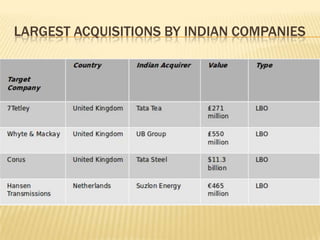
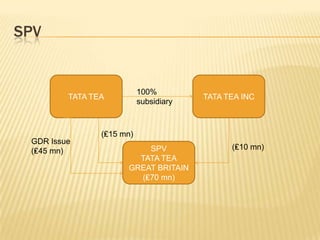
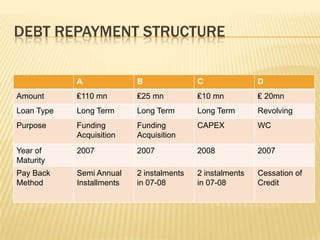
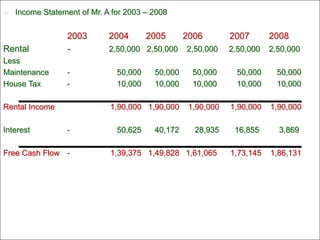
The document discusses Tata Tea's acquisition of Tetley in 2000 through a leveraged buyout (LBO). Key points:
1) Tata Tea formed a special purpose vehicle (SPV) called Tata Tea (Great Britain) to acquire Tetley's assets using £70M in equity and £235M in debt financing.
2) The SPV used a structured financing approach with multiple debt tranches to raise funds and acquire Tetley for £271M.
3) The deal provided synergies for both companies by giving Tata Tea access to Tetley's global distribution network and premium brands, and Tetley access to Tata Tea's production facilities.