Line diagrams - skull base 360 - part 2
- 1. Dr.B.D.CHAURASIA - Great anatomist of india whose books inspired me to take up surgical field . Simplified the anatomy with line diagrams . Line diagrams - Skull base 360°- Part 2 24-05-2017 2.38 pm
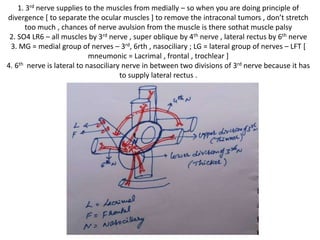
- 2. 1. 3rd nerve supplies to the muscles from medially – so when you are doing principle of divergence [ to separate the ocular muscles ] to remove the intraconal tumors , don’t stretch too much , chances of nerve avulsion from the muscle is there sothat muscle palsy 2. SO4 LR6 – all muscles by 3rd nerve , super oblique by 4th nerve , lateral rectus by 6th nerve 3. MG = medial group of nerves – 3rd, 6rth , nasociliary ; LG = lateral group of nerves – LFT [ mneumonic = Lacrimal , frontal , trochlear ] 4. 6th nerve is lateral to nasociliary nerve in between two divisions of 3rd nerve because it has to supply lateral rectus .
- 3. Red rings = thicker lower division , thinner upper division ; Green ring = 6th nerve ; Yellow ring = Nasociliary nerve Mneumonic = My left hand middle finger is thicker than left hand index finger , so Lower division of 3rd nerve is thicker than upper division of 3rd nerve . Nasociliary nerve present between two divisions of 3rd nerve & 6th nerve present lateral to nasociliary nerve
- 4. 1. In SOF [ superior orbital fissure ] & Orbital apex in nasal endosopic view - 3rd nerve devides into thicker lower division & thinner upper division – in between these two divisions 6th nerve & nasociliary nerve is seen . 2. 6th nerve is lateral to nasociliary nerve in between two divisions of 3rd nerve because it has to supply lateral rectus .
- 5. Levator palpebrae superioris originates from lesser wing of sphenoid
- 6. 1. Lateral part- LFT [ Liver functional tests ] Menumonic – Lacrimal N., Frontal N.,TrochlearN. & Superior Opthalmic Vein. 2. The frontal and trochlear nerves ascend above the Levator muscle & superior rectus muscle. Frontal N. devides into Sup.Troch.N. & Supraorb.N. – NOTE Fal.Lig
- 7. A segment of the orbital portion of the optic nerve has been removed. This exposes the branch of the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve, which passes below the optic nerve and enters the medial rectus muscle.
- 8. 1. In the posterior part of the CS the trochlear nerve is below the oculomotor nerve, while anteriorly it turns upward and becomes the most superior structure of the CS (at the level of the optic strut) (Iaconetta et al. 2012 ) . 2. Trochlear nerve is always superior to V1.
- 9. 1. 6th nerve crosses para-clival & para-sellar carotid junction in the dorellos canal 2. in SOF 4TH nerve is above the 3rd nerve where as in cavernous sinus 3rd nerve above 4th nerve 3. supratrochlear & infratrochlear triangle above & below the 4th nerve .
- 10. 1. Thicker inferior division of 3rd N. & thinner superior division of 3rd N . 2. Nasociliary N passes between divisions of 3rd N. 3. In the annulus, the nasociliary nerve passes medially, and it is located between the two divisions of the oculomotor nerve; the abducens nerve runs superiorly and laterally to reach the lateral rectus muscle.
- 11. M-OCR
- 12. Two potential iatrogenic carotid injury areas We have to very careful at m-OCR in transtubercular & transplanum drilling because praclinoidal & supraclinoidal junction is exactly m-OCR Posterior genu is the most common area of iatrogenic injury of carotid
- 13. The optic chiasm is referred to as prefixed when it is located above the tuberculum sellae and as a postfixed chiasm when it is situated superior to the dorsum sellae
- 14. Parasagittal cadaveric specimen with a postfixed chiasm. Note the more inclined pituitary stalk (stalk). For reference, note the left and right optic nerves
- 15. Parasagittal cadaveric specimen with a normally positioned optic chiasm. For reference, note the right optic nerve (II)
- 16. Subfrontal cadaveric dissection in a specimen found to have a prefixed chiasm. Note the anterior location of the pituitary stalk (arrow). For reference, note the optic nerves (II) and left internal carotid artery (ICA)
- 18. Fig. 2.21 Sagittal sections and superior views of the sellar region showing the optic nerve and chiasm and the carotid artery. The prefixed chiasm is located above the tuberculum. The normal chiasm is located above the diaphragma. The postfixed chiasm is situated above the dorsum.
