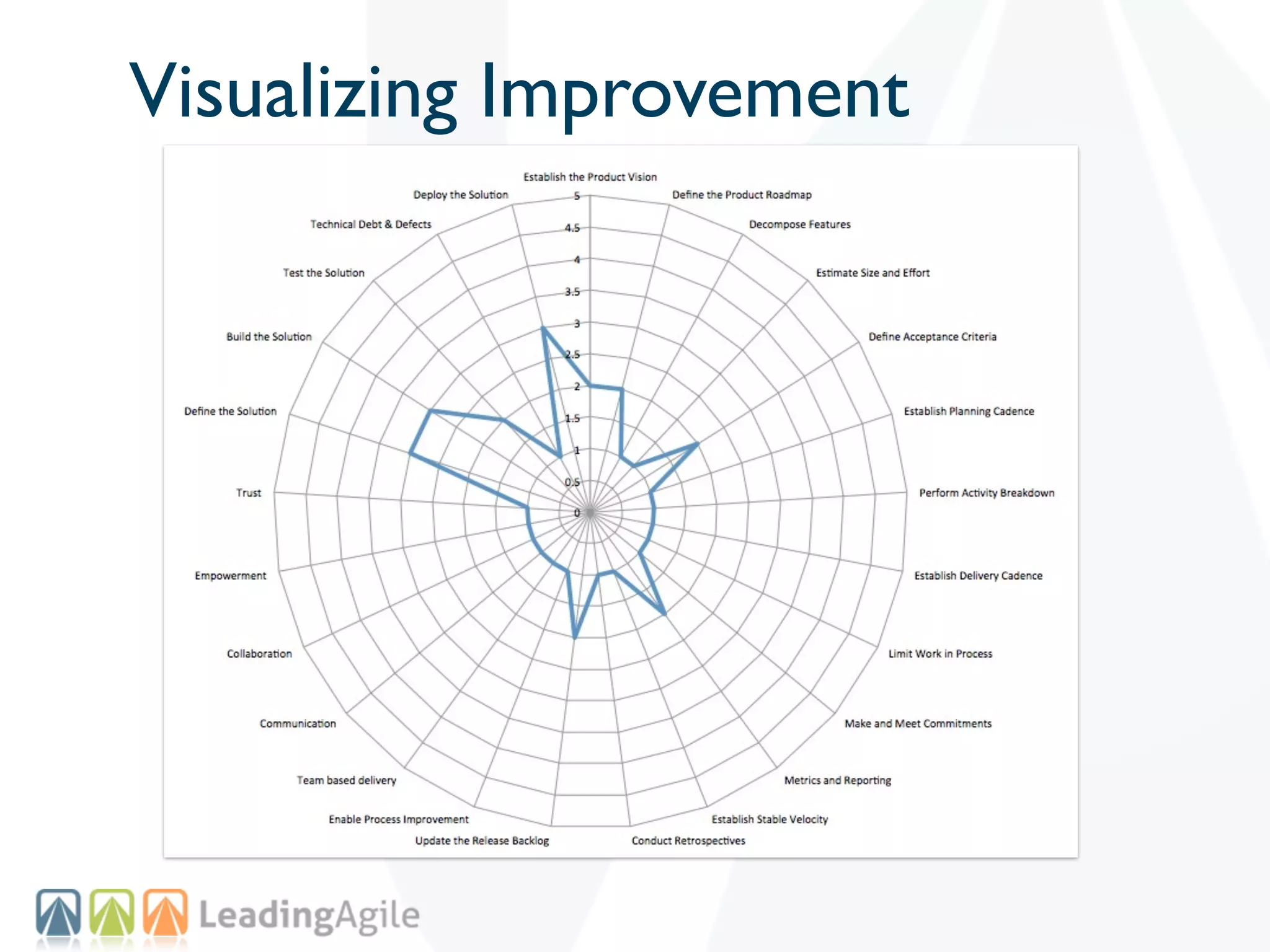
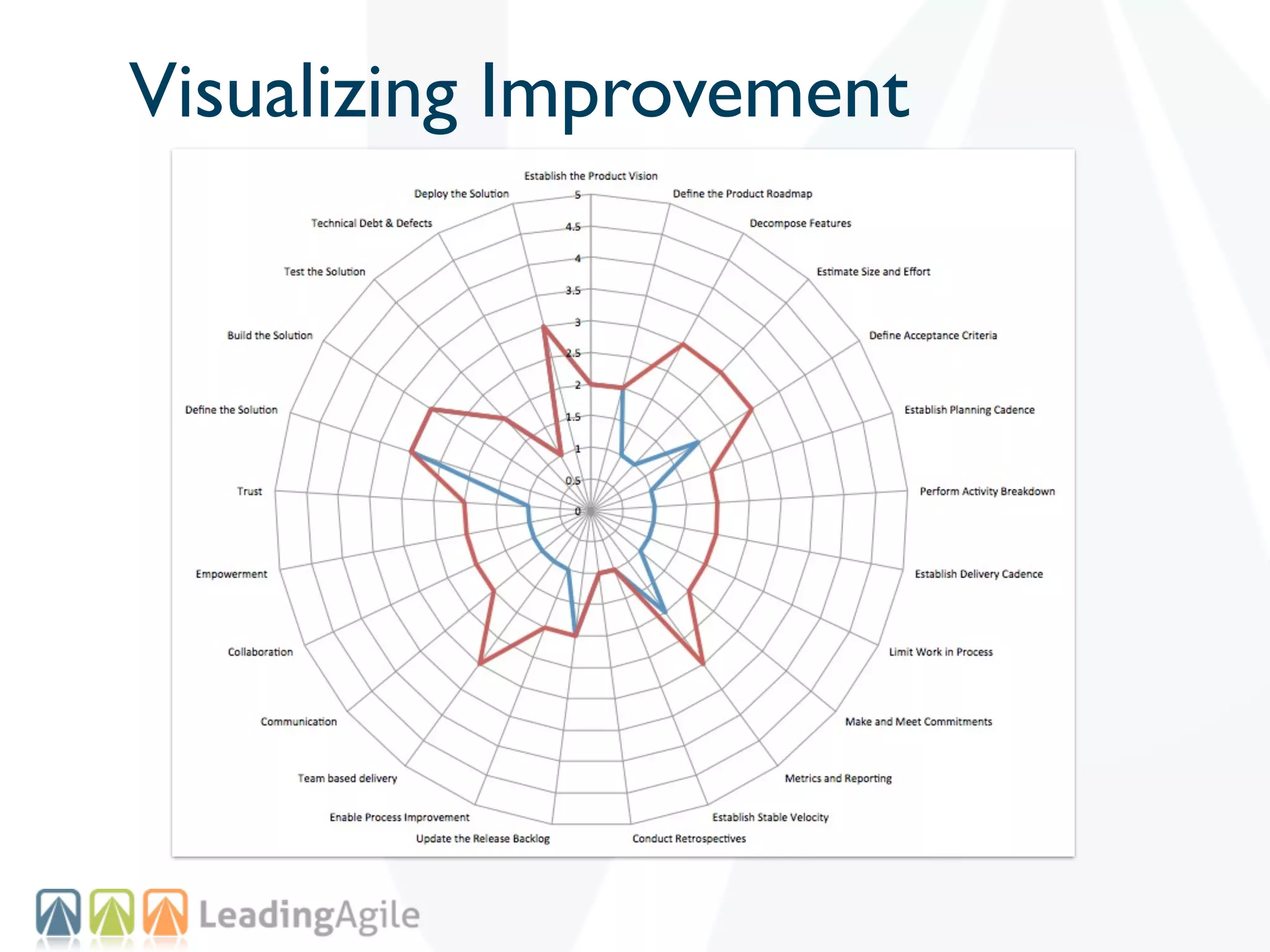
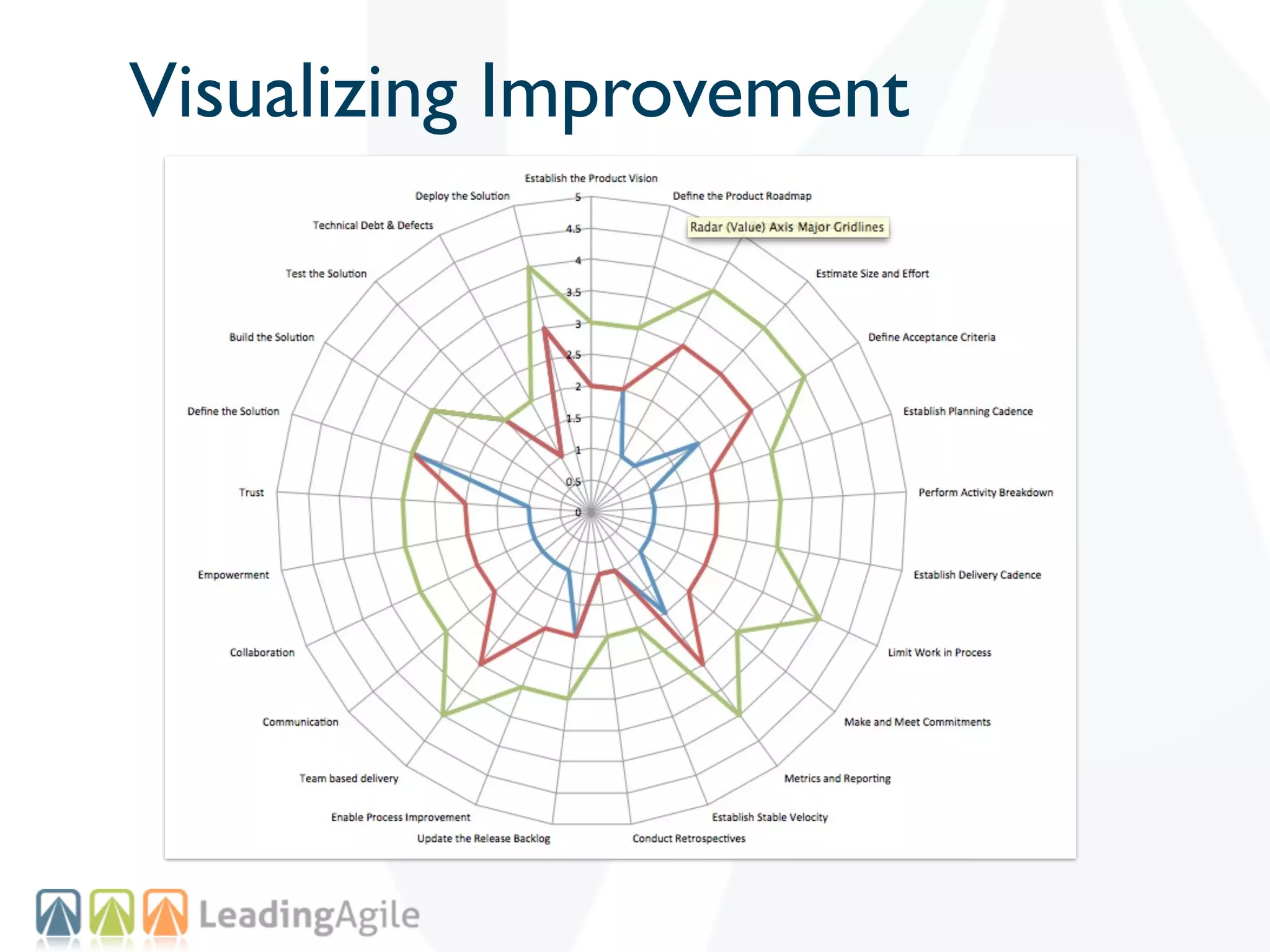
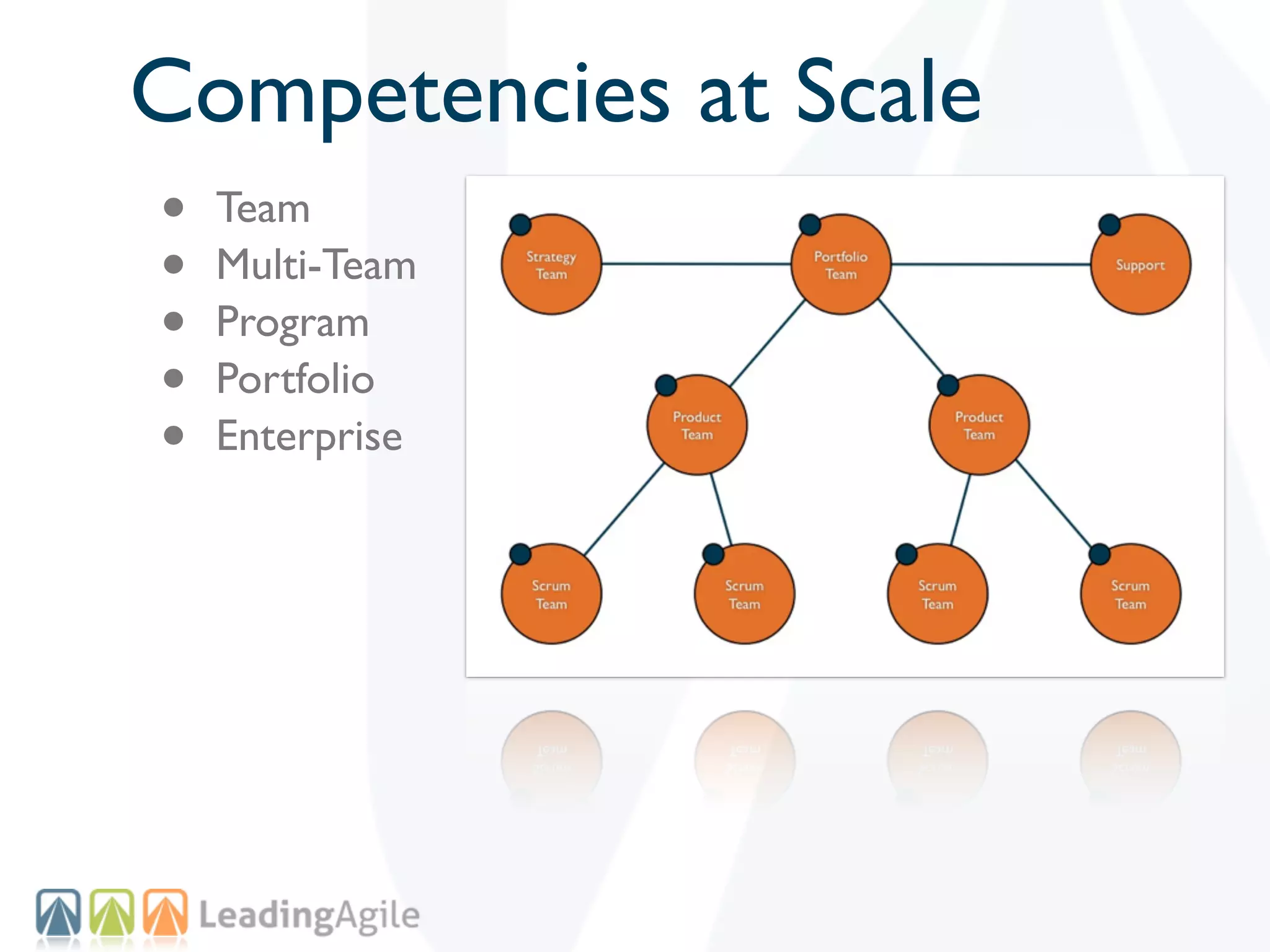
