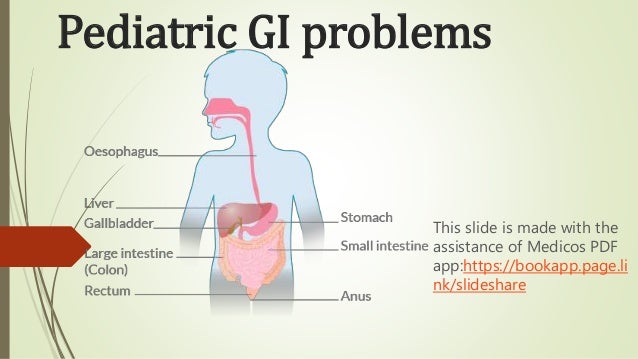
Pediatric gi problems
- 1. Pediatric GI problems This slide is made with the assistance of Medicos PDF app:https://bookapp.page.li nk/slideshare
- 2. Abdominal pain in children DDx: Acute abdominal pain Inflammatory: Abdominal infection: appendicitis, gastroenteritis, UTI, mesenteric adenitis (post URTI), mumps pancreatitis, hepatitis. Lower lobe pneumonia. Autoimmune: IBD, HSP , DKA.
- 3. Anatomical: GI obstruction, constipation. Meckel's complication e.g. obstruction, inflammation. However, Meckel's is usually asymptomatic. Renal and genitourinary: hydronephrosis, menstruation. Compressed anatomy: strangulated inguinal hernia, testis torsion. Acute abdominal pain in children often has no specific cause ('non- specific abdominal pain'), and resolves in 24h.
- 4. DDx: Chronic and recurrent abdominal pain It is usually non-organic (aka functional), but organic causes include: Upper GI: GORD, PUD. Dietary: Cow's milk protein allergy, lactose intolerance, coeliac disease. Lower GI: IBD, constipation. Malrotation Abdominal migraines: headaches, paroxysmal midline pain, facial pallor, and nausea. Family history of migraine often found. Genitourinary: recurrent UTI, gynaecological problems. Hepatobiliary: pancreatitis, hepatitis.
- 6. Definitions Posseting: non-forceful return of milk with wind. Regurgitation: non-forceful but more volume than posseting, usually due to GORD Vomiting: forceful return of upper GI contents. Most commonly due to GORD or gastroenteritis. Worry if it is bilious, prolonged, or accompanied by systemic symptoms.
- 7. Differential diagnosis Acute vomiting: Infection: gastroenteritis, respiratory tract infection, UTI, meningitis. Pyloric stenosis. Blood-stained vomit: Oesophagitis/PUD. Malrotation Pertussis
- 8. Differential diagnosis Bile-stained vomit suggests GI obstruction. Chronic vomiting: GORD Overfeeding
- 9. DDx: Diarrhoea in children
- 10. Non-bloody diarrhoea: Infection: gastroenteritis (GE), or potentially any infection e.g. UTI, appendicitis. Malabsorption: coeliac (also causes constipation), CF. Dietary: cow's milk protein allergy, lactose intolerance. IBD, with Crohn's commoner than UC in kids. IBS
- 11. Bloody diarrhoea: Infectious and inflammatory: bacterial GE, IBD (UC > Crohn's if bloody), necrotising entero-colitis, haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Obstruction: intussusception, midgut volvulus. Cow's milk protein allergy (flecks of blood). Juvenile polyps or Meckel's may cause PR bleeding without diarrhoea.
- 12. Toddler diarrhoea: Common, chronic diarrhoea syndrome, but the child is otherwise well. Bits of poorly-digested vegetables often seen in the diarrhoea. Usually resolves by 5 years old.
- 13. GI obstruction in children
- 14. Causes Pyloric stenosis. Duodenal atresia. Usually presents in first 24 hrs of life. Intussusception Malrotation and volvulus. Meckel's diverticulum.
- 15. Causes Strangulated inguinal hernia. Hirschsprung's Meconium ileus. Signs and symptoms Vomiting, possibly bile-stained if obstruction is below the sphincter of Oddi. Abdominal distention, especially if lower.
- 16. Intussusception
- 17. Pathophysiology and epidemiology Telescoping of bowel, usually of ileum into cecum. Usual age 6-36 months. May be linked to infection (e.g. rotavirus, adenovirus), leading to Peyer's patch (lymphatic) hypertrophy. In older children and adults (rare), it is often secondary to a polyp or tumour.
