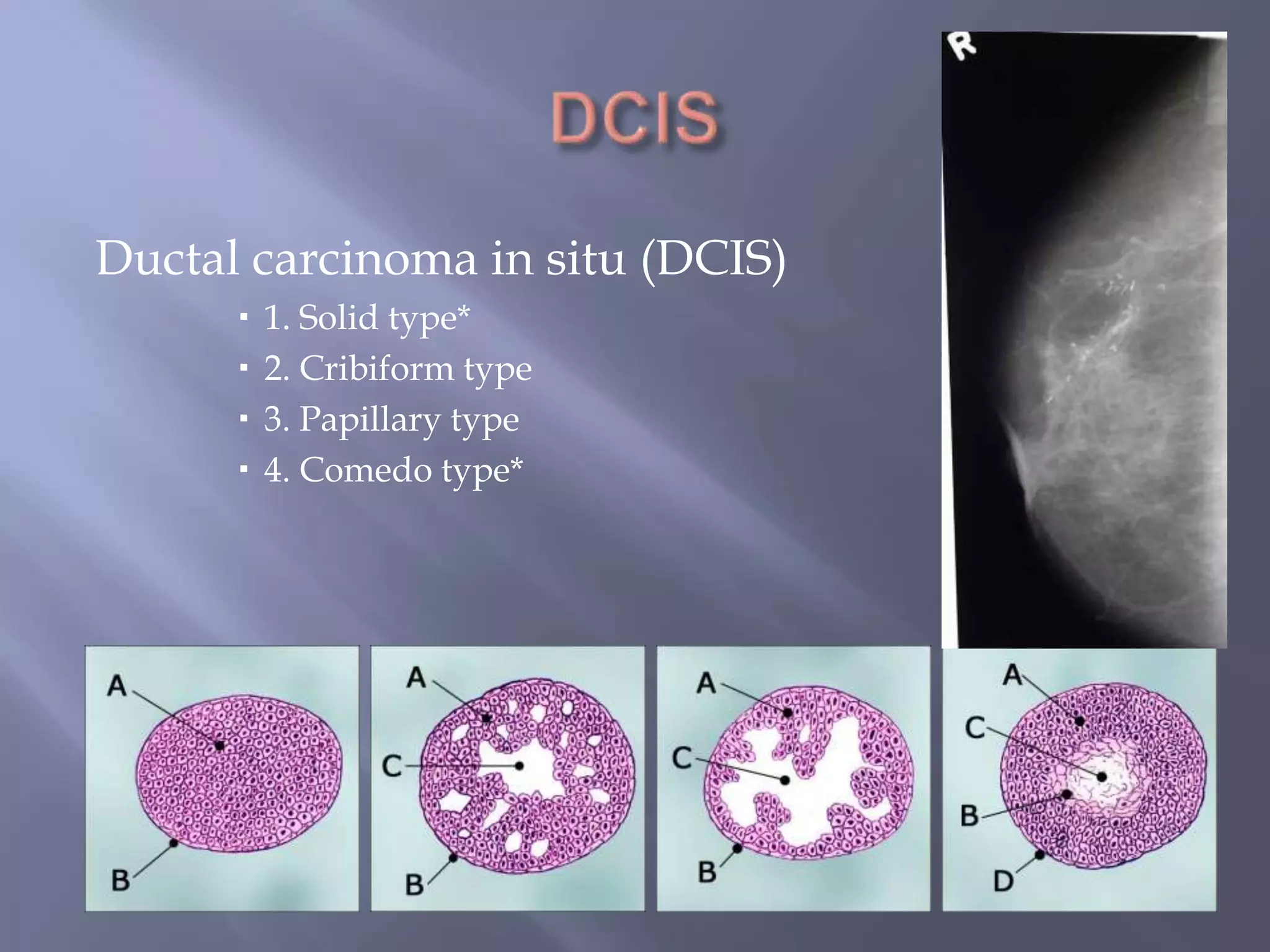
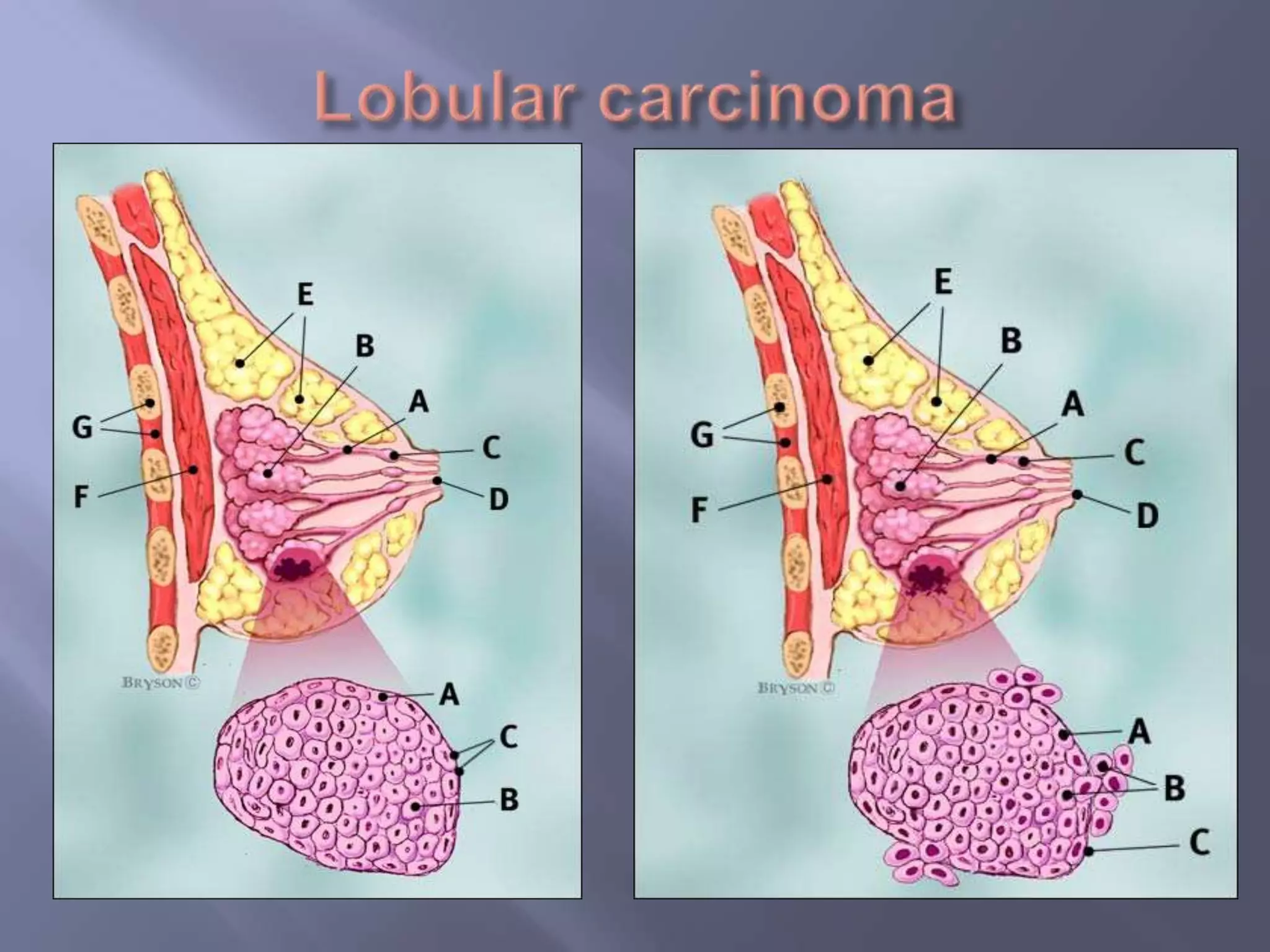
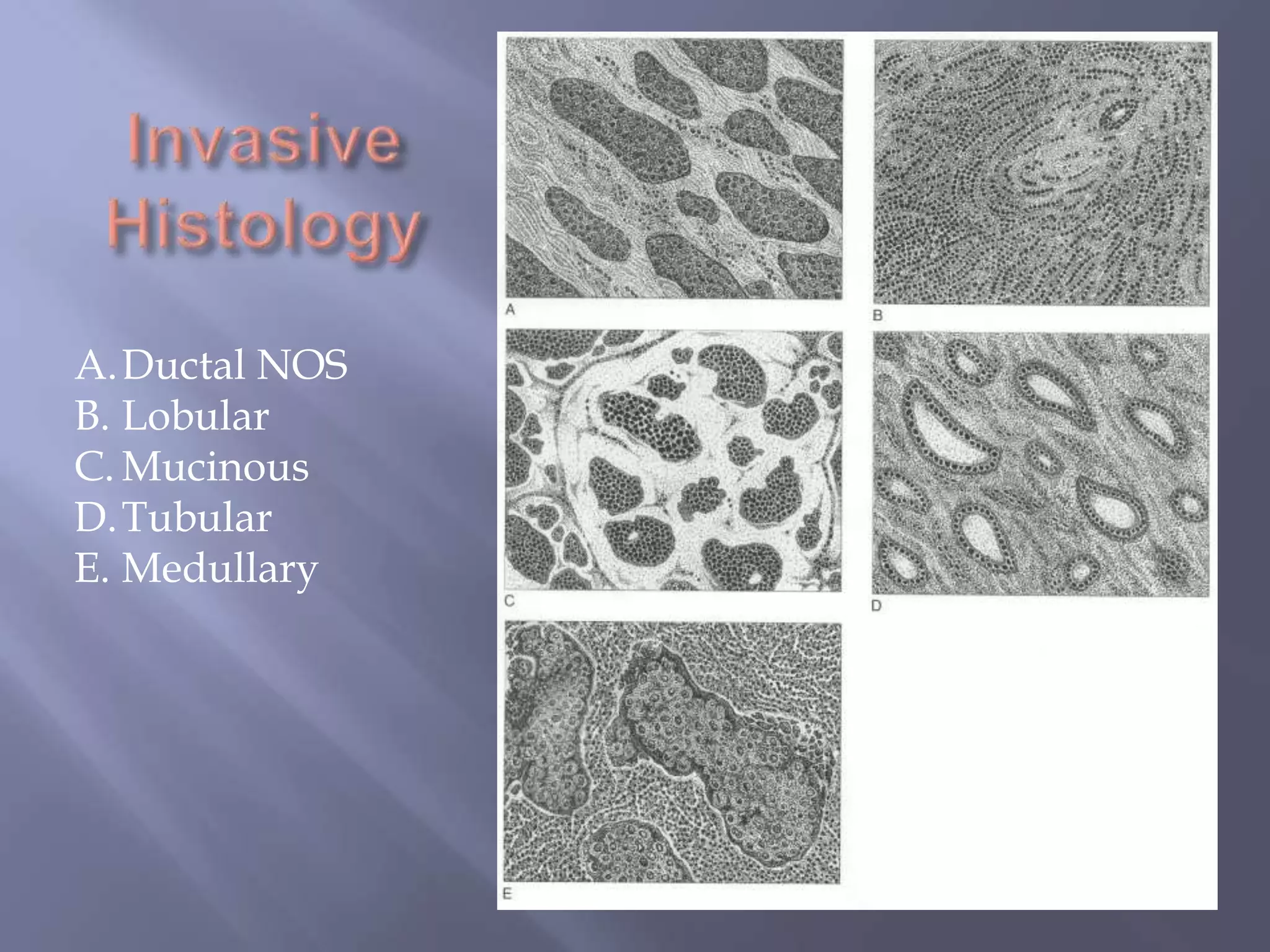
