Neurons
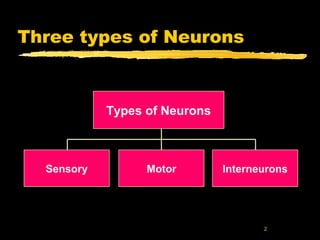
- 1. 2 Three types of Neurons Types of Neurons Sensory Motor Interneurons
- 2. 3 Sensory Neuron Also called AFFERENT Neurons Transmit impulses from the receptors in our sense organs (the eyes, ears, skin, nose, tongue and muscles, organs ) to the brain. Vision, hearing, taste and smell nerves are cranial and do NOT use the spinal cord Touch ( pressure, temperature & pain) nerves travel up the spinal cord and then to the brain. Deals with INCOMING messages from the outside world Also can transmit incoming messages from internal organs for pain ( ulcer, appendicitis) They have very long axons.
- 3. 4 Motor Neurons Also called EFFERENT Neurons Carry messages FROM the brain or spinal cord to Muscles and Tendons throughout the body ( including the heart, diaphragm, intestines, bladder and glands) Deals with OUTGOING messages from the brain/spinal cord to act upon the outside world They have very long axons
- 4. 5 INTERNEURONS Only found in the brain, spinal cord, and eye. Intervene between sensory neurons and motor neurons. They carry messages between other interneurons in the spinal cord and brain. Many more interneurons than sensory or motor neurons Easy to recognize – they have short axons
- 5. 6 Spinal Cord BrainSensory Neuron Sensory Neurons INPUT from sensory organ (skin) to the brain and spinal cord. Drawing shows a red sensory neuron in the skin for touch.
- 6. 7 Spinal Cord BrainSensory Neuron Motor Neuron Motor Neurons OUTPUT from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles telling you to move hand from source of pain.
- 7. 8 Spinal Cord BrainSensory Neuron Motor Neuron Interneurons Interneurons carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord.
- 8. 9 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Central Nervous System CNS: * brain & Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System PNS * sensory and motor neurons OUTSIDE of the brain and spinal cord * connects CNS to muscles, glands, and sense receptors
- 9. 10 The Peripheral Nervous System Divided into two parts: A) SOMATIC nervous system = controls body’s muscles and is VOLUNTARY Ex. scratch nose, move arm, squint…. B) AUTONOMIC nervous system = controls action of internal organs and glands and is INVOLUNTARY Ex. heart rate, digestion, respiration, bladder, sex organs…
- 10. 11 SOMATIC OR AUTONOMIC? Climbing stairs Colon contracts Curl tongue Pick up a toy Clench fist Get Goosebumps Heart beats Raise hand Pupils dilate Release of cortisol
- 11. 12 AUTONOMIC Nervous System Divided into two additional systems: a) SYMPATHETIC Nervous System = prepares body for emergency (“Fight or Flight”) Helps us deal with stress. b) PARASYMPATHETIC Nervous System = brings body back to rest/calm after a stressful event (homeostasis)
- 12. 13 AUTONOMIC Nervous System Sympathetic Parasympathetic EYES pupils dilate pupils contract SALIVATION decreases increases SKIN perspires dries RESPIRATION increases decreases HEART accelerates slows DIGESTION shuts down activates LIVER increase glucose decrease glucose ADRENAL GLAND secretes stress hormones decrease stress hormones
- 13. 14 Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system
- 14. 15 Divisions of the Nervous System
- 15. 16 Structures of a neuron
- 16. 17 The cell body or Soma Round, centrally located structure Contains DNA Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling Contains the cell’s Nucleus
- 17. 18 Dendrites: INPUT MANY short branching extensions from the cell body Information COLLECTORS Conduct impulses TO the cell body RECEIVE inputs/messages from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands
- 18. 19 Dendritic Growth Mature neurons generally can’t divide But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning
- 19. 20 Axon: OUTPUT Single LONG extension from the cell body The cell’s OUTPUT structure that SENDS messages to other neurons or muscles/glands 2 distinct parts tubelike structure branches at end of tube called “terminals” that connect to dendrites of nearby cells
- 20. 21 Myelin sheath White fatty casing on axon Acts as an electrical insulator Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. Myelination is not completed until about age 20 - 25. Special diseases of the myelin sheath are Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and Guillain- Barre syndrome. Myelin Sheath
- 21. 22 Glial Cell Means “glue” Nonneural white fatty cells that cover the axon to create myelin sheath. These are call “schwann” cells in the peripheral nervous system. Also interspersed among the neurons in the brain to give it support, structure, and supply nutrients. Holds the brain together like glue! These are called “astrocytes”. Brain has approx. 10 billion to I trillion neurons BUT 100 billion to 10 trillion glial cells. Tumor in the brain is made of glial cells NOT neurons. Glial cells can rapidly reproduce. Neurons can regenerate but not very rapidly.