- 18. Signs and symptoms Episodic, severe colicky pain and pallor, with knees drawn up. Sausage-shaped mass in abdomen and/or abdominal distention. Redcurrant jelly stool (blood stained). A late sign, suggesting bowel ischaemia has occurred. Bile-stained vomit. Shock
- 19. Investigations Ultrasound: doughnut sign. Management US-guided air enema insufflation. Surgery is needed in 25%
- 21. Pathophysiology and epidemiology Congenital absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric and submucosal plexus. Usually affects the rectosigmoid, but can be whole colon. Absence of parasympathetic action leads to bowel obstruction. Usually presents Around 1/10 patients also have Down's. Prevalence: 1/5000.
- 22. Signs and symptoms Abdominal distention. Delayed meconium passage is seen in 50% of Hirschsprung's, and Hirschsprung's causes 50% of delayed meconium passage. Chronic constipation and occasionally overflow diarrhoea. Vomiting, which may be bilious. Enterocolitis is a serious complication, leading to explosive diarrhoea and potentially sepsis.
- 23. Investigations Barium enema X-ray will show dilated proximal colon and contracted distal colon. Plain abdominal XR is less useful, but may show a dilated colon. Rectal biopsy can confirm the diagnosis, showing absence of ganglion cells.
- 24. Management Surgical removal of aganglionic bowel segment. Preceded by bowel irrigation to clear it out and reduce distention. Tube place in rectum, saline enters, then exits through tube with bowel contents. Differs form enema, in which fluid is retained. Fluid and antibiotics first in enterocolitis.
- 26. Pathophysiology and epidemiology Malrotations are a range of congenital anatomical abnormalities of the GI tract. Volvulus is a severe complication in which a loop of bowel twists around its mesenteric attachment, causing intestinal obstruction. Midgut volvulus, twisting around the superior mesenteric artery (SMA), is a common site. Volvulus usually occurs
- 27. Signs and symptoms Bilious (green) vomiting. Severe, acute abdominal pain. Abdominal distention. Systemic symptoms if there is ischaemia e.g. ↑HR, ↓BP. Malrotation alone is often asymptomatic, or may cause intermittent, self-resolving obstruction.
- 28. Investigations Upper GI contrast study, with contrast through NG tube or bottle. Shows 'corkscrew' duodenum in volvulus. Management Volvulus: 'drip and suck' (IV fluids and nasogastric decompression) followed by urgent surgery. If patient is systemically unwell and diagnosis clear, skip imaging. Malrotation: elective surgery. Ladd's procedure is the commonest surgical approach, involving untwisting bowel, dividing congenital peritoneal bands which compress the duodenum, and widening the mesentery.
- 29. Pyloric stenosis
- 30. Risk factors Males 1st born. Family history. Signs and symptoms Presents at 2-7 weeks with: Projectile, non-bilious vomiting after feeds. Hunger Olive-shaped mass in RUQ. Visible peristalsis.
- 31. Investigations Ultrasound only needed if exam is unclear. U&E: ↓Cl-, ↓K+. Blood gas: metabolic alkalosis. Management Fluids Surgical repair through pylorotomy, which involves longitudinal splitting of the pyloric muscle.
- 33. Pathophysiology and epidemiology Congenital, 'true' diverticulum (includes all bowel layers) in the distal ileum. A vestige of the embryological vitelline duct which connects the yolk sac to the midgut lumen. Often comprises ectopic, acid-secreting gastric mucosa. Rule of 2s: 2% prevalence, 2 feet proximal to the ileocecal valve, 2 inches in length, 2:1 male:female ratio, usually presents <2 years old. It can lead to bowel obstruction from intussusception, midgut volvulus around a fibrotic attachment to the abdominal wall, and/or adhesions or strictures from chronic inflammation.
- 34. Presentation Usually asymptomatic, but in 5% it presents with a complication such as bleeding, bowel obstruction (commoner in kids), or diverticulitis (commoner in adults). Rarely, it can be part of herniated bowel (Littre hernia). Signs and symptoms: Painless, bright red, PR bleeding. Meckel's diverticulitis presents with diarrhoea and umbilical pain radiating to right iliac fossa. Hard to distinguish from appendicitis. Obstruction presents with severe constipation, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and red currant jelly stool (in intussusception).
- 35. Investigations Meckel's scan: technetium-99m pertechnetate scintigraphy, a nuclear medicine scan. Pertechnetate is preferentially taken up by the Meckel's gastric mucosa. Indicated in PR bleeding with suspected Meckel's. Abdo XR and abdo CT allows broader investigation of abdo disease. Indicated in suspected bowel obstruction. Skip imaging and use exploratory laparotomy/laparoscopy if unstable. FBC: may show anaemia.