- 19. Opthalmic artery
- 20. classification of the ophthalmic artery types http://www.springerimages.com/Images/MedicineAndPublicHealth/1-10.1007_s10143-006- 0028-6-1 a = intradural type, b = extradural supra-optic strut type [ Optic strut = L-OCR ] c = extradural trans-optic strut type
- 21. Type b = extradural supra-optic strut type [ Optic strut = L-OCR
- 22. In Type c = extradural trans-optic strut type , the Opthalmic foramen in Optic strut
- 23. classification of the ophthalmic artery types http://www.springerimages.com/Images/MedicineAndPublicHealth/1- 10.1007_s10143-006-0028-6-1 a = intradural type, b = extradural supra-optic strut type [ Optic strut = L-OCR ] c = extradural trans-optic strut type on optic nerve, pr proximal ring, cdr carotid dural ring= upper dural ring , ica internal carotid artery I think this variation is type c
- 24. In both type a = intradural type, b = extradural supra-optic strut types Opthalmic foramen is in Optic canal
- 25. In Type c = extradural trans-optic strut type , the Opthalmic foramen in Optic strut
- 26. http://www.nature.com/eye/journal/v20/n10/fig_tab/6702377f3.html#figure -title The upper diagram is Type a or b Opthalmic artery , the lower diagram is Type c Opthalmic artery Dup OC = Duplicate Opthalmic canal
- 27. Anterior limit of Transplanum approach is PEA – when we are removing a triangular piece of bone in Transplanum approach , the base of traingle is PEA
- 28. PEA roughtly corresponds with Optic tubercle continuation above
- 29. Petrous apex
- 30. Petrous bone has three surfaces with three boarders & divided into three 1/3rds
- 31. The petrous portion of the temporal bone or pyramid is pyramidal
- 32. Petrous apex =Anterior Triangular ( T ) area + Posterior Quadrangular ( Q ) area
- 34. Approaches to petrous apex LATERAL SKULL BASE 1. From above the labyrinth a. Middle cranial fossa transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach 2. From posterior to the labyrinth a. Retrolabyrinthine transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach / endoscopic retrolabyrinthine approach 3. From through the labyrinth a. Translabyrinthine transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach b. Transcochlear transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach 4. From below the labyrinth a. Infralabyrinthine/Infra-otic = Infratemporal fossa type A transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach b. POTS c. Infralabyrinthine/Infra-otic = Infratemporal fossa type B & C transpetrous [ = Trans-apical ] approach ANTERIOR SKULL BASE 1. From anterior to the labyrinth a. Suprapetrous approach b. Infrapetrous approach
- 35. Lateral skull base view
- 36. Middle cranial fossa transpetrous approach
- 37. the anterior petrosectomy with preoperative embolization of the inferior petrosal sinus is a time-conserving approach giving one of the best routes to reach the ventral brainstem while working in front of the cranial nerves and preserving hearing. http://www.worldneurosurgery.org/article/S0090-3019(00)00271-8/fulltext
- 38. Retrolabyrinthine transpetrous approach – dotted red line means trajectory medial to labyrinth & cochlea
- 39. Tranaslabyrinthine Transpetrous [= Transapical ] approach After drilling the LSC , PSC & SSC – IAC is exposed Transpetrous path is above & below the IAC & medial to cochlea
- 40. The Enlarged Translabyrinthine Approach with Transpetrous ( = Transapical ) Extension – intradurally above the IAC you will get 5th nerve where below the IAC you will get 6th nerve & lower cranial nerves . Schematic drawings showing the amount of bone removal around the internal auditory canal in the different variants of the translabyrinthine approach. Note that in the transapical modification the exposure is 320° and about 360° in types I and II, respectively. Abbreviations as in Fig. 5.1. cn, cranial nerve; CN, cochlear nerve; FN, facial nerve; IV, inferior vestibular nerve; SV, superior vestibular nerve.
- 42. Infratemporal fossa approach –A & B Transpetrous approach
- 43. POTS = Petro-occipital trans-sigmoid approach – sigmoid sinus is opened – dotted red line means trajectory medial to labyrinth & cochlea
- 44. Anterior skull base – suprapetrous & infrapetrous approach
- 45. CP angle
- 47. Various Transpetrous approaches to get lateral view of CP angle ( = to reach Lateral part of Posterior cranial fossa dura ) predominently to reach Level 1 = Trigeminal nerve area & Level 2 = AFB area 1. Retrolabyrinthine Transpetrous ( = Transapical ) 2. Translabyrinthine Transpetrous ( = Transapical ) 3. Transcochlear Transpetrous ( = Transapical ) predominently to reach Level 3 = Lower cranial nerve area 4. POTS = Petro-Occipital Trans- Sigmoid approach predominently to reach Level 4 = Foramen magnum area 5. Exrtreme lateral or Far lateral or Transcondylar approach
- 48. identify the superior ampullary nerve first and then find the facial nerve (F) after eliminating this nerve and the superior vestibular nerve (Vs).
