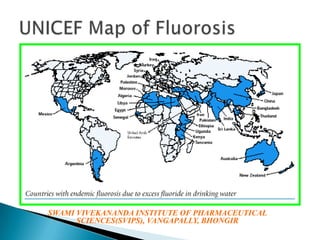
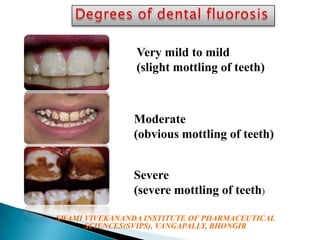
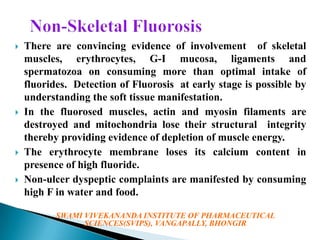
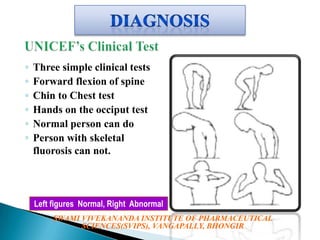
Fluorosis is a public health issue primarily caused by fluoride deposition affecting both hard and soft tissues, with varying degrees of severity and symptoms such as dental discoloration and skeletal pain. It is particularly endemic in regions like India and China, where its manifestation ranges from mild dental imperfections in children to severe skeletal issues in adults. Preventative measures, including de-fluoridation of water and dietary interventions, can help mitigate the effects of fluorosis.















![How does fluoride treatment prevent tooth
decay ?
Human teeth (and bones) are primarily composed of the
mineral calcium hydroxyapatite.
Calcium hydroxyapatite has the chemical formula:
Ca5[(PO4)3OH]. One of the main components of this mineral
is the hydroxyl ion.
Fluoride substitutes for the hydroxyl ion, producing calcium
fluoroapatite, with the chemical formula: Ca5[(PO4)3F]
Calcium fluoroapatite is chemically stable than calcium
hydroxyapatite in acid environment of the mouth.
This means that a higher concentration of calcium
fluoroapatite in tooth enamel decreases tooth dissolution, and
therefore can decrease the incidence of tooth decay.
SWAMI VIVEKANANDA INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL
SCIENCES(SVIPS), VANGAPALLY, BHONGIR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluorosis-131026035241-phpapp01/85/Fluorosis-20-320.jpg)