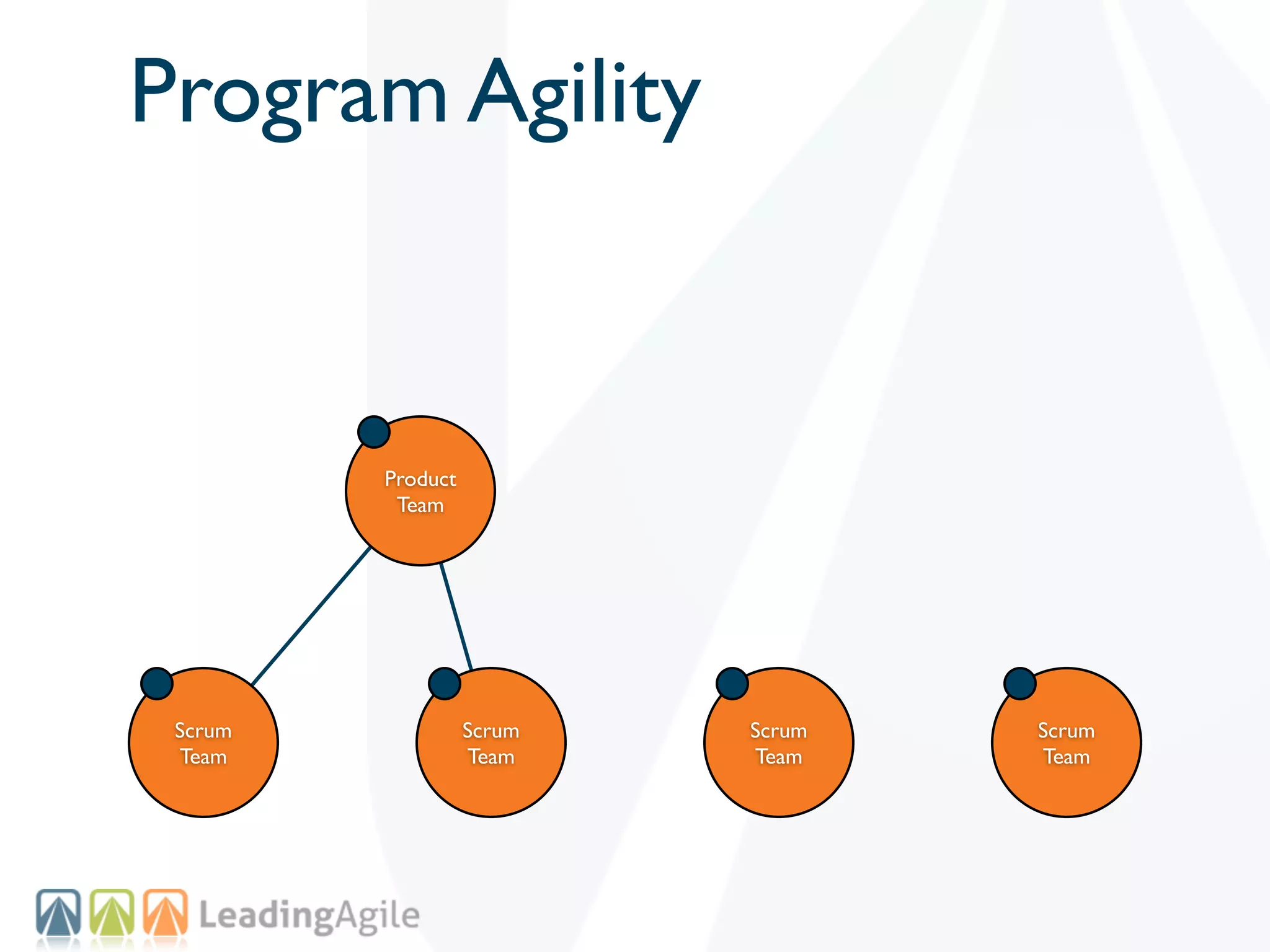
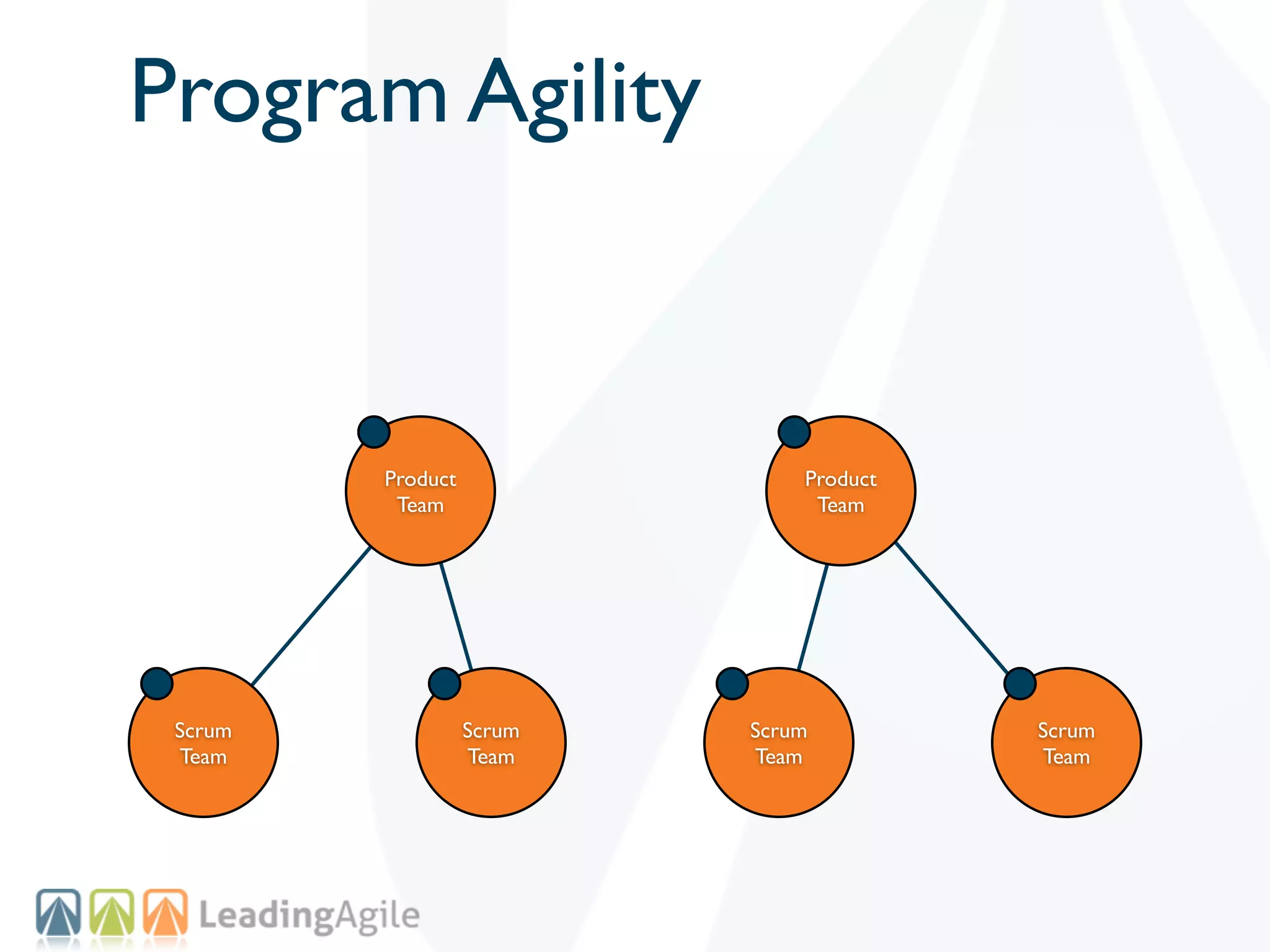
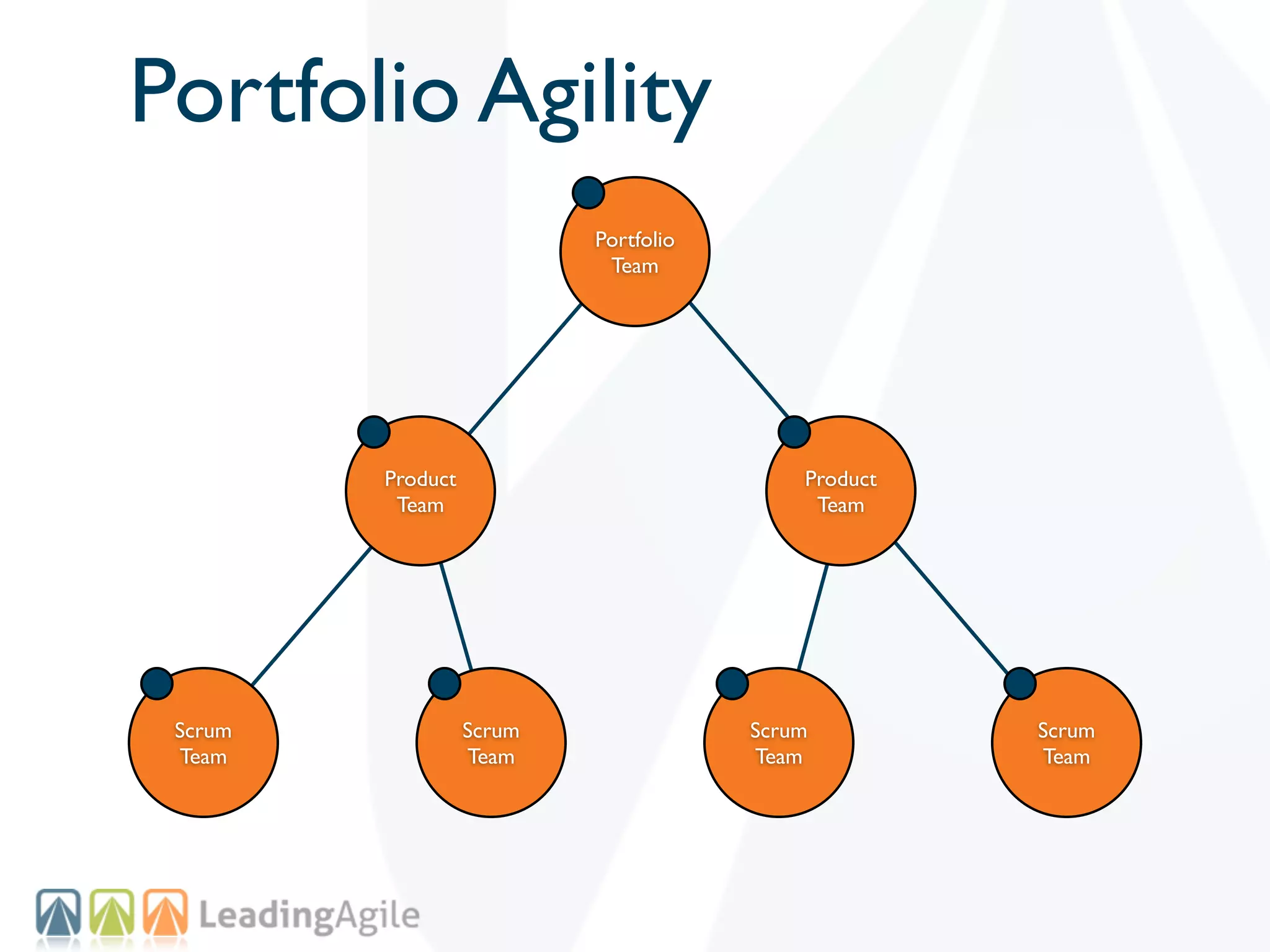