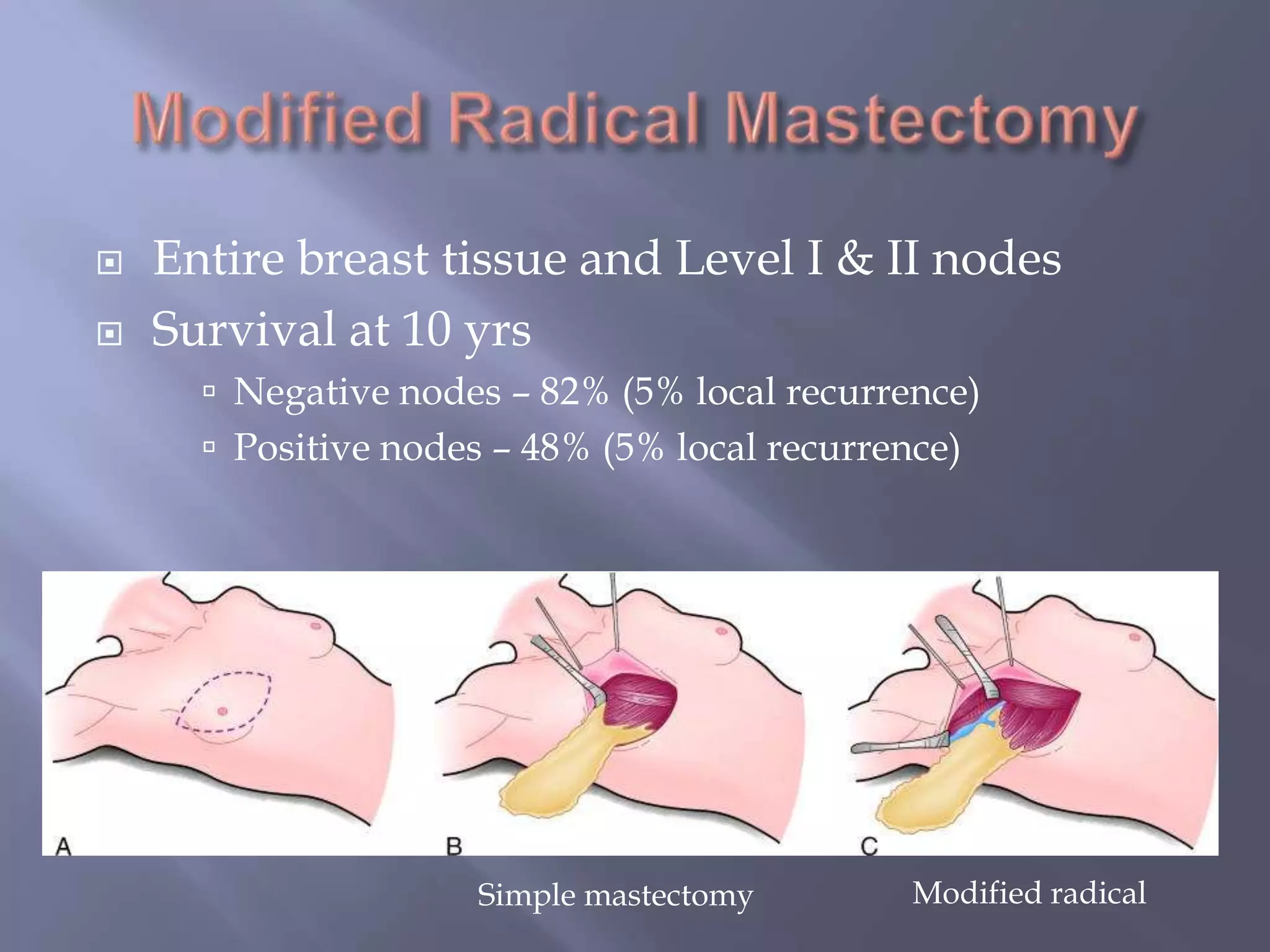
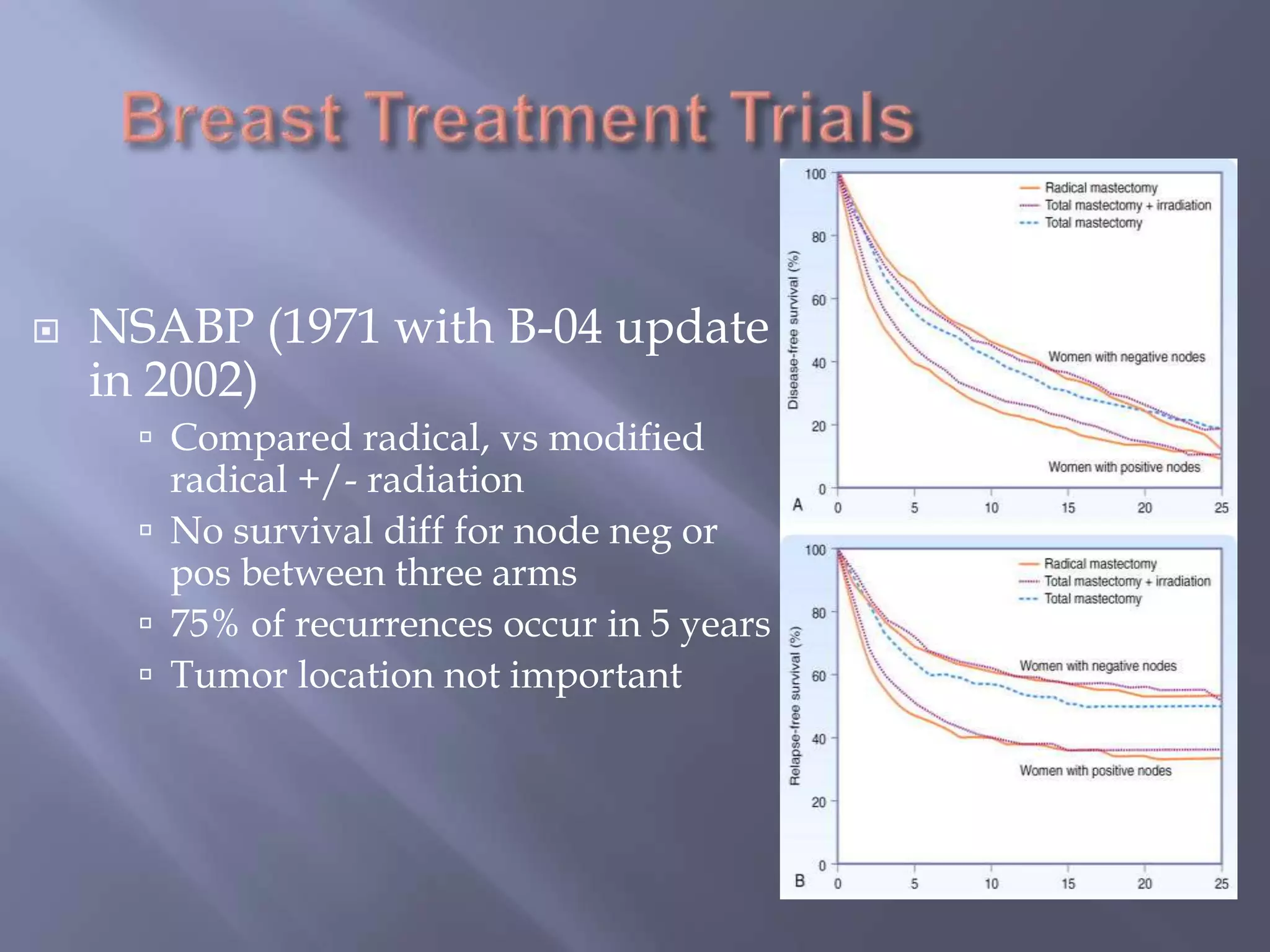
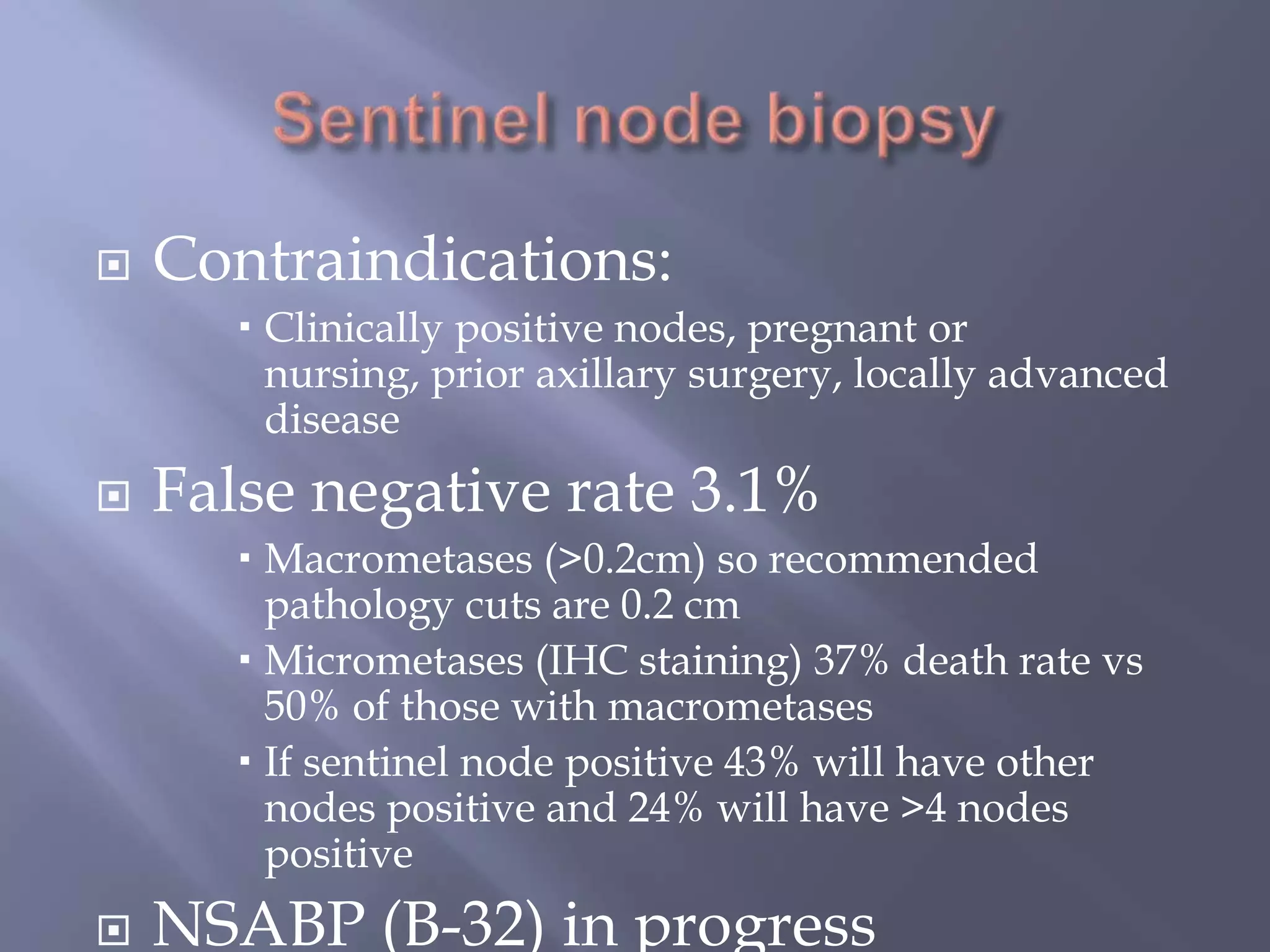