- 49. The Enlarged Translabyrinthine Approach with Transpetrous ( = Transapical ) Extension – intradurally above the IAC you will get 5th nerve where below the IAC you will get 6th nerve & lower cranial nerves . Schematic drawings showing the amount of bone removal around the internal auditory canal in the different variants of the translabyrinthine approach. Note that in the transapical modification the exposure is 320° and about 360° in types I and II, respectively. Abbreviations as in Fig. 5.1. cn, cranial nerve; CN, cochlear nerve; FN, facial nerve; IV, inferior vestibular nerve; SV, superior vestibular nerve.
- 51. Drill from inside to outside in middle cranial fossa approach of IAC
- 52. (Right ear) Diagram of the internal auditory canal near the fundus. The superior ampullary nerve (AN) is shown overlapping the superior vestibular nerve (SVN). CN, cochlear nerve; FN, facial nerve; HC, horizontal crest; IVN, inferior vestibular nerve; VC, vertical crest (Bill’s bar).
- 53. Cranial nerves
- 57. 1. 3th nerve between PCA & SCA 2. 4th nerve coming from dorsal brain stem passes above SCA [ some times SCA has two branches] 3. 6th nerve originates at VBJ [ Vertebro-basillar junction ] . 6th nerve may have two rootlets of origin , one above & one below the AICA 4. In 30 % of cases AICA passes in between 7th & 8th nerves 5. PICA passes between two bundles of 12th nerve & between two roots of 11th nerve [ 11c = 11th cervical , 11s = 11th spinal root ] 6. The exit zones of the 6th and 12th nerves are at the same level [ same vertical line when view from Transclival approah ( through lower clivus ) ] 7. 11th nerve behind left vertebral artery at cervico-medullary junction . 11th is closely related to the vertebral artery (VA) at the point of dural entrance
- 58. 1. 3th nerve between PCA & SCA 2. 4th nerve coming from dorsal brain stem passes above SCA [ some times SCA has two branches] 3. 6th nerve originates at VBJ [ Vertebro- basillar junction ] . 6th nerve may have two rootlets of origin , one above & one below the AICA 4. In 30 % of cases AICA passes in between 7th & 8th nerves 5. PICA passes between two bundles of 12th nerve & between two roots of 11th nerve [ 11c = 11th cervical , 11s = 11th spinal root ] 6. The exit zones of the 6th and 12th nerves are at the same level [ same vertical line when view from Transclival approah ( through lower clivus ) ] 7. 11th nerve behind left vertebral artery at cervico-medullary junction . 11th is closely related to the vertebral artery (VA) at the point of dural entrance
- 60. 1. 3th nerve between PCA & SCA 2. 4th nerve coming from dorsal brain stem passes above SCA [ some times SCA has two branches] 3. 6th nerve originates at VBJ [ Vertebro-basillar junction ] . 6th nerve may have two rootlets of origin , one above & one below the AICA 4. In 30 % of cases AICA passes in between 7th & 8th nerves 5. PICA passes between two bundles of 12th nerve & between two roots of 11th nerve [ 11c = 11th cervical , 11s = 11th spinal root ] 6. The exit zones of the 6th and 12th nerves are at the same level [ same vertical line when view from Transclival approah ( through lower clivus ) ] 7. 11th nerve behind left vertebral artery at cervico-medullary junction . 11th is closely related to the vertebral artery (VA) at the point of dural entrance
- 61. 1. Laceral carotid & jugular tubercle & lower cranial nerves 9th ,10th ,11th are in the same line . 2. hypoglossal canal present between occipital condyle/foramen magnum & jugular tubercle
- 62. 1. Laceral carotid & jugular tubercle & lower cranial nerves 9th ,10th ,11th are in the same saggital line . 2. hypoglossal canal present between occipital condyle/foramen magnum & jugular tubercle 3. PICA passes between two bundles of 12th nerve & between two roots of 11th nerve [ 11c = 11th cervical , 11s = 11th spinal root ] & encirlces lower cranial nerves 9th ,10th ,11th
- 65. 3rd nerve is sandwiched between posterior cerebral artery [ PCA ] & superior cerebellar artery [ SCA ]
- 66. 1. 3rd nerve from interpeduncular fossa 2. Only cranial nerve which comes from dorasal surface is 4th nerve 3. 6th nerve originates from ponto-medullary junction = vertebro- basillar junction
- 67. Both sides 6th nerves in dorello’s canals present medial to para-clival carotids in mid-clivus & crosses Para-clival & Para- sellar carotids juction in cavernous sinus