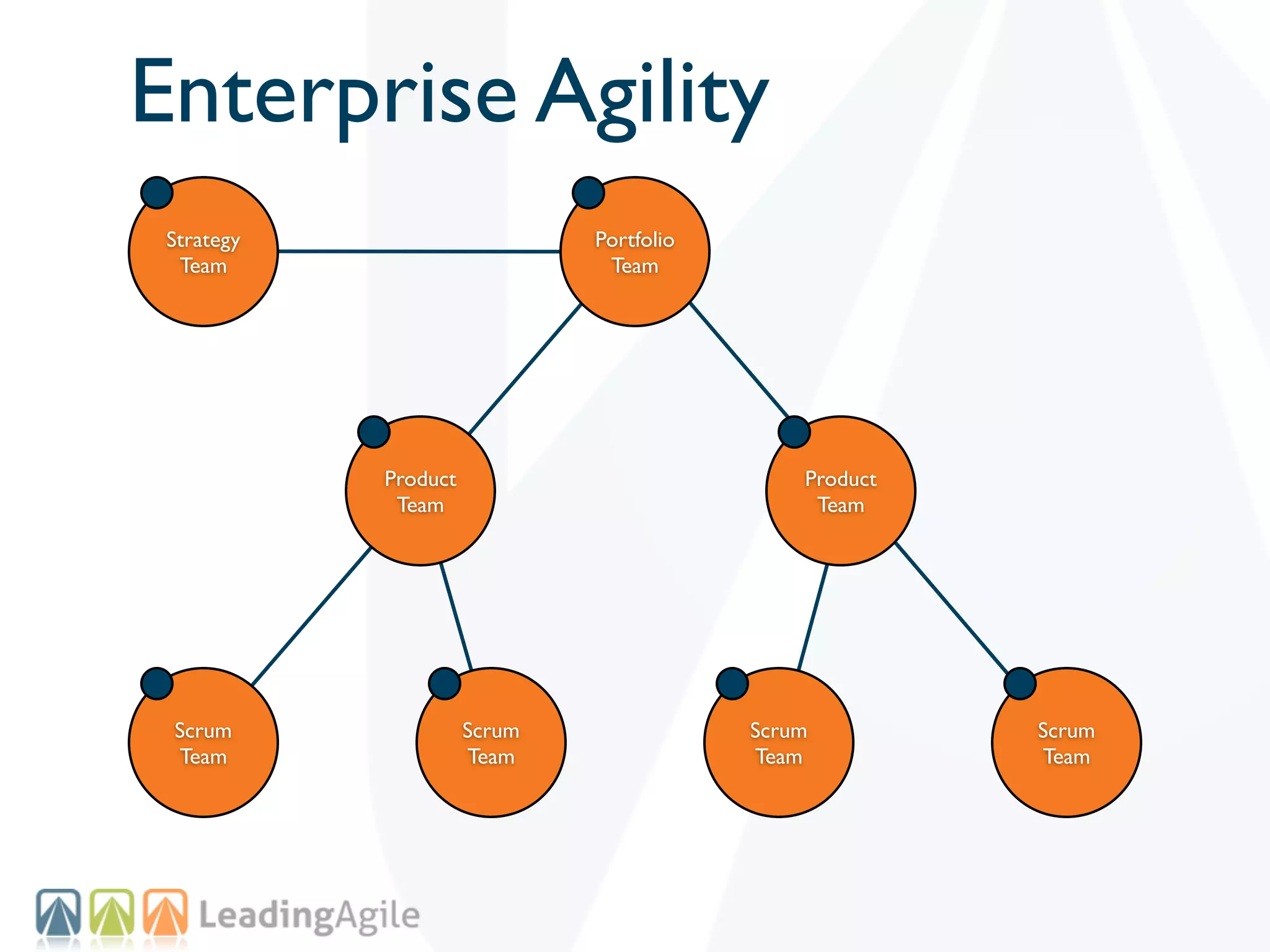
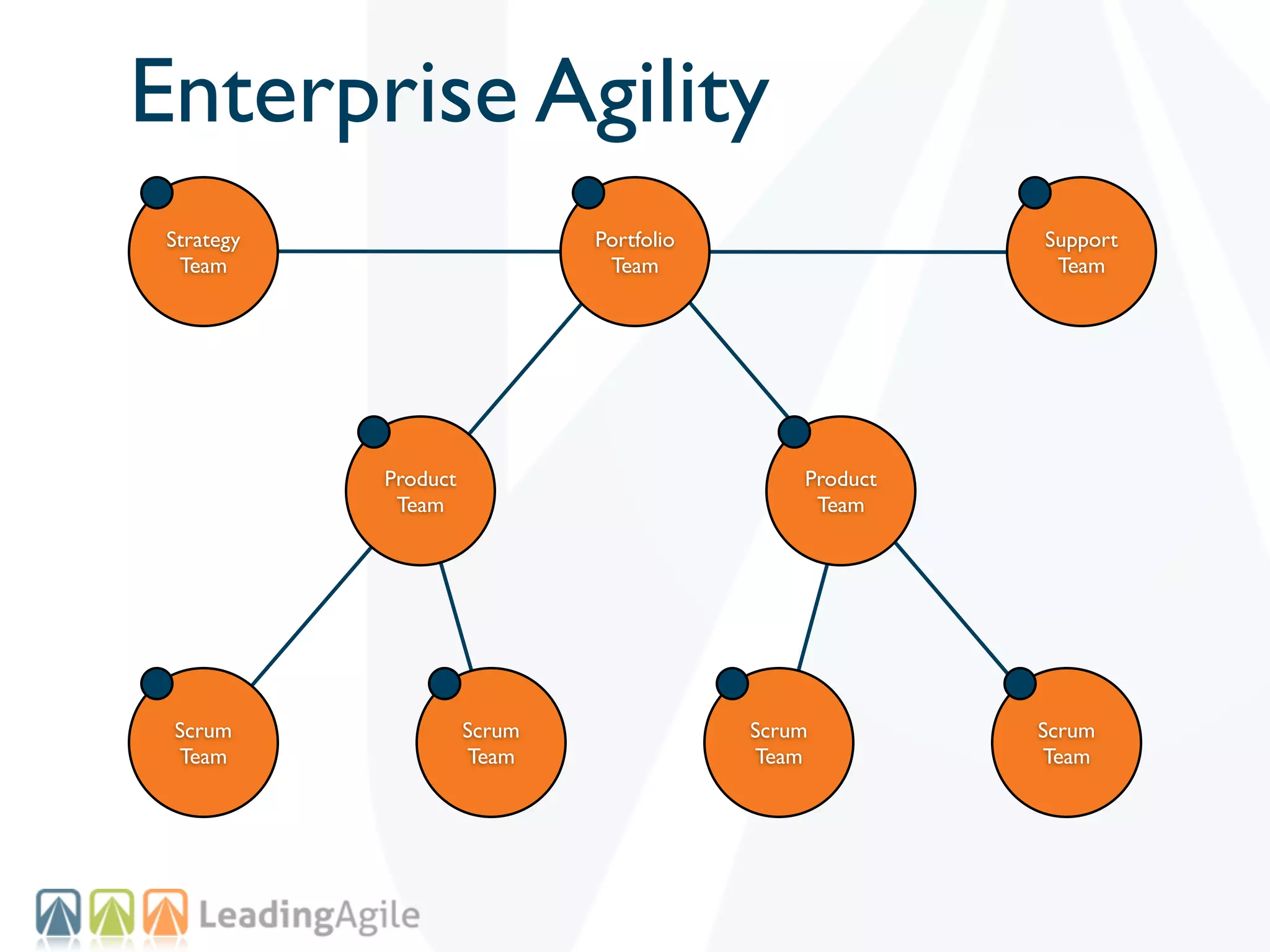
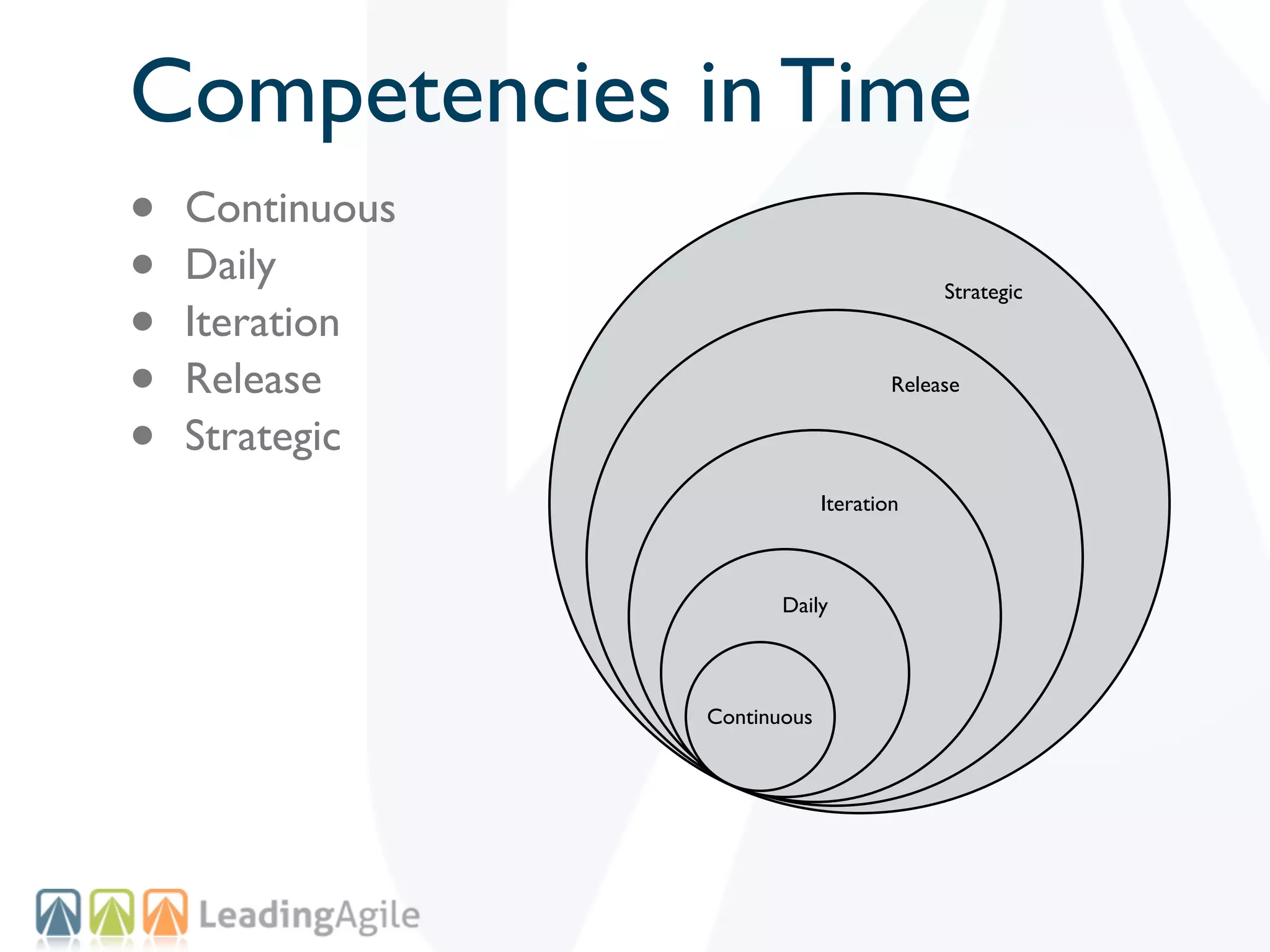
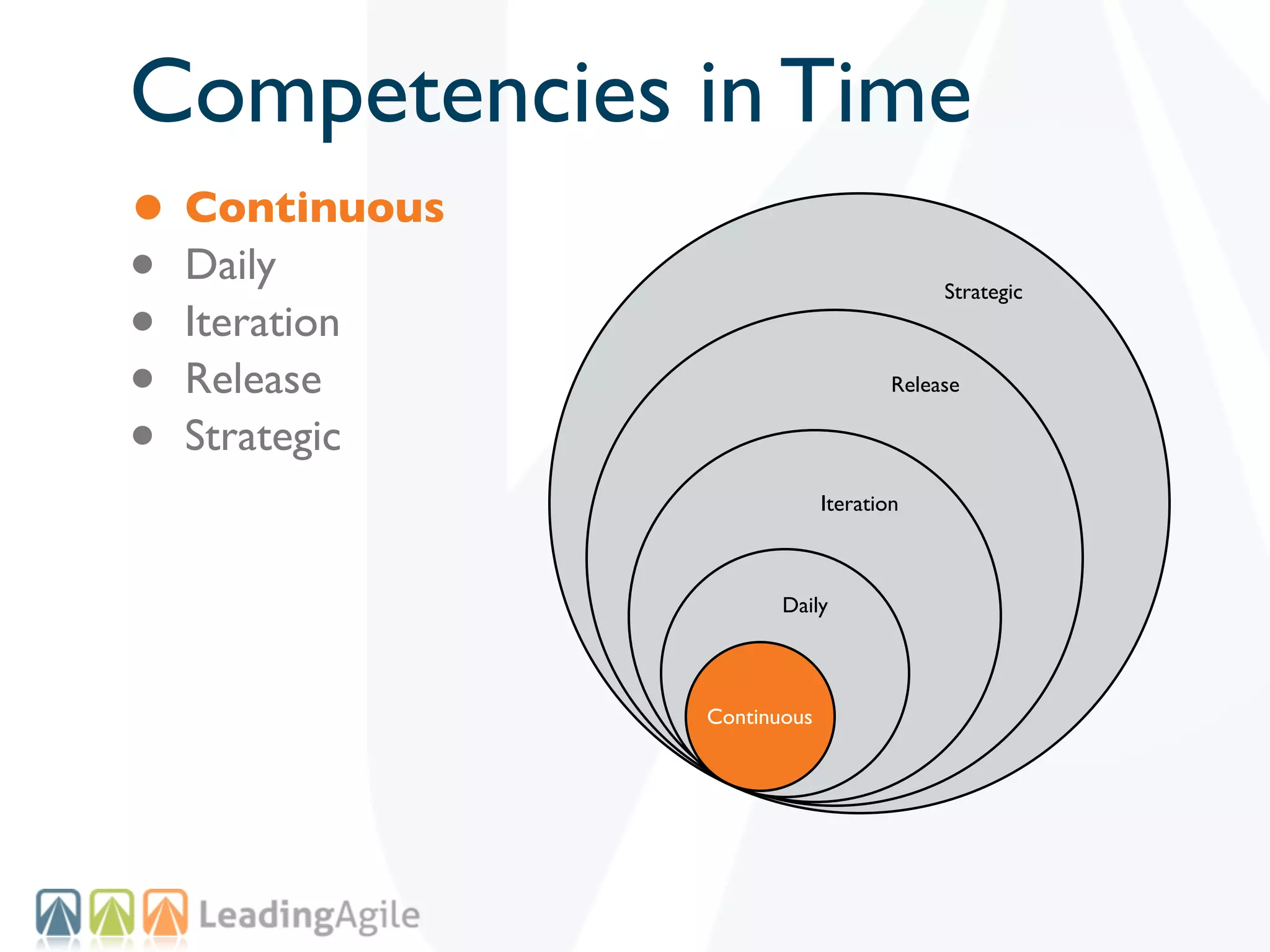