- 36. Management If symptomatic, laparoscopic resection. If asymptomatic, no treatment is usually needed, though some advocate it due to the (very) small risk of malignancy developing.
- 37. Gastroenteritis in children Causes Viral: rotavirus (60%), adenovirus, norovirus. Bacterial: Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella, Shigella, E. coli.
- 39. Signs and symptoms Diarrhoea: usually lasts 5-7 days. Vomiting: usually lasts 1-2 days. May have bloody stool if bacterial. Fever Dehydration
- 40. Investigations Stool microscopy, culture, and sensitivity (MC+S) indications: Blood or mucus in stool. >7 days of diarrhoea. Immunosuppression Recent travel. Possible E. coli contact e.g. farm. Bloods – e.g. U&E, FBC – only required if severely ill.
- 41. Management Correct dehydration. Oral rehydration first line, and anti-emetics (e.g. ondansetron) can facilitate if frequent vomiting (and age >4). Antibiotics rarely indicated and may increase the risk of haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS) in E. coli O157. Complications Post-gastroenteritis enteropathy e.g. lactose intolerance. HUS after E. coli O157.
- 43. Signs and symptoms Anorexia Vomiting Abdominal pain which is central then in the right iliac fossa. Peritonism: abdominal pain on moving or cough. However, guarding and rebound tenderness may be minimal. Fever
- 44. Diagnosis Diagnosis can usually be made clinically. If unclear, consider abdo US (75% sensitive, 97% specific), or CT (>95% sensitivity and specificity, but radiation exposure). Management Appendectomyst
- 45. Mesenteric adenitis Pathophysiology Mesenteric lymph node enlargement, associated with URTI or other viral infection. Presentation Generalized abdominal pain. Main differential of appendicitis in children. May have headache and photophobia.
- 46. Investigations ↑Lymphocytes (not ↑neutrophils like in appendicitis). Management Simple analgesia. If exploratory laparotomy done, remove appendix anyway to prevent future confusion.
- 48. Pathophysiology and epidemiology Common Worse in cow's milk protein allergy, CF, and premature babies. Infants are predisposed to GORD for 3 reasons: the lower oesophageal sphincter is underdeveloped, they have a liquid diet, and they're often lying flat. Signs and symptoms Regurgitation or vomiting. Distress after feeds.
- 49. Management Reassure parents that it will usually improve by 6 months, and especially by 1 year. Advice: avoid overfeeding (>200 ml/kg/day). Consider fluid thickeners: Gaviscon, Thick and Easy. No evidence for ranitidine, but some evidence for omeprazole in young infants, especially if there is oesophagitis.
- 50. Complications All of these are rare: Oesophagitis → oesophageal pain and bleeding, haematemesis, anaemia. Peptic stricture. Failure to thrive. Respiratory: apnoea, pulmonary aspiration leading to pneumonia. Sandifer syndrome: GORD, dystonia, and spasmodic torticollis (involuntary contraction of neck muscles).
- 51. Non-organic abdominal pain Aka functional abdominal pain, recurrent abdominal pain syndrome. Epidemiology 90% of recurrent abdominal pain in children is non-organic, especially when older. There may be a family history.
- 52. Signs and symptoms Usually presents as umbilical pain in a child who is otherwise well and with normal growth. May improve on weekends and holidays. May report extreme tenderness on palpation but easily tolerate a firm stethoscope press. Alarm symptoms suggesting non-organic cause: involuntary weight loss, GI bleed, severe vomiting or diarrhoea, fever, persistent right upper or lower quadrant pain, family history of IBD.
- 53. Specific syndromes IBS Non-ulcer dyspepsia. Management Education and reassurance to patient and family. It is common and it will usually resolve. Consider referral to CAMHS. CBT and family therapy may help
- 54. Management While accepting the pain is real, don't overplay it, and ensure continued normal activities including return to normal school attendance. Investigations are not usually needed. Basic testing can be done if there is a suspicion of organic disease e.g. FBC and urine MC+S. Medication or specific dietary interventions are rarely needed or useful, unless there are severe, specific symptoms
- 55. Prognosis Most resolve, but 25% continue into adulthood. Worse prognosis if parents don't accept functional nature of illness, there is a family history, or there are stressful life events.
- 56. Infant colic
- 57. Infant colic Paroxysms of inconsolable crying in an otherwise well child. It can be idiopathic, or linked to a GI cause, including cow's milk protein allergy, GORD, or constipation. May be worse in the late afternoon/evening. Usually occurs under 4 months age and self-resolves. Reassure parents, and advise that baby may be soothed by being held, gentle motion, white noise, or a warm bath.