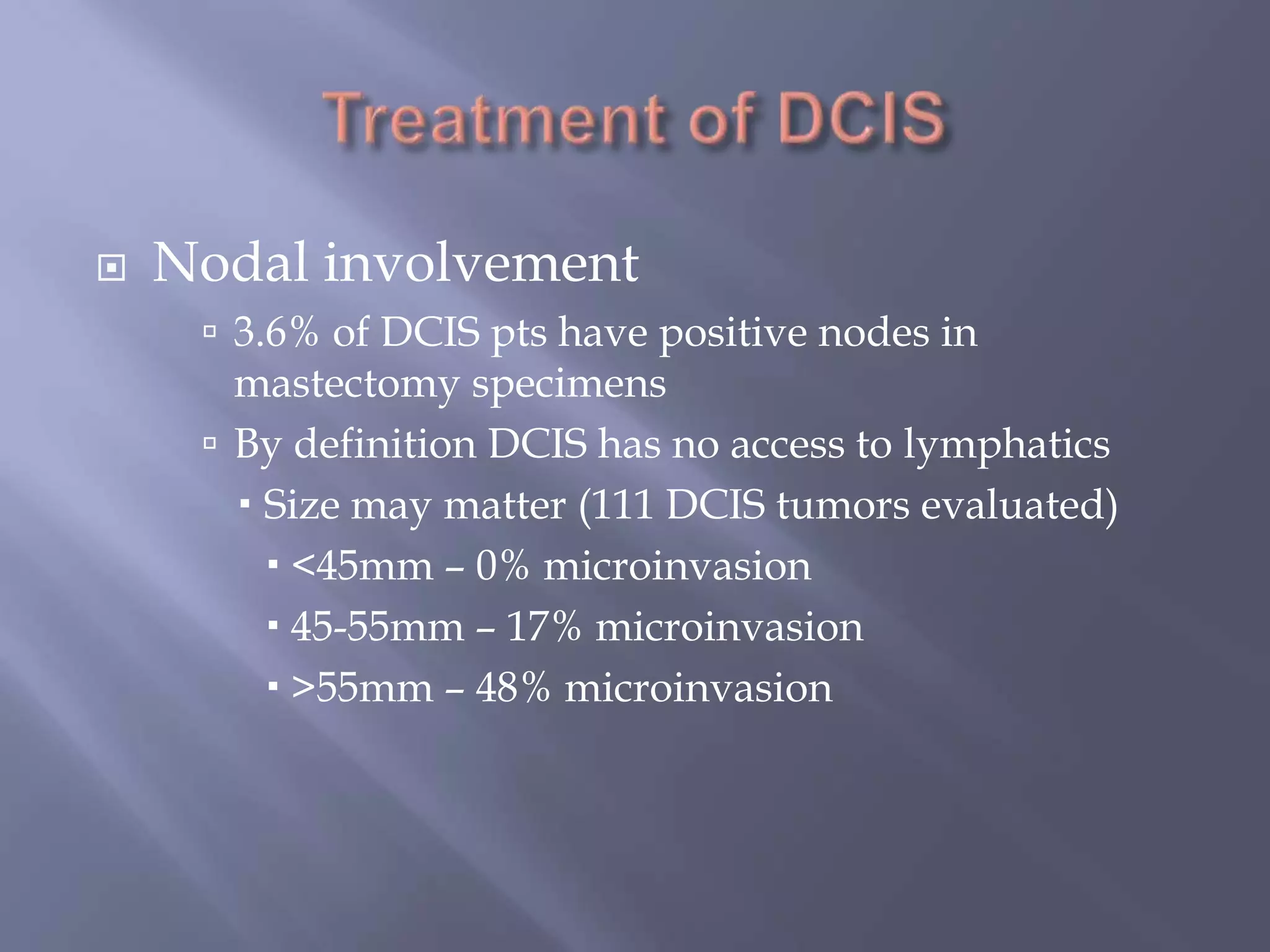
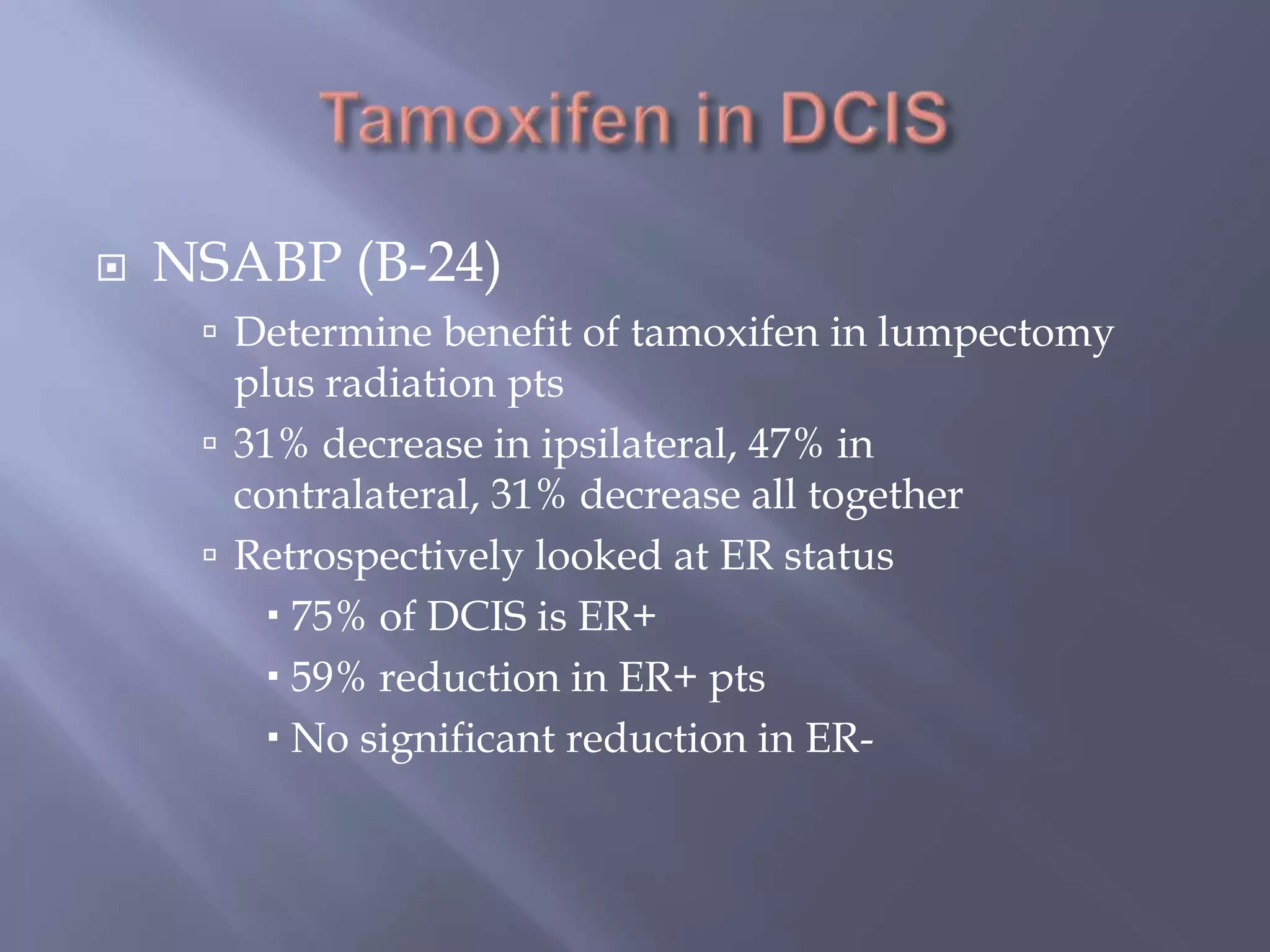
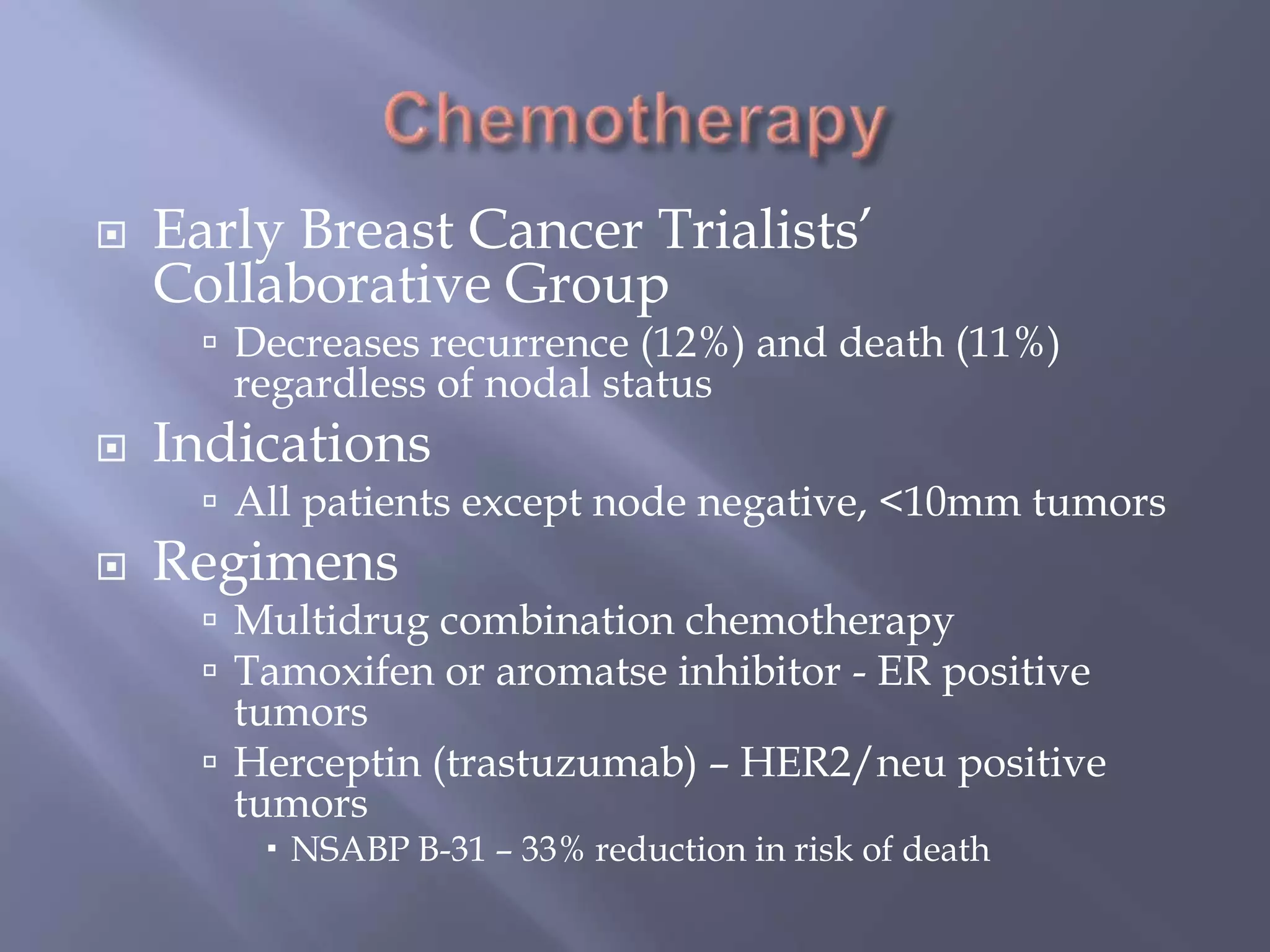
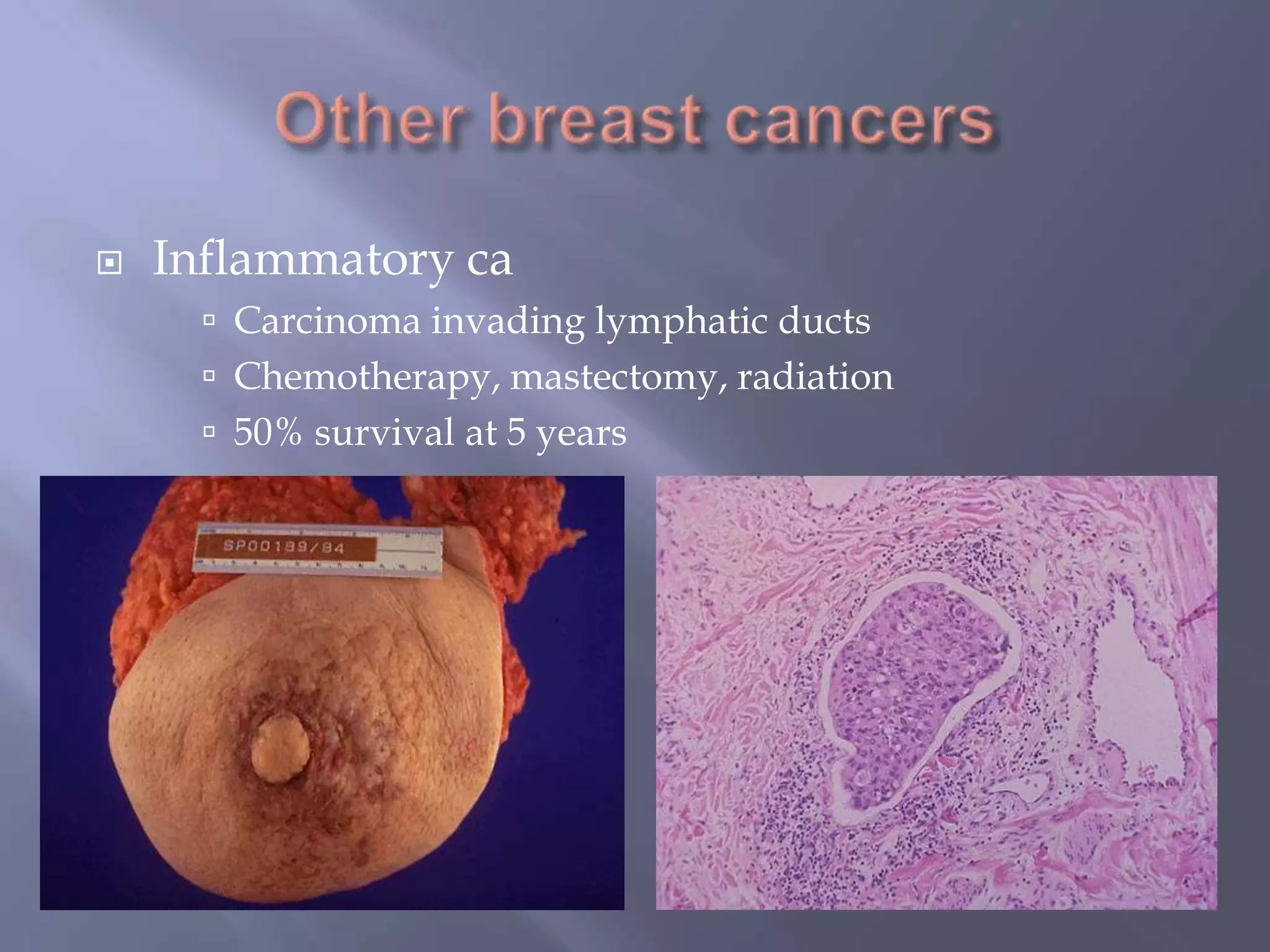