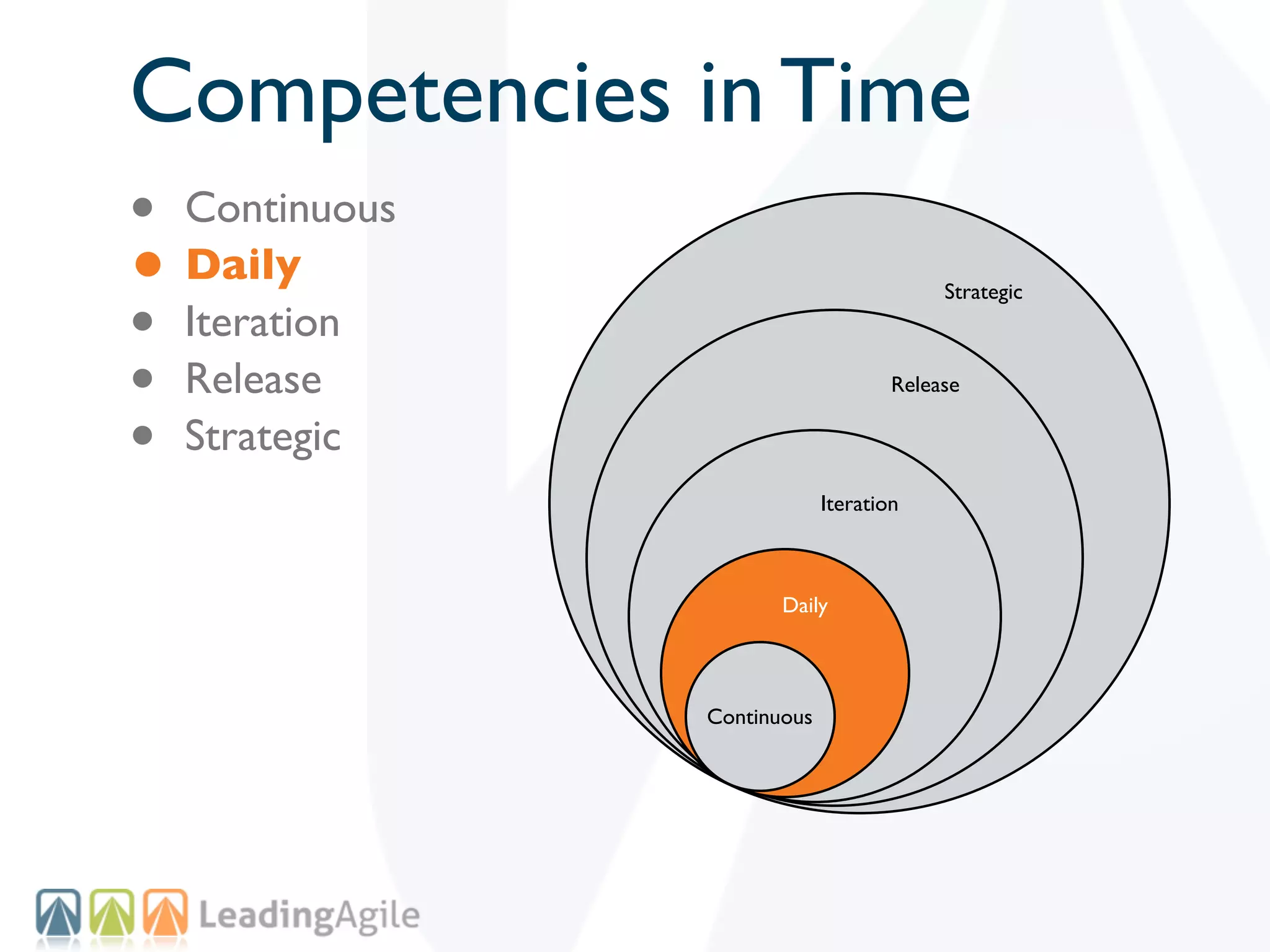
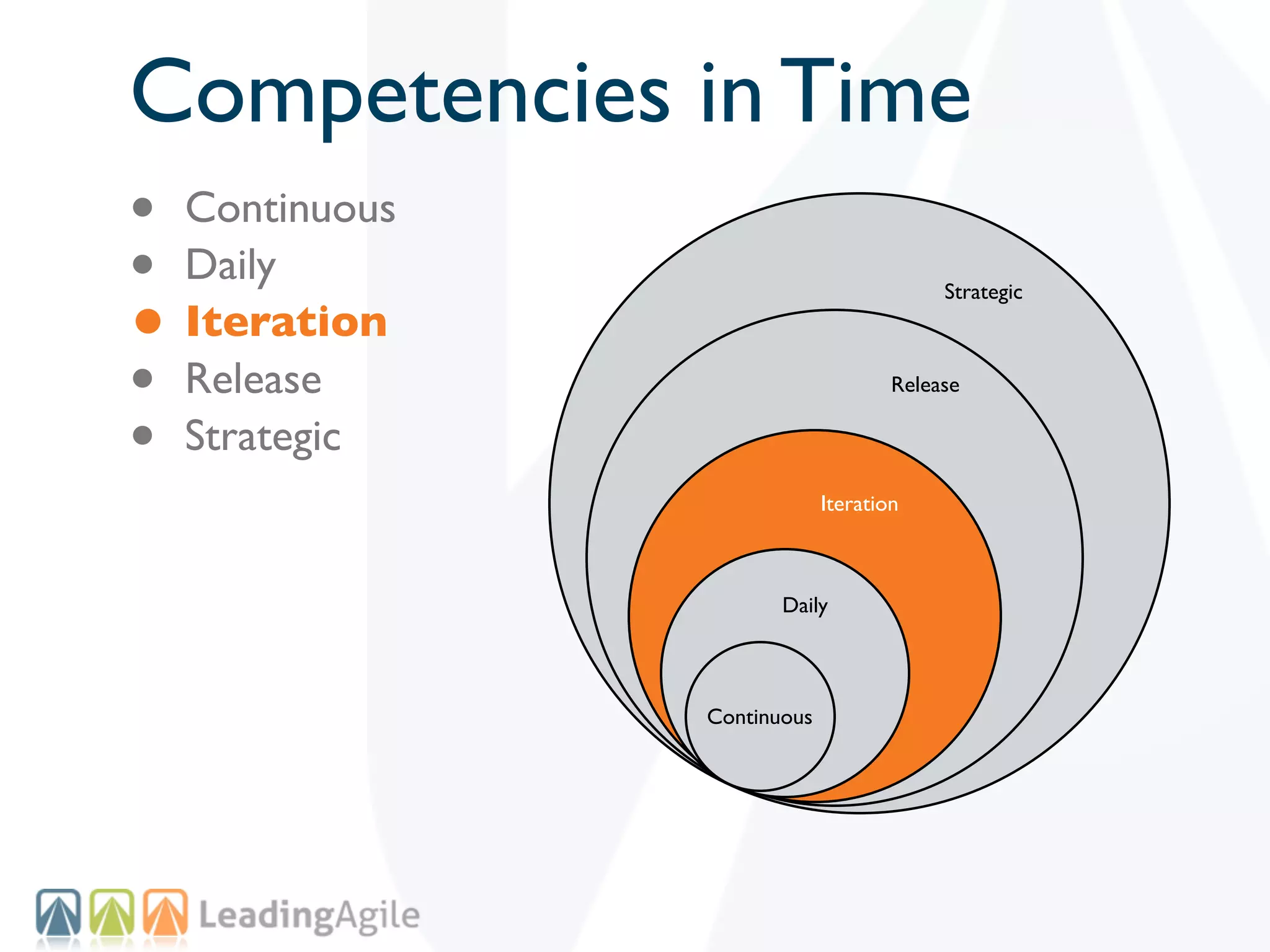
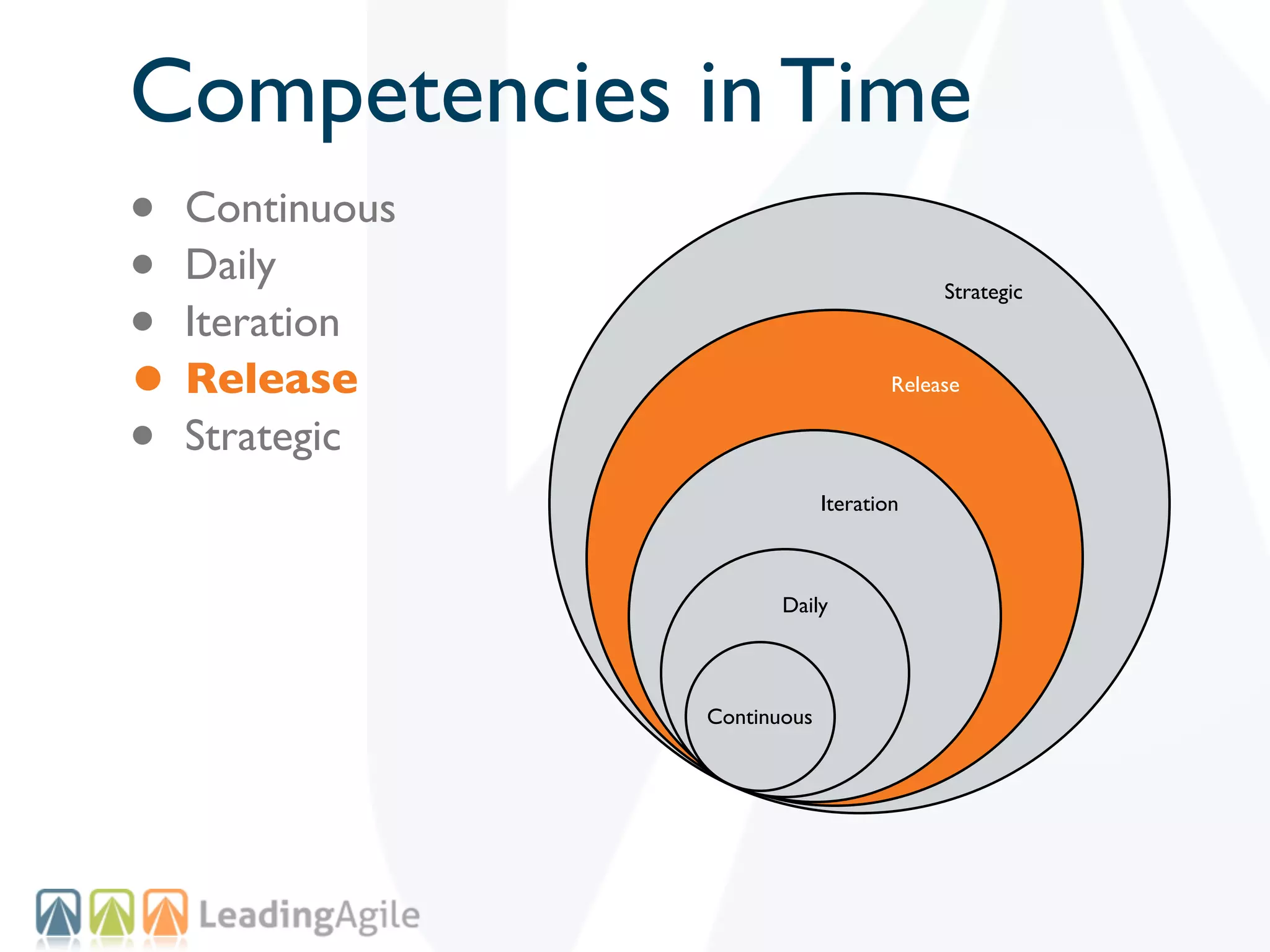