- 22. 23 Nodes of Ranvier small gaps in the myelin sheath where each glial cell ends.
- 23. 24
- 24. 25 Neurons – magnified view
- 25. 26 How neurons communicate Neurons communicate by means of an electrochemical signal. The signal that travels WITHIN a Neuron is ELECTRICAL The signal that travels between neurons is CHEMICAL
- 26. 27 ELECTRICAL SIGNAL within a Neuron Electricity can flow within a neuron due to properties of the CELL MEMBRANE SEMI-PERMEABLE ( selectively permeable) Some things can go through but other things are trapped either on the inside or outside. PUMPS spend energy to force things to go into or out of a neuron CHANNELS are proteins with holes in them. They sit in the cell membrane and serve as gates to let certain things flow into or out of the cell.
- 27. 28 Electrical signals - cont Ion PUMPS keep an UNEVEN distribution of electrical charges inside and outside the neuron cell. IONS – atoms that carry units of (+) or (–) electrical charge. SODIUM (Na+) is a + charged ion that has a difficult time getting through the membrane. Chloride (Cl-) is a – charged ion that also has a hard time getting through the membrane. POTASSIUM (K+) is a + charged ion that easily travels inside and outside the neuron’s membrane.
- 28. 29 RESTING POTENTIAL When a neuron is not being stimulated and is not sending out signals. The inside of the cell is electrically negative relative to the outside which is positive. The inside of the neuron is 70mV less than the outside. ( -70mV) There is more sodium outside and more potassium inside the neuron. The cell is said to be POLARIZED
- 29. 30 Ion concentrations Cell Membrane in resting state K+ Na+ Cl-K+ A- Outside of Cell Inside of Cell Na+ Cl-
- 30. 31 The Cell Membrane is Semi- Permeable Cell Membrane at rest Na+ Cl-K+ Na+ Cl- K+ A- Outside of Cell Inside of Cell Potassium (K+) can pass through to equalize its concentration Sodium and Chlorine cannot pass through Result - inside is negative relative to outside - 70 mv
- 31. 32 ACTION POTENTIAL A stimulation ( sight, sound, touch ..etc) opens the ion channels so that sodium starts to get pumped into the cell . This changes the internal charge and when it rises from -70mV to -55mV it reaches a THRESHOLD and it triggers a nerve IMPULSE or ACTION POTENTIAL. The cell is now firing! The firing is an “ALL OR NONE” response – it either fires or doesn’t fire – there are no levels of intensity. The cell is said to be DEPOLARIZED.
- 32. 33 Depolarization leading to an Action Potential membrane allows sodium (NA+) into cell as channels open INSIDE of cell rapidly becomes more positive than outside
- 33. 34 Action Potential Within a Neuron
- 34. 35 Neuron Communication All-or-None Principle The principle that if a neuron fires it will always fire at the same intensity All action potentials are of the same strength. A neuron does NOT fire at 30%, 45% or 90% but at 100% each time it fires.
- 35. 36 REPOLARIZATION After cell fires it will reach a peak at +40 to +30mV THEN sodium channels shut down and potassium channels open as + charged ions are pushed out of the cell. This brings the internal charge back down toward -70mV HOWEVER – so much potassium flows out of the cell that it’s internal charge drop BELOW the resting potential of -70mV and goes down to -80mV.