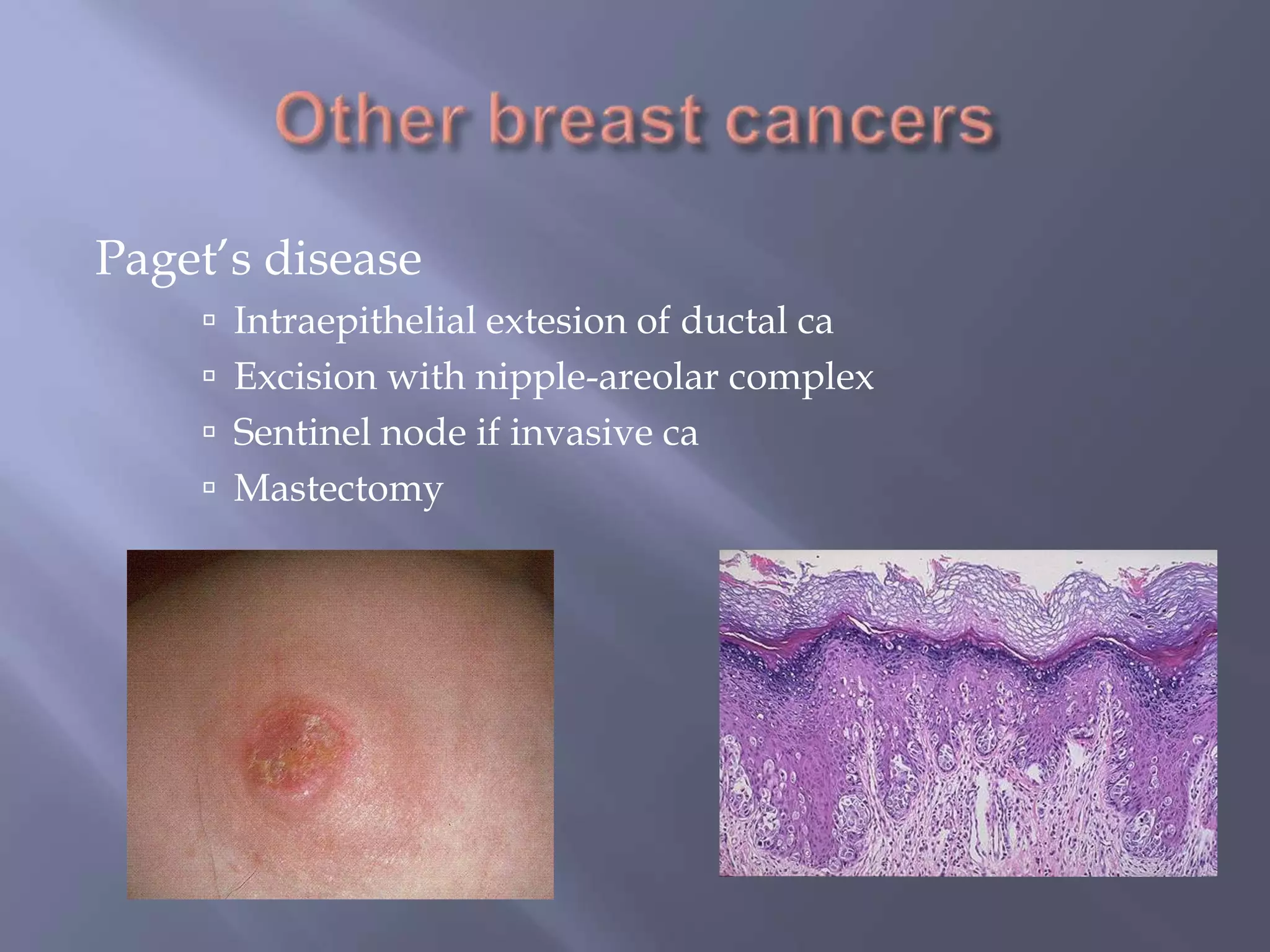
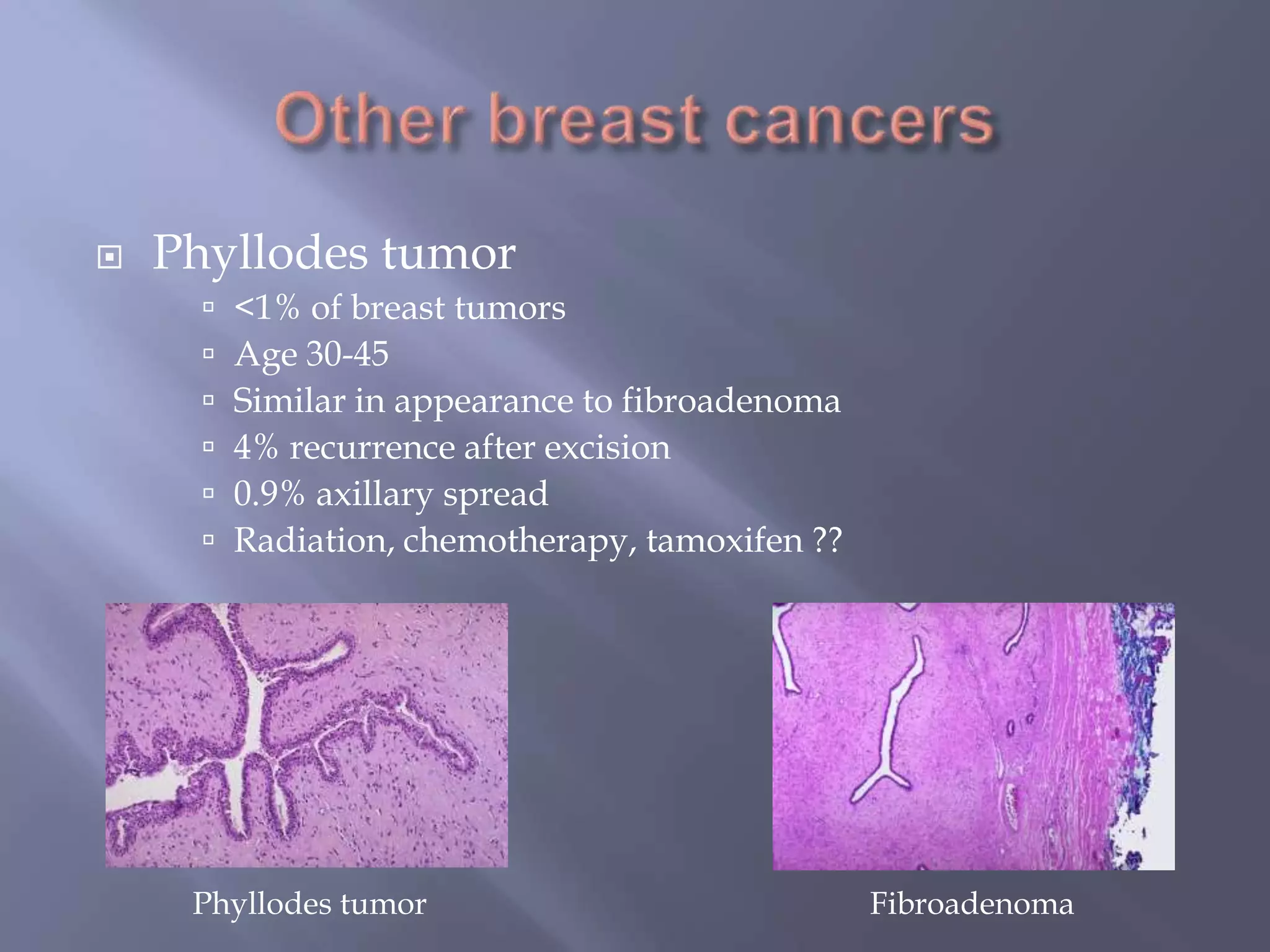
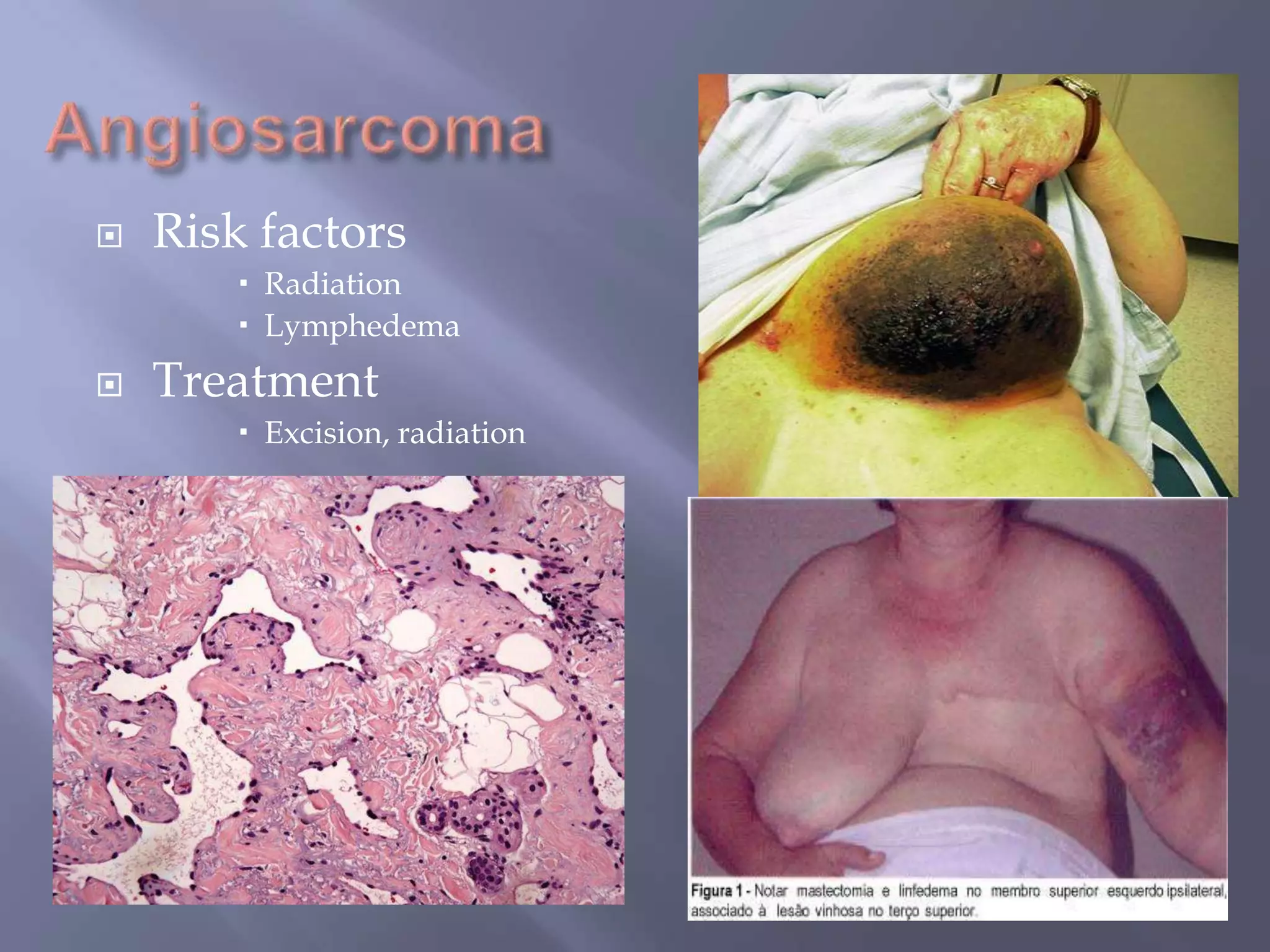
Breast cancer is the most common female cancer, accounting for over 200,000 new cases yearly in the United States. Screening mammography is recommended annually starting at age 50 to detect breast cancer early. Treatment options depend on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and receptor status, and may involve lumpectomy or mastectomy with radiation and/or chemotherapy, tamoxifen, or other targeted therapies. While most breast cancers are carcinomas, other rare types include angiosarcoma and phyllodes tumors.