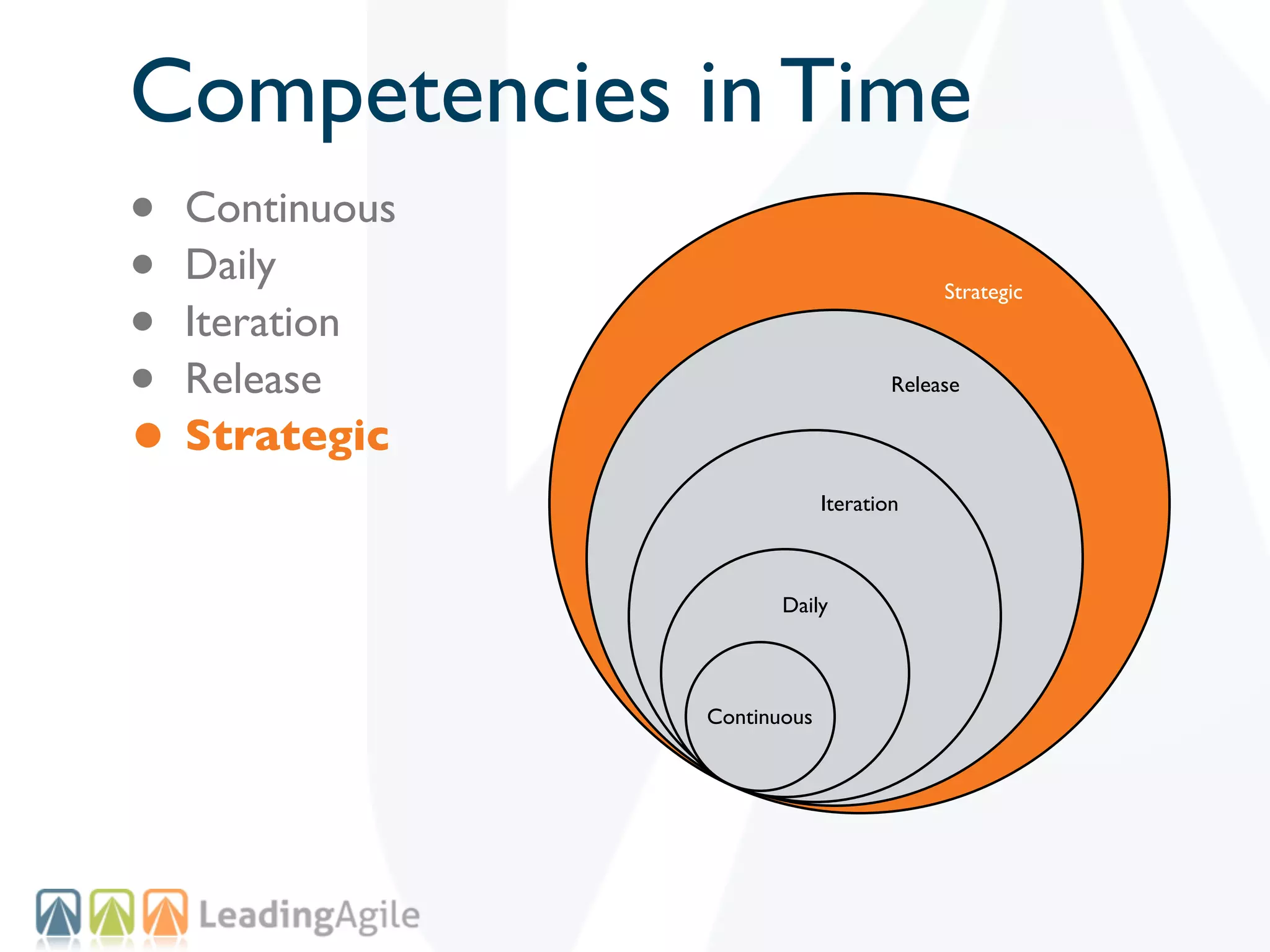
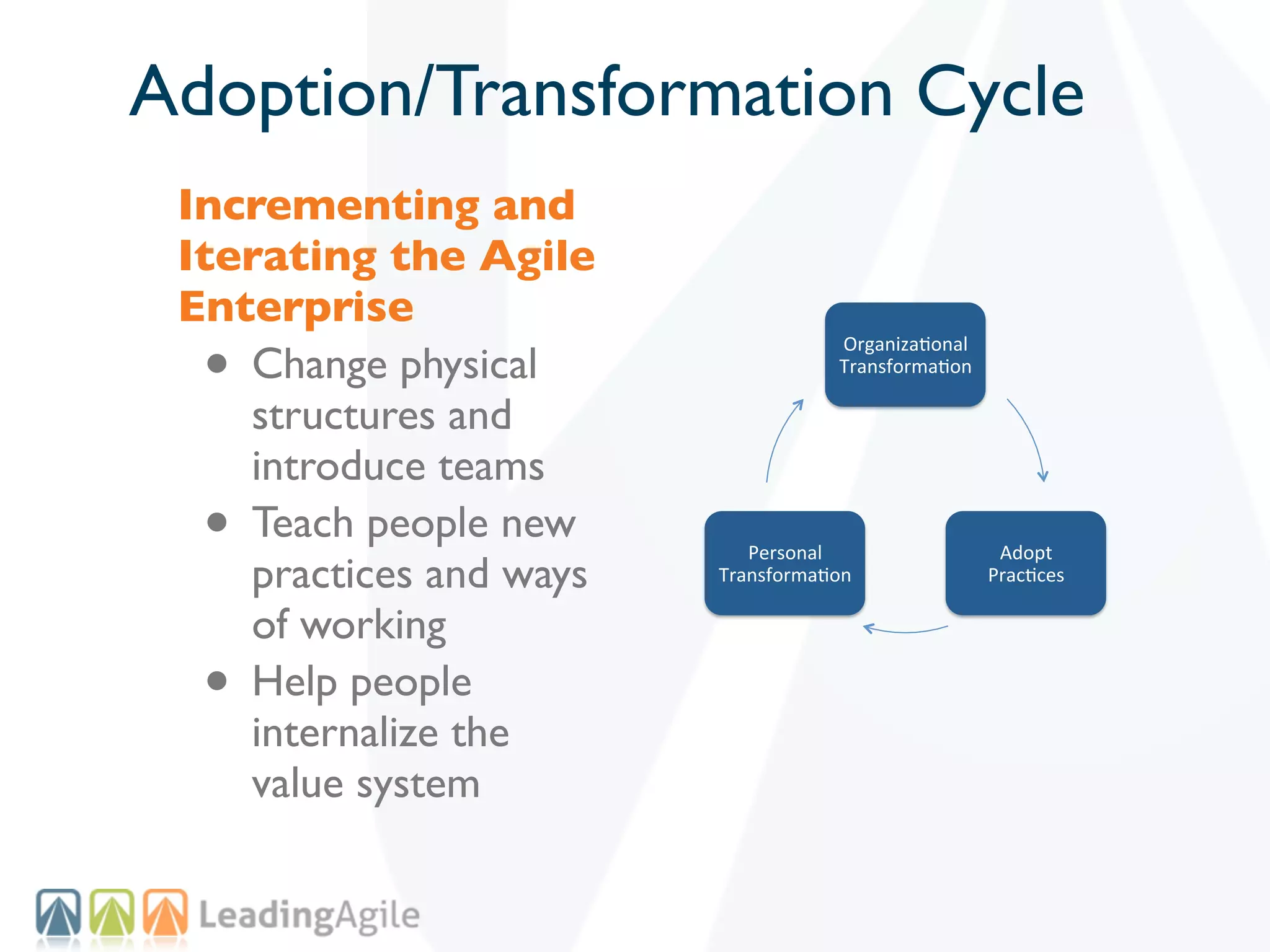
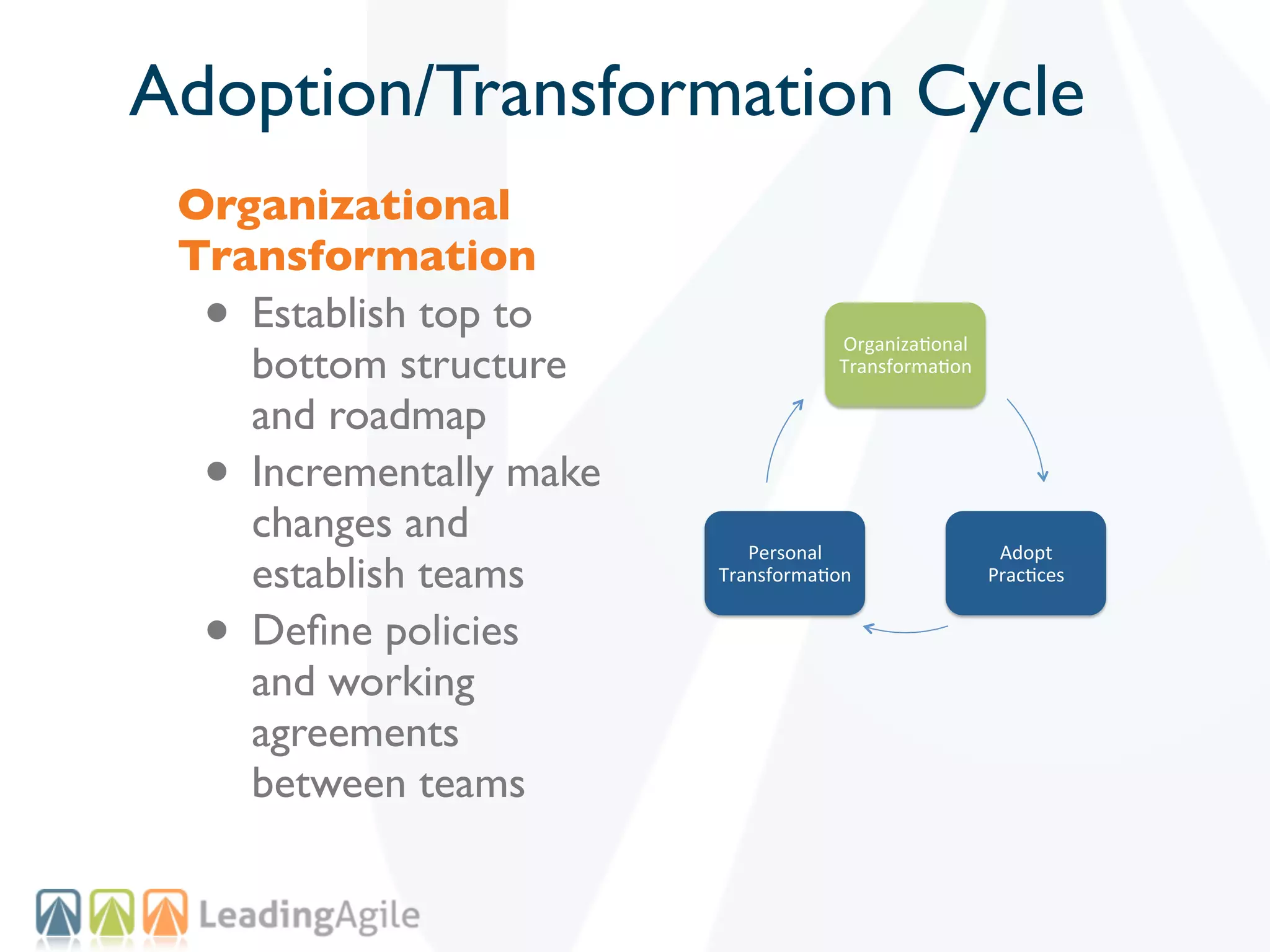
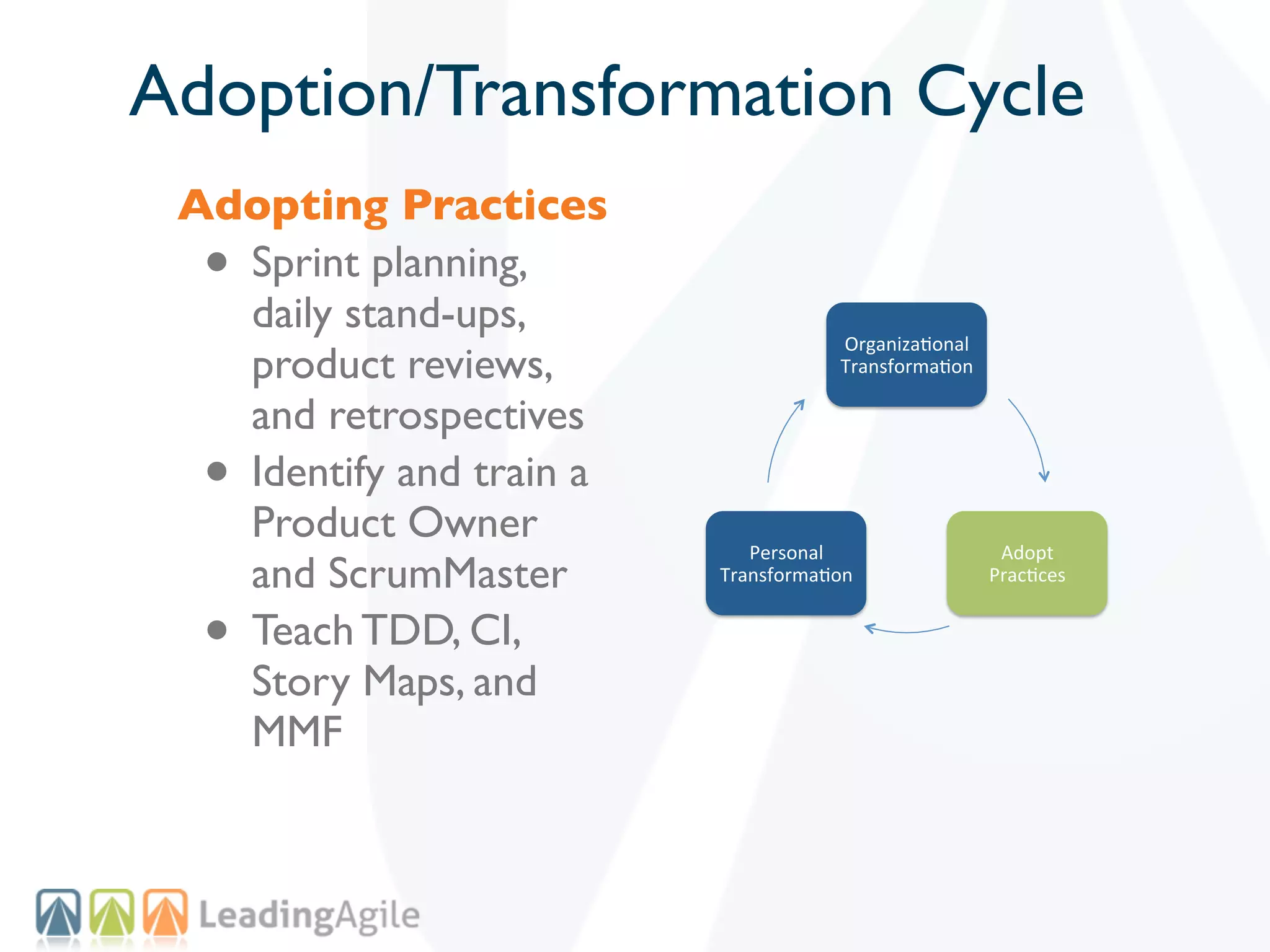
