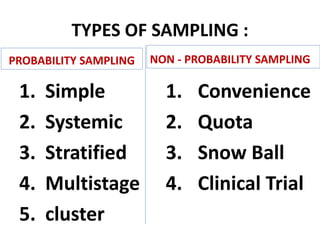
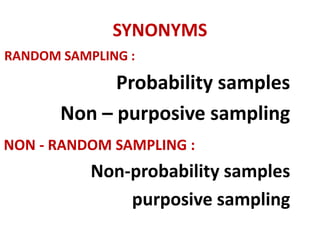
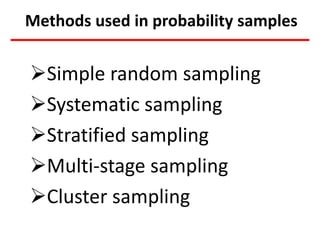
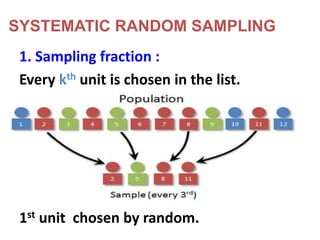
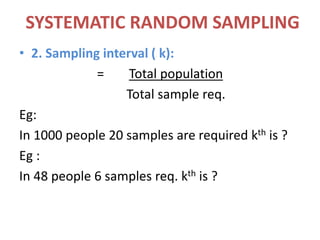
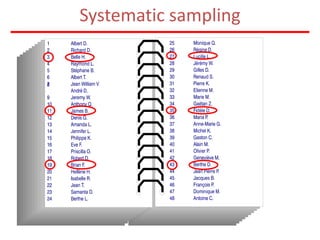
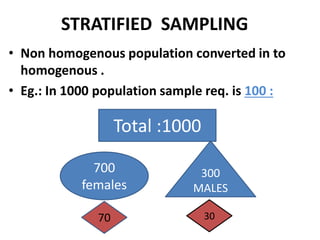
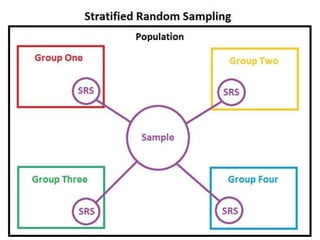
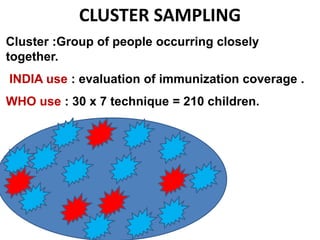
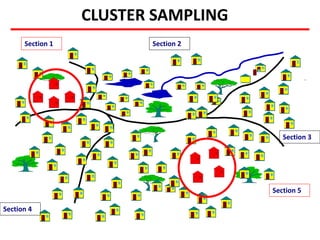
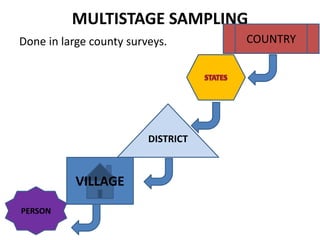
This document discusses different types of sampling procedures used in statistics and population studies. It defines key terms like population and sample. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, multistage sampling, and cluster sampling ensure each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Non-probability methods like convenience sampling, quota sampling, snowball sampling, and clinical trials sampling do not use random selection. Probability sampling allows for better accuracy and generalizability of results to the overall population. The document provides examples and definitions of different sampling methods.