- 58. Constipation in children Causes Behavioural causes (common): Often due to functional faecal retention, appearing after 3 years old when children get voluntary control over their anal sphincter. A painful episode of defecation may lead to deliberate retention, leading to rectal dilatation and eventual weakening of defecation reflex. May also be caused by diet: low fluid or low fibre. May present after switch to solids.
- 59. Organic causes: Neurological: Hirschsprung's, spina bifida. Endocrine and metabolic: hypothyroidism, ↑Ca2+. Other: coeliac, CF, anal ring stenosis, opioids.
- 61. Signs and symptoms Abdominal pain and distention. Gross distention suggests underlying pathology such as coeliac disease. Abdominal mass. PR bleeding due to fissure caused by hard stool. Usually presents as blood on tissue, but can also appear 'on' the stool (but not within it). Encopresis (aka soiling), and overflow diarrhoea. Need to differentiate between them. Anorexia. Recurrent UTI, due to compression which prevents urinary outflow. Abdominal mass or overflow diarrhoea suggest impaction.
- 62. Investigations Investigations are only needed if it is treatment-resistant or there is a suspicious history. However, a careful examination is useful: Base of spine and feet (club foot?) for signs of spina bifida. Anus: fissures may be present. Fistulae suggest IBD and absent anal wink suggests neurological disease. Digital rectal exam is for specialists, and only if there is suspicion of impaction, Hirschsprung's, or an anatomical abnormality. Reflexes to check for neurological disease. Colon transit study may be useful if you suspect overflow diarrhoea and are considering a complete clear out.
- 63. Management 1st line treatment is a combination of laxatives, non-punitive encouragement of regular toileting, and dietary modification. Laxative choice: use polyethylene glycol 3350 + electrolytes (Movicol Paediatric Plan), and add senna if ineffective. In impaction, use an escalating dose regime to disimpact initially. Warn that laxatives might initially increase risk of soiling and abdominal pain. When regular bowel habits are well-established, consider gradually weaning from laxatives.
- 64. Management Non-medical: manual evacuation or antegrade colonic enema (ACE). However, these are rarely required, as most treatment failure is due to poor adherence. Recurrences are common. If you suspect organic causes, treat the constipation and investigate as appropriate e.g. coeliac and TFT if growth faltering.
- 65. Cow's milk protein allergy
- 66. Pathophysiology Allergic reaction to cow's milk, which may be IgE- mediated – type 1 hypersensitivity – or non IgE-mediated – type 4 hypersensitivity. Non IgE-mediated CMPA is still an allergy, but often mistakenly referred to as an intolerance. Allergy is to casein or whey proteins in milk, not to lactose. Common: affects around 5%.
- 67. Risk factors Family history of atopy. Breast-feeding increases the risk of non-IgE, but reduces the risk of IgE-mediated. Signs and symptoms: non IgE-mediated Failure to thrive and poor feeding. Loose stools which may contain blood streaks. Sometimes straining followed by passage of loose stool, due to proctocolitis. Less commonly, constipation.
- 68. Signs and symptoms: non IgE-mediated Abdominal pain. Vomiting, possibly with blood. May present as treatment-resistant gastro-oesophageal reflux, eczema, or colic. Signs and symptoms: IgE-mediated Immediate urticaria and face swelling. If severe: diarrhoea, vomiting, and anaphylaxis
- 69. Investigations Skin prick testing if IgE-mediated suspected. Withdrawal of cow's milk for 4 weeks. Rechallenge is desirable, but often not wanted by parents if there is a good response to withdrawal. Management Extensively hydrolyzed cow's milk formula, in which proteins are broken down e.g. Aptamil Pepti. If severe, may need amino acid formula e.g. Neocate.
- 70. Management Rechallenge with cow's milk at 1 year. Other mammalian milk (e.g. goat) is not appropriate as it will have the same effect. Soya milk is not appropriate as it may affect male gonadal development. Prognosis Usually outgrown by 3 years, if not much sooner.st
- 71. Coeliac disease in children
- 72. Background Can start as early as weaning, when infants first exposed to gluten. Signs and symptoms Similar to adults (altered stool, anaemia), plus some more specific features: Constipation and/or diarrhoea. Poor growth, ↓stature. Irritable Wasted buttocks. Abdominal protrusion. ↑RR.
- 73. Thank you Keep supporting Medicos PDF app. To find lots of books, slides and news visit the app:https://bookapp.page.link/slideshare