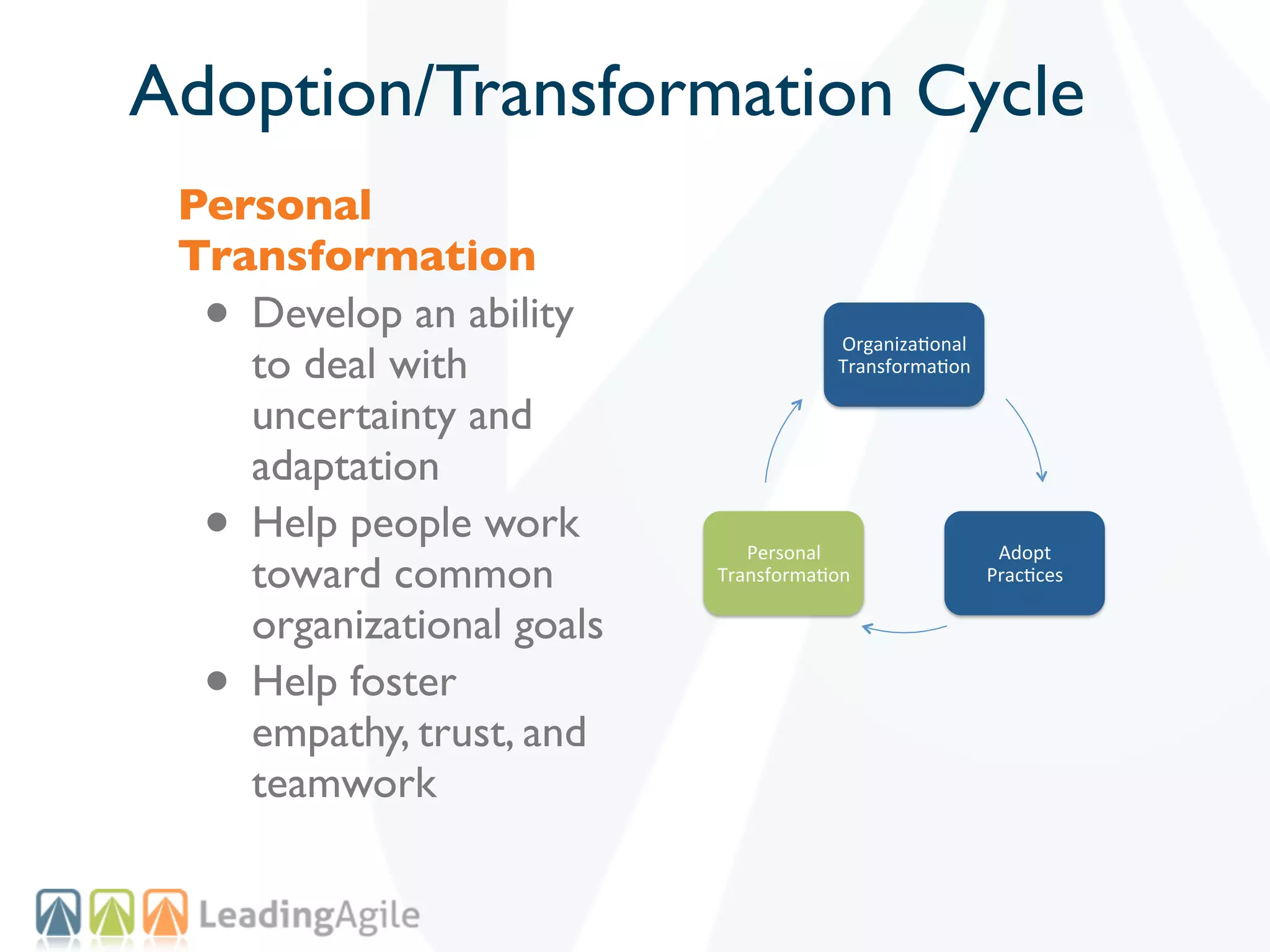
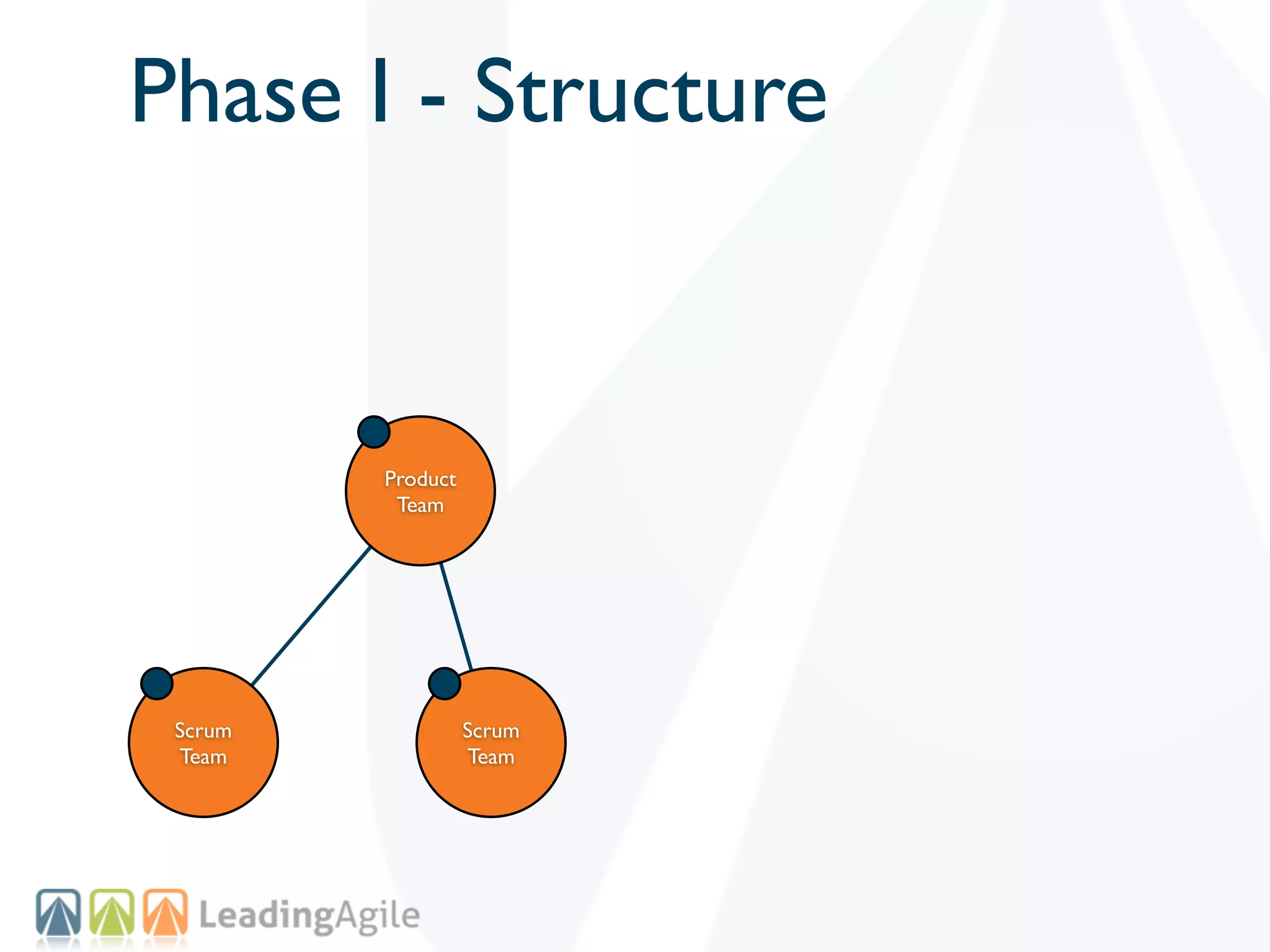
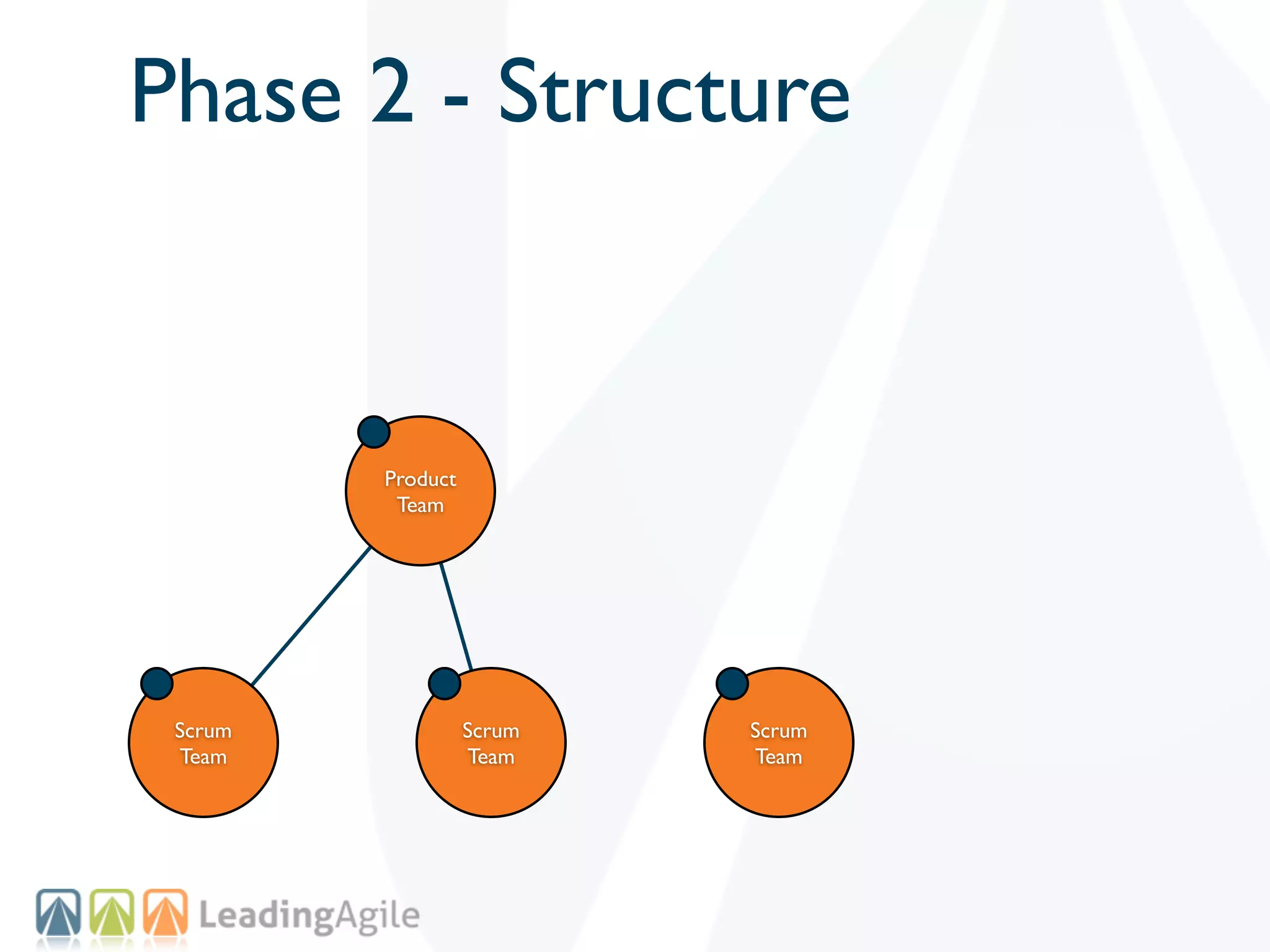
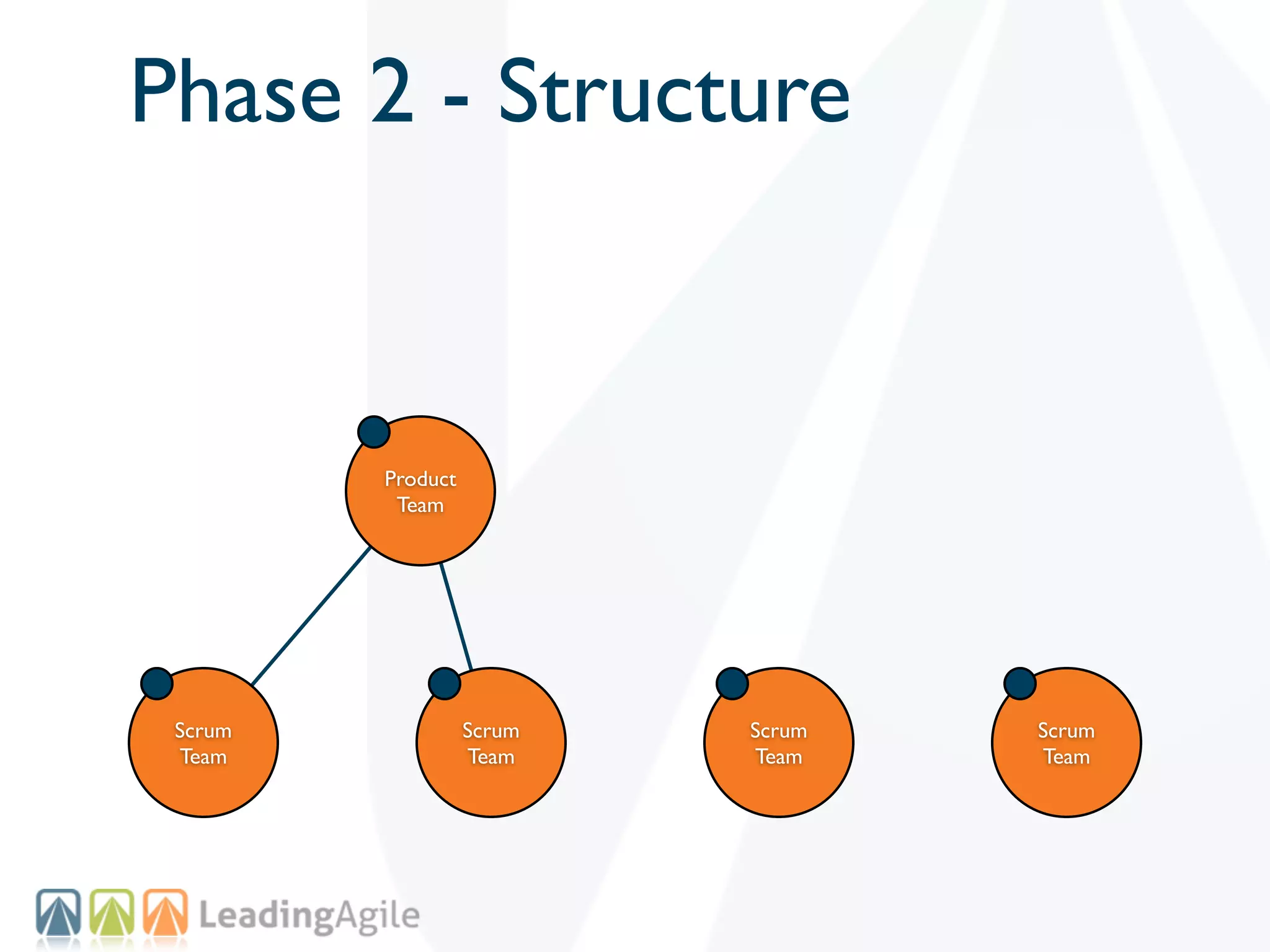