- 36. 37 Repolarization follows After depolarization potassium (K+) moves out restoring the inside to a negative voltage This is called repolarization
- 37. 38 REFRACTORY PERIOD When the internal charge of a neuron drops below -70mV the neuron CANNOT FIRE. This refractory period lasts about .001 seconds. Eventually the ion pumps bring the internal charge back up to -70mV and the cell is once again at rest and ready for an action potential to occur. Action Potentials always begin at the cell body of the neuron and travel down the AXON
- 38. 39 Finally, Hyperpolarization Repolarization leads to a voltage below the resting potential, called hyperpolarization Now neuron cannot produce a new action potential This is the refractory period
- 39. 40
- 40. 41 Animation of action potential down an axon http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yQ-wQsEK21E& http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U0NpTdge3aw&
- 41. 42 Self-propagation – Moving electrical charge down the axon When an electrical impulse travels down the axon from the cell body it will form a domino effect at each node of Ranvier. Na+ channels will open and then close causing the electrical message to move in only one direction down the axon toward the axon terminal branches.
- 42. 43 Chemical Signal – between neurons When an impulse reaches the ending terminal of an axon it stimulates the opening of SYNAPTIC VESICLES ( sacs) that contain chemical NEUROTRANSMITTERS. These chemicals flow into the SYNACTIC CLEFT which is the space between the end of one neuron’s axon and the dendrite of a nearby neuron. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that travel across the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving dendrite.
- 43. 44 Synapse axon terminals contain small storage sacs called synaptic vesicles vesicles contain neurotransmitter molecules Sending Neuron Synapse Axon Terminal
- 44. 45 Neuron to Neuron Axons branch out and end near dendrites of neighboring cells Axon terminals are the tips of the axon’s branches A gap separates the axon terminals from dendrites Gap is the Synapse Cell Body Dendrite Axon
- 45. 46 SYNAPSE Specific neurotransmitters “bind” with specific postsynaptic receptor sites on the dendrite. LOCK and KEY model – neurotransmitters MUST match receptor site on dendrite. Neurotransmitter can either stimulate (depolarize) the next neuron causing it to fire or they can inhibit ( hyperpolarize) the next neuron and stop any transmission of electrical charge.
- 46. 47 Locks and Keys Neurotransmitter molecules have specific shapes positive ions (NA+ ) depolarize the neuron negative ions (CL-) hyperpolarize the neuron When NT binds to receptor, ions enter: Receptor molecules have binding sites
- 47. 48 Postsynaptic Firing Excitatory synapse – Neurotransmitter binds at receptor and makes the neuron more positive by opening sodium channels. This, in turn, will pass the firing message along to next neuron. Inhibitory synapse –Neurotransmitter binds at receptor and makes the neuron more negative by closing sodium channel and opening chloride channels. This, in turn, will stop the firing message. The SUM TOTAL of all inhibitory and excitatory incoming messages at the receptor sites on the dendrite will determine if the cell will fire or not.
- 48. 49 RE-UPTAKE Released neurotransmitters are eventually removed from the synapse by Re-Uptake. Neurotransmitters are sucked back up into the vesicles on the terminal button of the axon. Some neurotransmitters are also removed by enzymes that destroy the neurotransmitter while it is floating in the synapse.
- 49. 50
- 50. 51 View of Neuron communication http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r71RoIkftd4
- 51. 52 Animation of neuron firing down the axon to synapse http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TKG0MtH5crc
- 52. 53 CLASS LAB Passing neural messages Seconds to pass simple message from shoulder to brain –down arm to hand. Seconds to pass message from ankle to brain and then down arm to hand ( longer pathway) Time to pass message from shoulder to brain - PROCESS MESSAGE – then pass back down arm to hand. (more complex) Compare dollar drop SELF (internal signal at release of bill) OTHER ( external signal (EYES) at release of bill)
- 53. 54 Types of Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine (ACh) Found in neuromuscular junctions Involved in muscle movements learning and memory attention and arousal Problems: Too little = Alzheimer’s and paralysis Too much = muscle spasms /convulsions
- 54. 55 Disruption of Acetylcholine Functioning Curare & botulin are poisons that blocks ACh receptors (botox injections) paralysis results Nerve gases and Black Widow spider venom create too much ACh leads to severe muscle spasms and possible death
- 55. 56 Dopamine (DA) Involved in muscle movement attention/arousal learning & thought mood/emotion Too little = Parkinson’s disease Too much = Schizophrenia
- 56. 57 Parkinson’s Disease Results from loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra of the brain’s basal ganglia Symptoms include difficulty starting and stopping voluntary movements tremors at rest stooped posture rigidity poor balance
- 57. 58 Parkinson’s Disease Treatments L-dopa ( levodopa) agonist transplants of fetal dopamine-producing substantia nigra cells thalamotomy – destroy area of the thalamus that sends motor messages to the limbs electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors
- 59. 60 Serotonin Involved in sleep mood/depression hunger arousal Too little= depression Too much = anxiety, inhibits dreaming Prozac and SSRI’s (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are used to treat depression. They work by keeping serotonin in the synapse longer, giving it more time to exert an effect.
