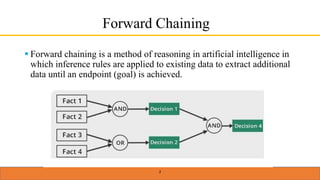
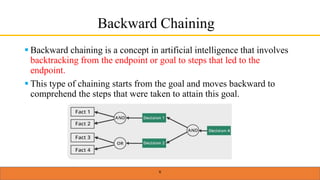
This document provides an overview of forward chaining and backward chaining in artificial intelligence. Forward chaining applies inference rules to existing data to derive new facts until reaching a goal. It proceeds from known facts to a conclusion. Backward chaining starts from a goal and moves backward to determine what facts must be true to satisfy the goal. It uses modus ponens inference to break the goal into subgoals until reaching initial conditions. Examples are given to illustrate the difference between the two approaches.