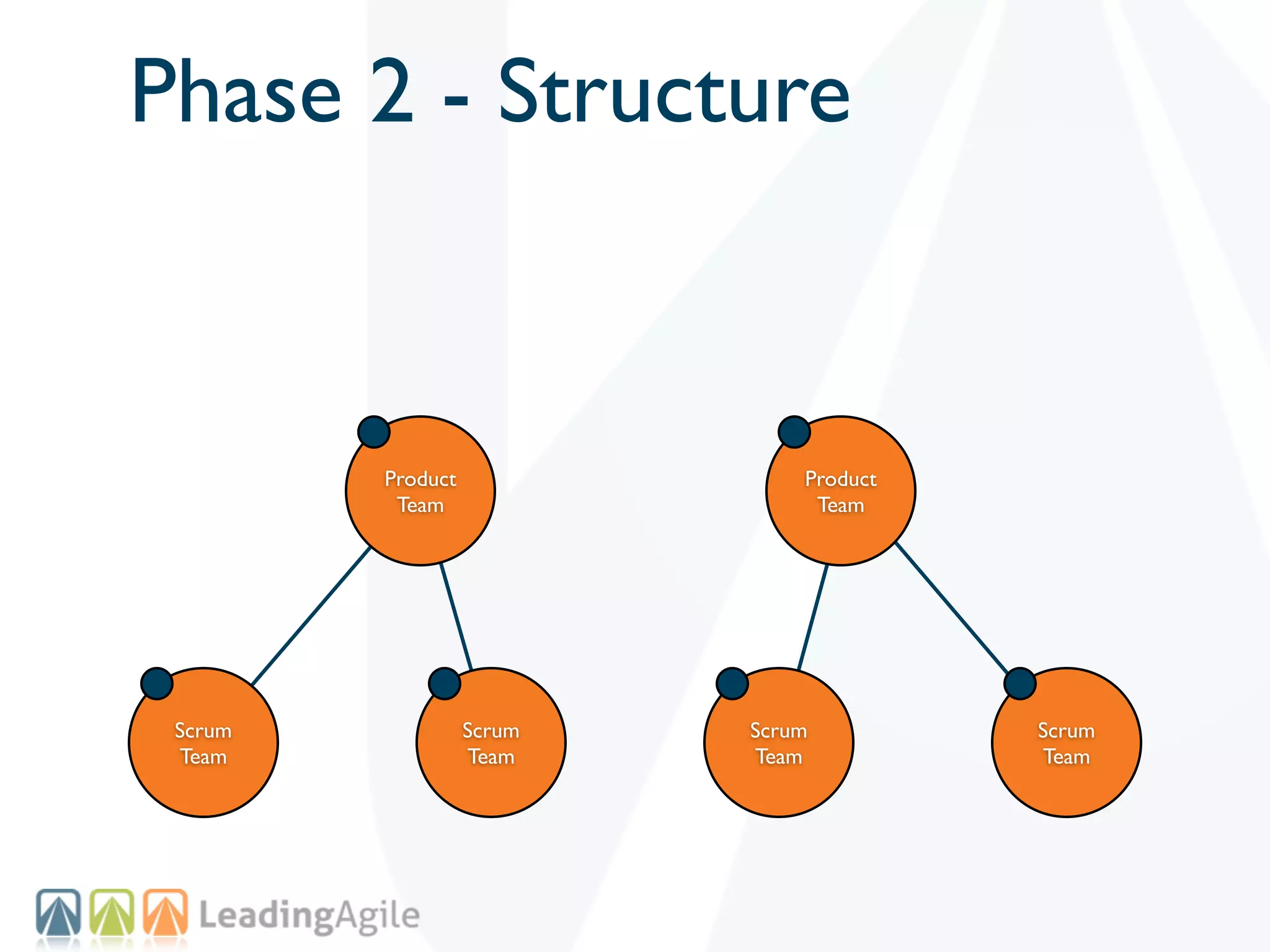
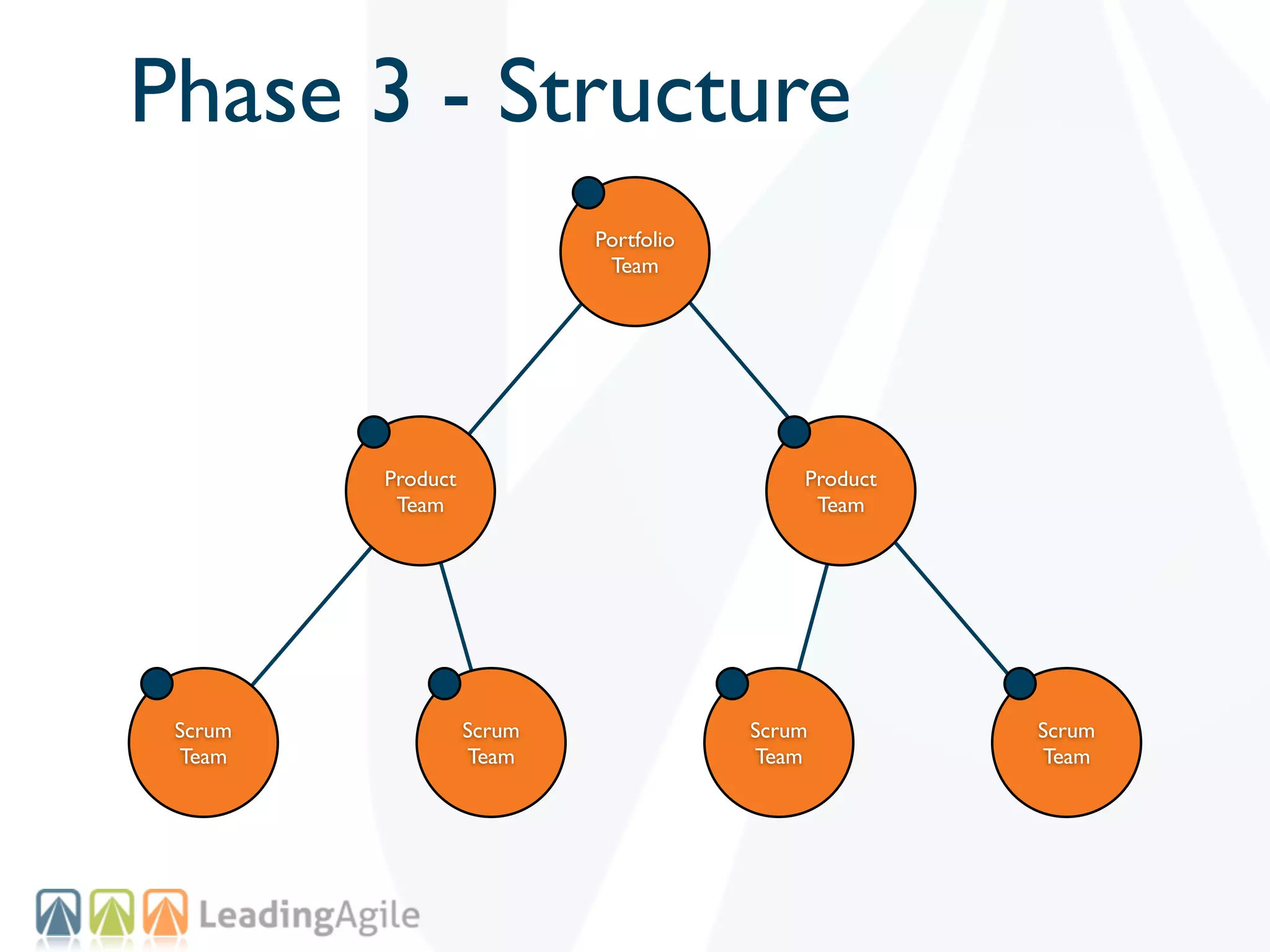
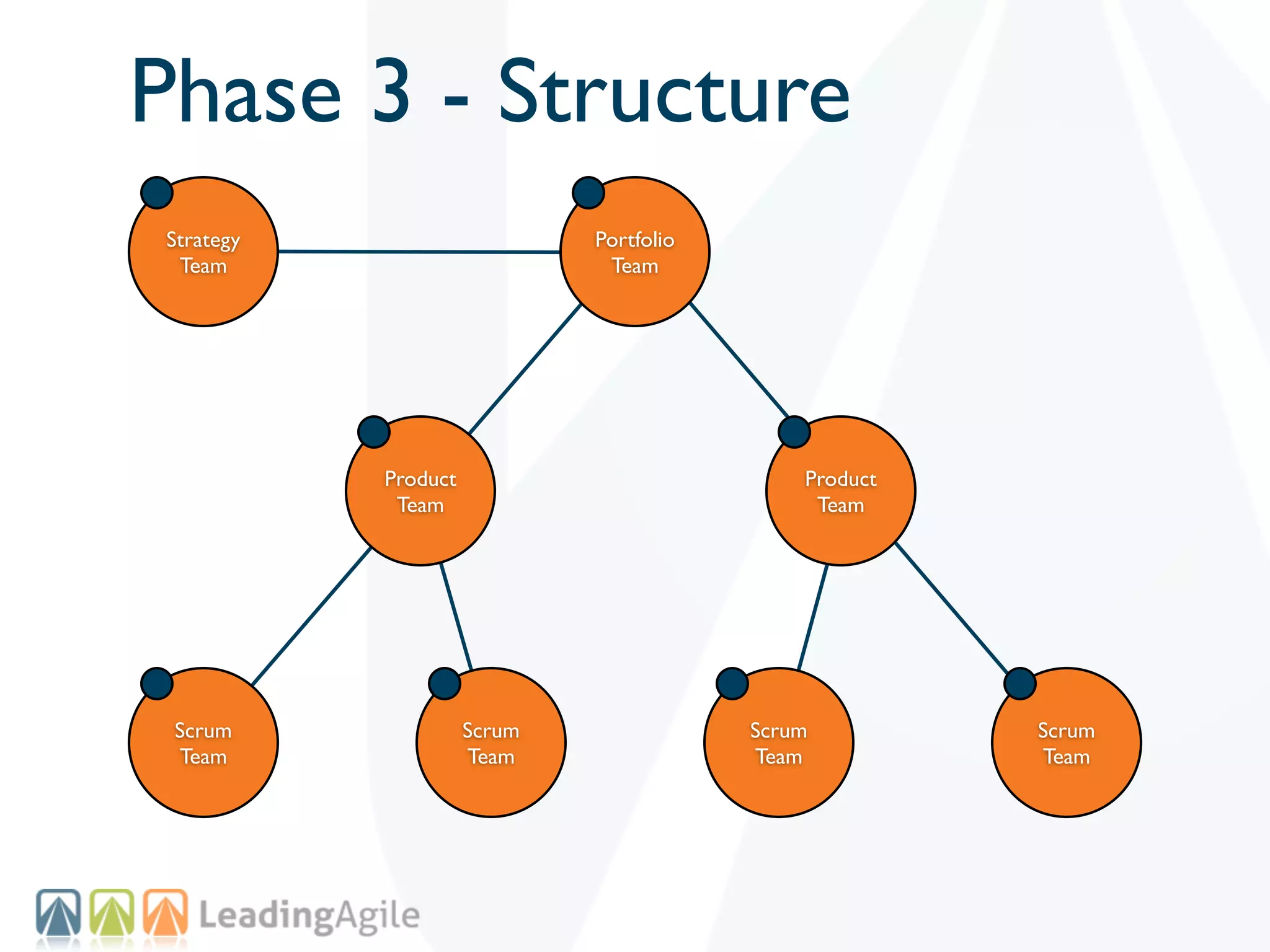