- 60. 61 How SSRI’s work to > serotonin in the synapse
- 61. 62
- 62. 63 Endorphins Natural opiates in brain Controls pain and pleasure Too little = pain, discomfort, depression Too much = euphoric high Runner’s high— feeling of pleasure after a long run is due to heavy endorphin release to offset pain in muscles. No pain during catastrophic accident
- 63. 64 Norepinephrine (NE) Involved in Mood Arousal from stess Learning & memory Too little = depression Too much = anxiety
- 64. 65 GABA - Gama Amino Butyric Acid Inhibition of brain activity Too little = eating disorders, sleep disorders, epilepsy, anxiety and Huntington’s disease Symptoms: jerky involuntary movements mental deterioration
- 65. 66 Melatonin Affects biological clock or circadian rhythm and mood. Created in the pineal gland near the brain Lack of sunlight to the eye increases melatonin Too much = seasonal depression, sleepiness Too little = alertness, insomnia
- 66. 67 Glutamate Involved in memory Too much = migraine Too little = memory problems
- 67. 68 Some Drugs work on neuron receptors in the synapse Agonist : drug that is so similar to the neurotransmitter that it mimics it and fits into the receptor site acting just like the real neurotransmitter. Ex. opiates–endorphin l-dopa – dopamine cocaine- dopamine Problem: Can cause the brain to stop making the real neurotransmitters.
- 68. 69 Drugs Antagonist - drug that is shaped like the neurotransmitter BUT fits the receptor site poorly and ends up BLOCKING the real neurotransmitter from passing. Inhibits. Ex. beta blockers – block adrenaline botulin – blocks acetylcholine
- 69. 70 Agonists
- 70. 71 Figure 2.7 How Drugs Affect Synaptic Transmission Hockenbury: Psychology, Fourth Edition Copyright © 2005 by Worth Publishers
- 71. 72 REFLEXES – Reflex Arc Part of the autonomic system. Most sensory messages travel up the spinal cord to the brain and then back down spinal cord to muscles. REFLEXES bypass the brain and travel directly to the spinal cord and back to the muscle. PURPOSE : Faster responses
- 72. 73
- 74. 75 Ganglion A clump of neuron cell bodies.
- 75. 76 The Nerves Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system, and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. They are part of the peripheral nervous system, and connect muscles
- 76. 77 NEURAL NETWORKS Cluster of neurons in the CNS that carry on a specific function. Ex. memory, learning, problem solving strategy,…
- 77. 78 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Set of glands that secrete HORMONES in into the bloodstream. The body’s “slow” chemical communication system. Communication is carried out by hormones synthesized by a set of glands. Very closely connected to the nervous system.
- 79. 80 Hormones Hormones are chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands and secreted in the bloodstream. Some are identical to neurotransmitters but work much SLOWER. Their effects last LONGER than neurotransmitters. Example: the hormone ADRENALINE (neurotransmitter epinephrine) increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar and feelings of excitement during emergency situations.
Editor's Notes
- Key words: Types of neurons; sensory neurons; motor neurons; interneurons; afferent nerves; efferent nerves
- Key words: sensory neurons; afferent nerves; types of neurons
- Key words: Motor neurons; efferent nerves; types of neurons
- Key words: interneurons; types of neurons
- Kolb & Whishaw, An Introduction to Brain and Behavior How is the Brain Organized? Figure 2.29
- Key words: Neuron; sructures of neurons
- Key words: Cell body; soma; cell nucleus Interesting facts: The DNA in the nucleus of the cell has lost its ability to divide. therefore, when a neuron dies,for the most part, the adult brain cannot simply grow new neurons. (Note there are a few exceptions to this rule.) The relative inability to grow new neurons leads to two interesting questions: Q1: How do brain tumors (cancer) occur? A: Unlike neurons, glial cells can divide and grow new cells throughout one's lifetime. Most brain tumors are limited to glial cells, not neurons. Q2: If a person cannot grow new neurons, how does the brain change in order to accomodate new learning? A: One mechanism by which the brain adapts to help you learn new information involves the structure on the next slide: the dendrites.
