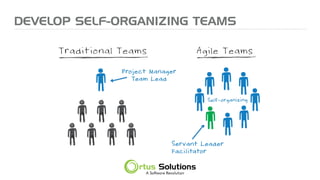
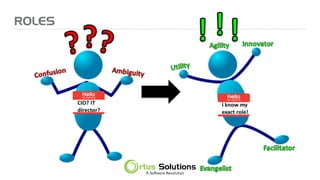
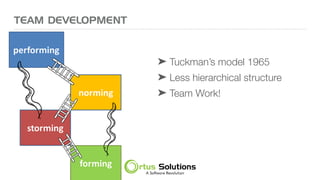
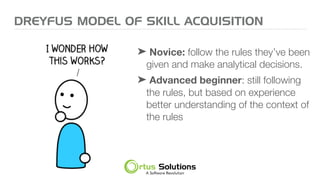
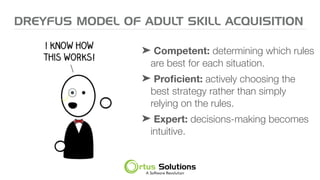
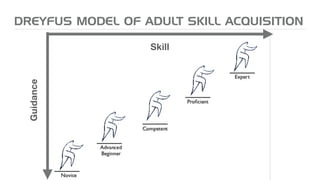
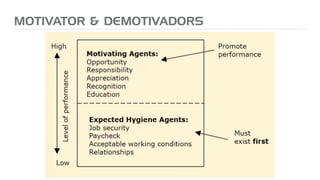
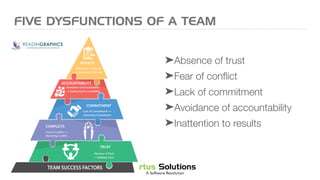
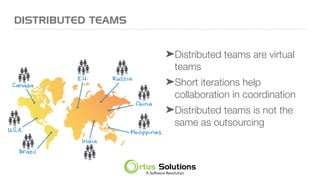
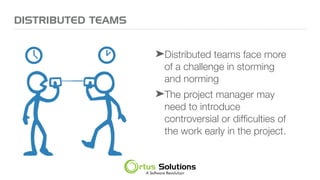
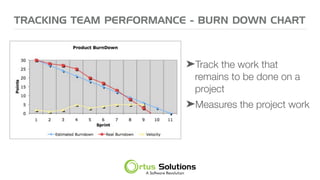
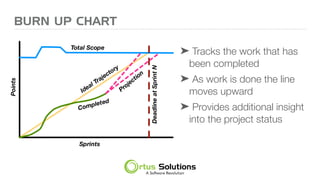
The document outlines key principles for building high-performance teams (HPT), emphasizing the importance of people over processes, servant leadership, and the development of self-organizing teams. It details team dynamics using Tuckman's model and highlights roles such as business representatives, scrum masters, and project sponsors. The text also discusses tools for communication and project management, as well as fostering an engaging culture that encourages experimentation and constructive conflict.