- 71. 6th nerve (the snake nerve) 6th nerve originates above the VBJ [ vertebro-basillar junction ] – Prof. Amin Kassam
- 72. 3rd ventricle
- 73. Anterior choraoid arteries goes towards optic tract
- 76. Optic chiasma – infundibulum – Mamillary bodies
- 77. Circle of willis
- 79. In anterior skull base approach
- 80. Middle cranial fossa approach
- 81. In anterior skull base approach - Type C Modified Transcochlear Approach – after cutting the tentorium With mild retraction of the temporal lobe, the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery (ICA) into the anterior (ACA) and middle cerebral (MCA) arteries is seen. The ipsilateral (ON) and contralateral (ONc) optic nerves are seen. The oculomotor nerve (III) is embraced by the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) superiorly and the superior cerebellar artery (SCA) inferiorly
- 82. In the descriptive analysis of the 20 specimens, the PCoAs distance was 9 to 18.9 mm, mean of 12.5 mm, median of 12.2 mm, standard deviation of 2.3 mm.
- 83. http://www.ajnr.org/content/27/8/1770/F2.expansion.html Classification of the anatomic variations in the circle of Willis. In the “textbook” type, both the precommunicating segment of the anterior cerebral artery (A1) and that of the posterior cerebral artery (P1) were normal in size. The next group included both right and left A1 hypoplasia. Because no significant difference between cerebral arteries on the right and left sides has been established,5,18 we combined right and left A1 hypoplasia into A1 hypoplasia. The next group included right and left P1 hypoplasia, which again were treated as a single category, P1 hypoplasia. “Other” type included a combination of A1 hypoplasia and P1 hypoplasia, bilateral P1 hypoplasia, as well as other unclassified variations. ACA indicates anterior cerebral artery; ACo, anterior communicating artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery; ICA, internal cerebral artery; PCo, posterior communicating artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; BA, basilar artery
- 84. http://www.ajnr.org/content/27/8/1770/F3.expansion.html Relative contribution of proximal arteries to total volume flow in variations in the circle of Willis. Values signify mean percentage ± SD. The upper left value corresponds to the relative contribution of the right internal carotid artery in the “textbook” type or of the internal carotid artery ipsilateral to hypoplastic A1 or P1 in the other variations. The upper right value corresponds to the relative contribution of the left internal carotid artery in the “textbook” type, or of the internal carotid artery contralateral to hypoplastic A1 or P1 in the other variations. The value at the bottom corresponds to the relative contribution of the basilar artery. * The value for A1 hypoplasia variation was significantly smaller than those for “textbook” type and P1 hypoplasia variation. The value for P1 hypoplasia variation was significantly larger than that for “textbook” type. ** The value for A1 hypoplasia variation was significantly larger than that for “textbook” type. *** The value for P1 hypoplasia variation was significantly smaller than that for “textbook” type.
- 85. http://stroke.ahajournals.org/content/30/12/2671/F2.expansion.html Scheme of anatomic variations of the posterior part of the CW: variant types a through c are complete, whereas the remainder are incomplete. a, Bilateral PCoA present. b, PCA originating predominantly from the ICA. This type is known as a unilateral fetal-type PCA (FTP), indicated by the arrows; the PCoA on the other side is present. c, Bilateral FTP, with both P1 segments patent. d, Unilateral PCoA present. e, Hypoplasia or absence of both PCoAs, with isolation of the anterior and posterior circle parts at this level. f, Unilateral FTP, with hypoplasia or absence of the P1 segment. g, Unilateral FTP, with hypoplasia or absence of the contralateral PCoA. h, Unilateral FTP, with hypoplasia or absence of the P1 and PCoA. i, Bilateral FTP, with hypoplasia or absence of both P1 segments. j, Bilateral FTP, with hypoplasia or absence of one P1 segment.
- 86. Open skull base approaches
- 93. For Other powerpoint presentatioins of “ Skull base 360° ” I will update continuosly with date tag at the end as I am getting more & more information click www.skullbase360.in - you have to login to slideshare.net with Facebook account for downloading.