- Key words: dendrite Interesting facts: - The word DENDRITE comes from the Greek word for tree. This may serve as a useful analogy in discussing the dendrites for several reasons: 1. The dendrites branch repeatedly from the cell body (to increase the surface area of the cell to better allow the cell to receive incoming information). These radiations from the cell body are often referred to as a dendritic tree. 2. In terms of function, the dendrites function similiarly to the roots of a tree. Just as the roots take water and other nutrients from the soil and carry them to other parts of the tree, the dendrites collect information and and spread it to other parts of the neuron.
- Key words: dendrite Interesting facts: - The word DENDRITE comes from the Greek word for tree. This may serve as a useful analogy in discussing the dendrites for several reasons: 1. The dendrites branch repeatedly from the cell body (to increase the surface area of the cell to better allow the cell to receive incoming information). These radiations from the cell body are often referred to as a dendritic tree. 2. In terms of function, the dendrites function similiarly to the roots of a tree. Just as the roots take water and other nutrients from the soil and carry them to other parts of the tree, the dendrites collect information and and spread it to other parts of the neuron.
- Key words: axon; action potentials Interesting facts: - The diameter of an axon may vary from approximately 1mm-20mm. - An axon may travel long distances to reach it's destination (longest axon is approximately 3 feet in humans and 10 feet in giraffes).
- Key words: myelin sheath; action potentials; axon Interesting facts: - The myelin sheath is NOT a part of the axon. The myelin sheath is actually formed of glial cells (oligodendricytes and Schwann cells) that wrap around the axon. - You may have often heard the brain referred to as either white matter or gray matter. The myelin sheath appears white in nature. Hence, the term white matter refers to areas of the brain that are myelinated. Gray matter refers to areas of the brain that are unmyelinated. - When you accidentally cut yourself, you often visually notice that you've cut yourself before you actually feel any pain from the cut. The reason for this is that visual information uses myelinated axons; whereas, pain information uses unmyelinated axons. - The loss of myelin is a significant factor in the disease multiple sclerosis (MS). When myelin is lost, the high-speed transmission of information is slowed down or blocked completely, which could lead the person with the inability to walk, write or speak.
- Key words: ion concentrations; cell membrane; intracellular fluid; extracellular fluid; Na+; Cl-; K+ Slide ten represents a schematic of the typical concentrations of the intracellular and extracellular fluids. There are large concentrations of sodium and chloride ions concentrations of on the outside of the cell (relative to inside the cell). There are large concentrations of potassium ions and protein molecules on the insde of the cell (relative to concentrations on the outside of the cell).
- Key words: Cell membrane; semi-permeable; K+; Na+; Cl- The cell membrane is semi-permeable. That is, when the neuron is at rest, the cell membrane allows some ions (K+) to pass freely through the cell membrane, whereas other ions (such as Na+ and Cl-) cannot. Hit enter once and K+ ions will slowly pass through the cell membrane. After K+ animation is finished, hit enter again and animation showing that Na+ and l- ions cannot pass through the membrane will occur.
- key words: axon terminal; synaptic vesicles; neurotransmitters
- Key words: axon terminal .
- Graphic, Hockenbury slides
- key words: Basal ganglia; Parkinson's disease; dopamine
- L-Dopa facts: The purpose of this drug is to increase the amount of dopamine in the system. L-dopa is a precursor to dopamine. It will eventually be converted into dopamine. Question: Why not just give the patient dopamine? Answer: Dopamine cannot cross the blood brain barrier. If you take a dopamine pill, you will see increased levels of doapmine in the body, but not in the brain. L-dopa can enter the brain.
- OBJECTIVE 4-10| Describe the nature and functions of the endocrine system and its interaction with the nervous system.