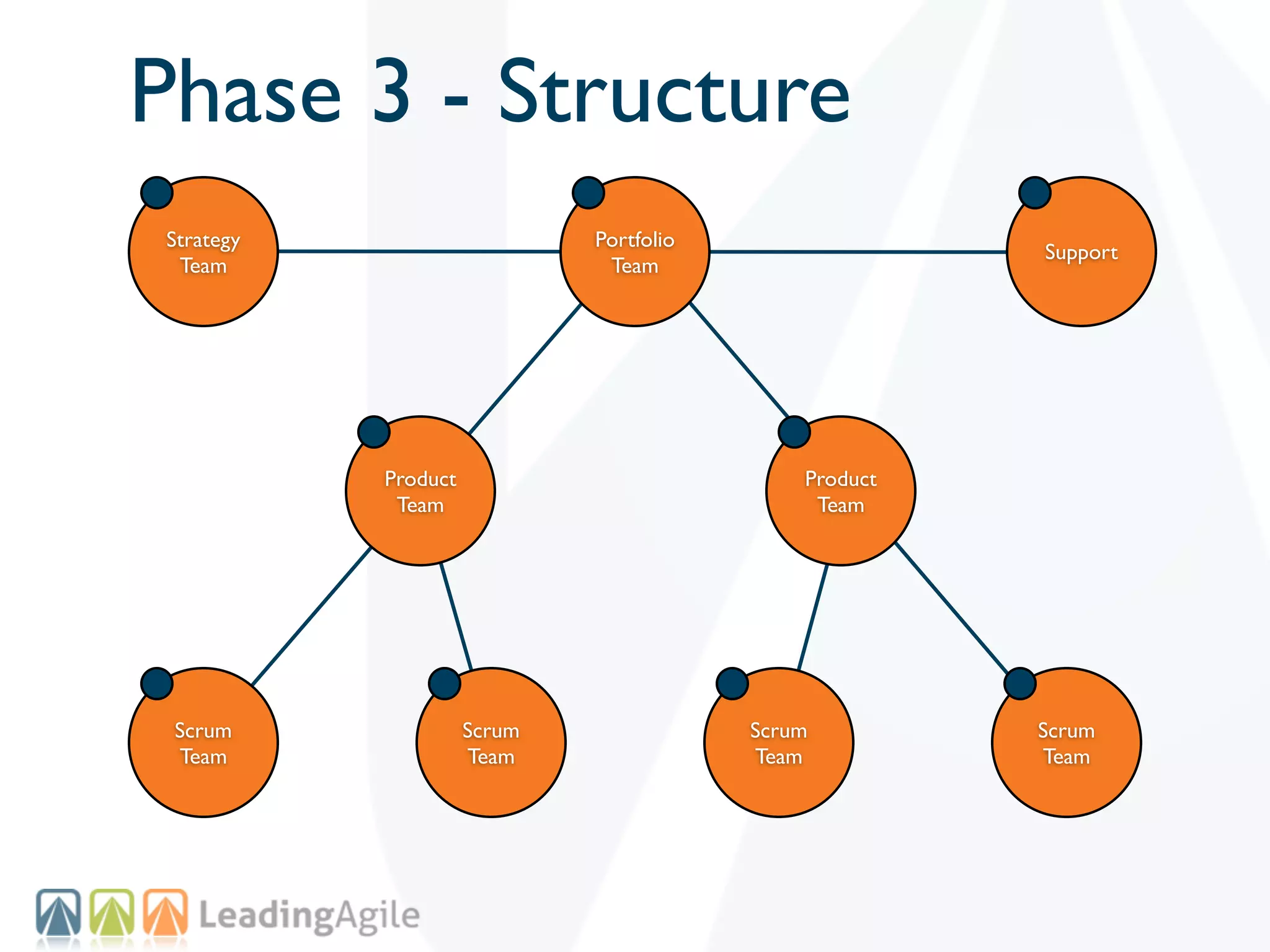
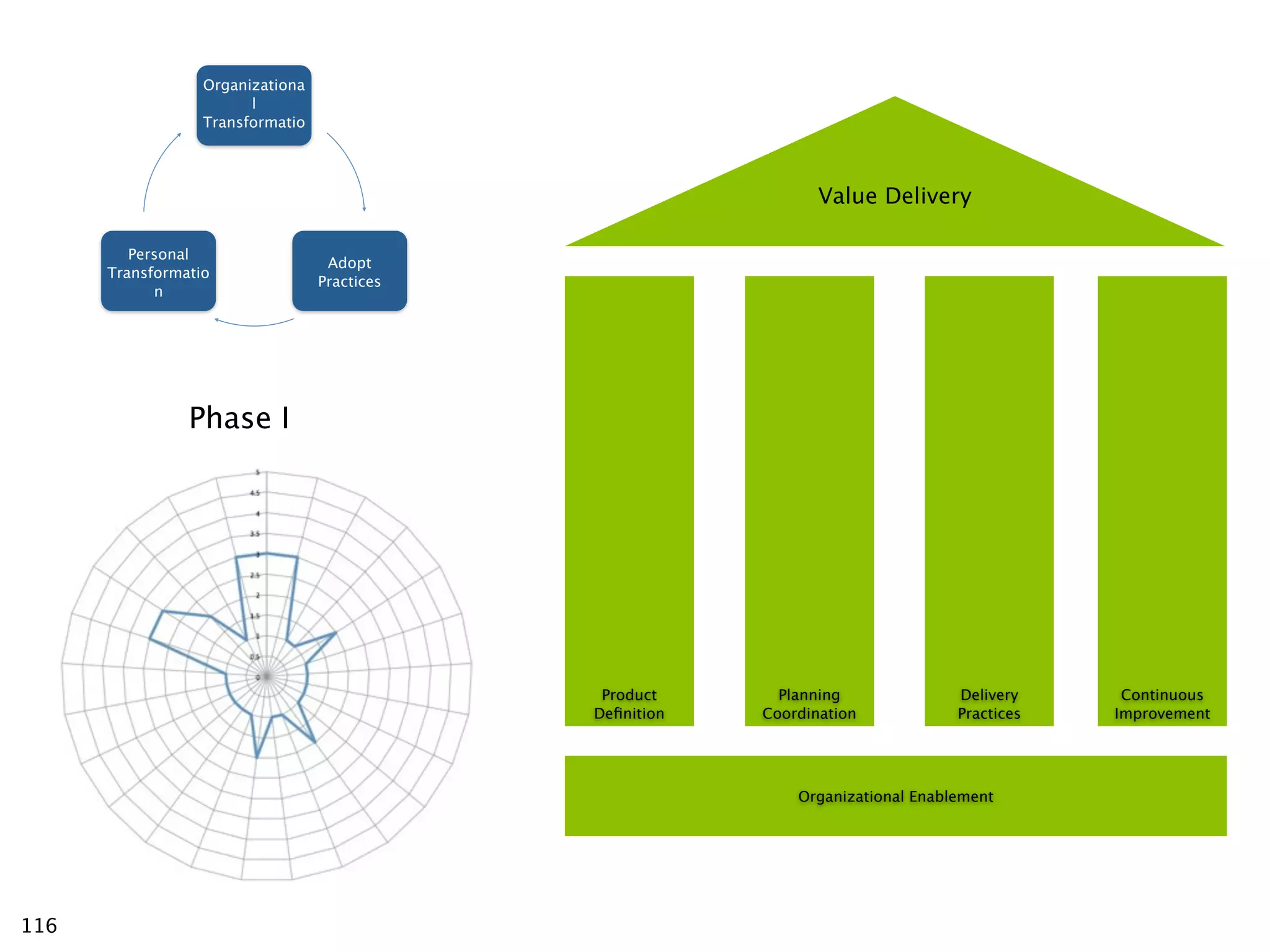
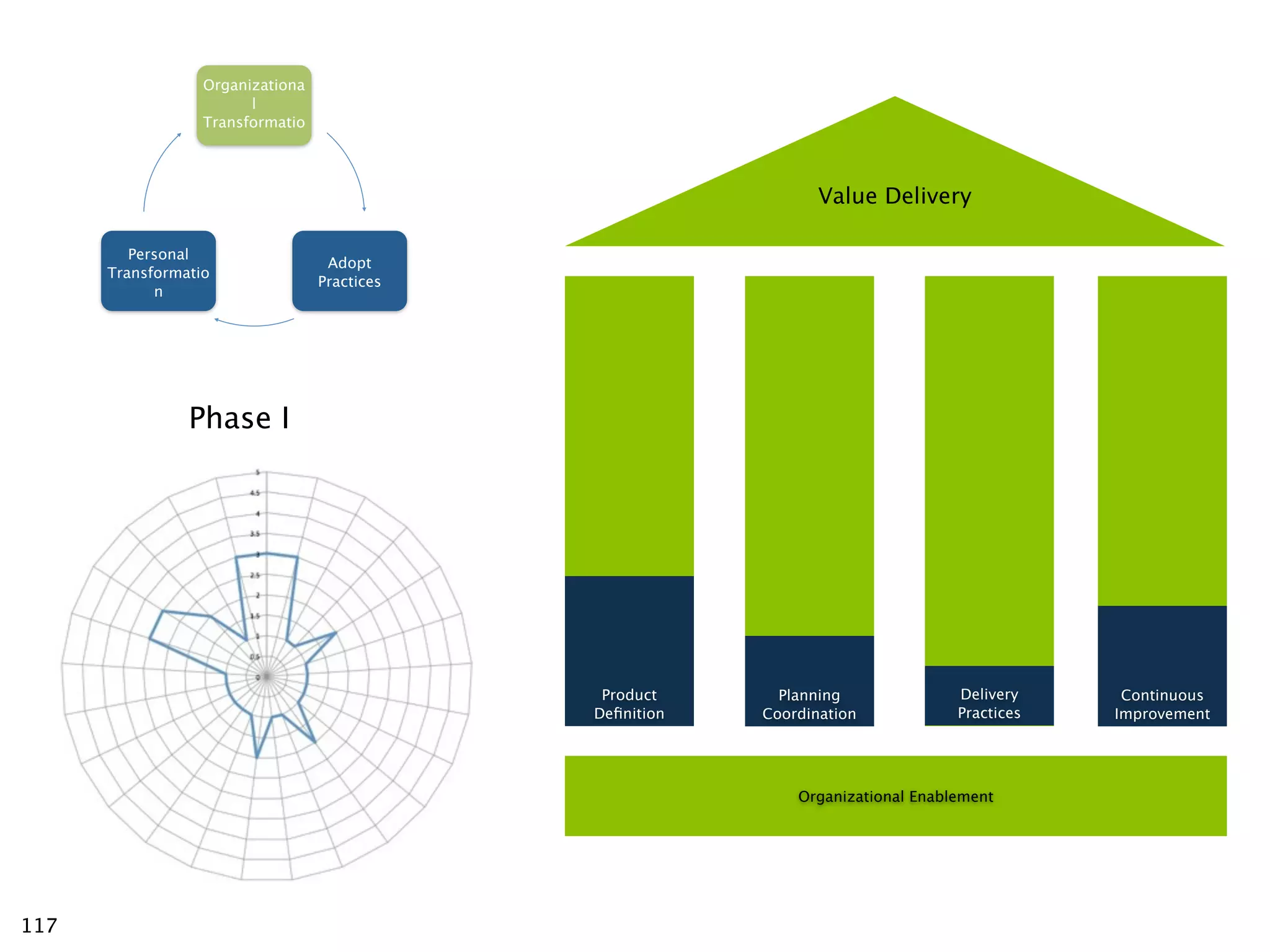
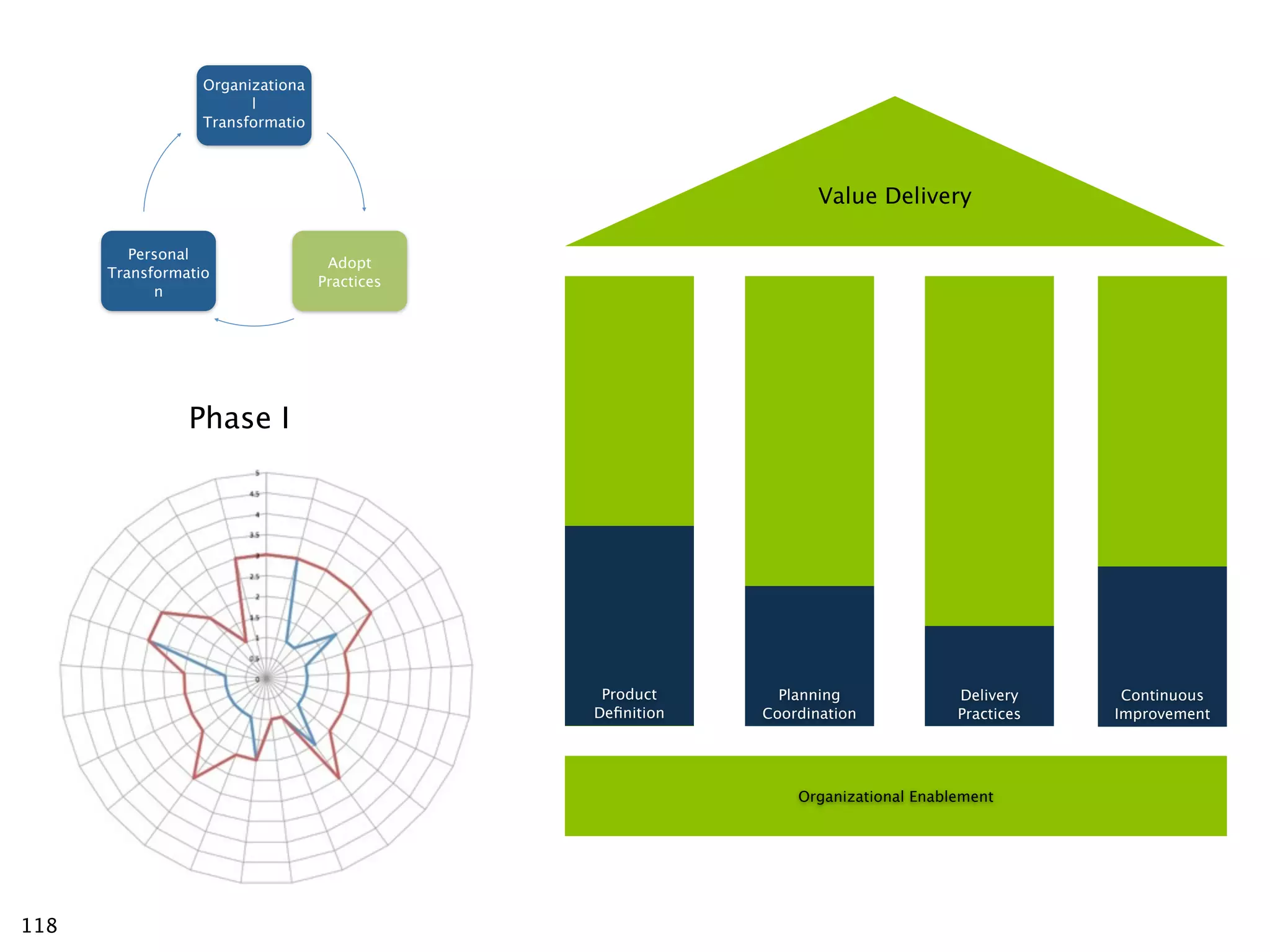
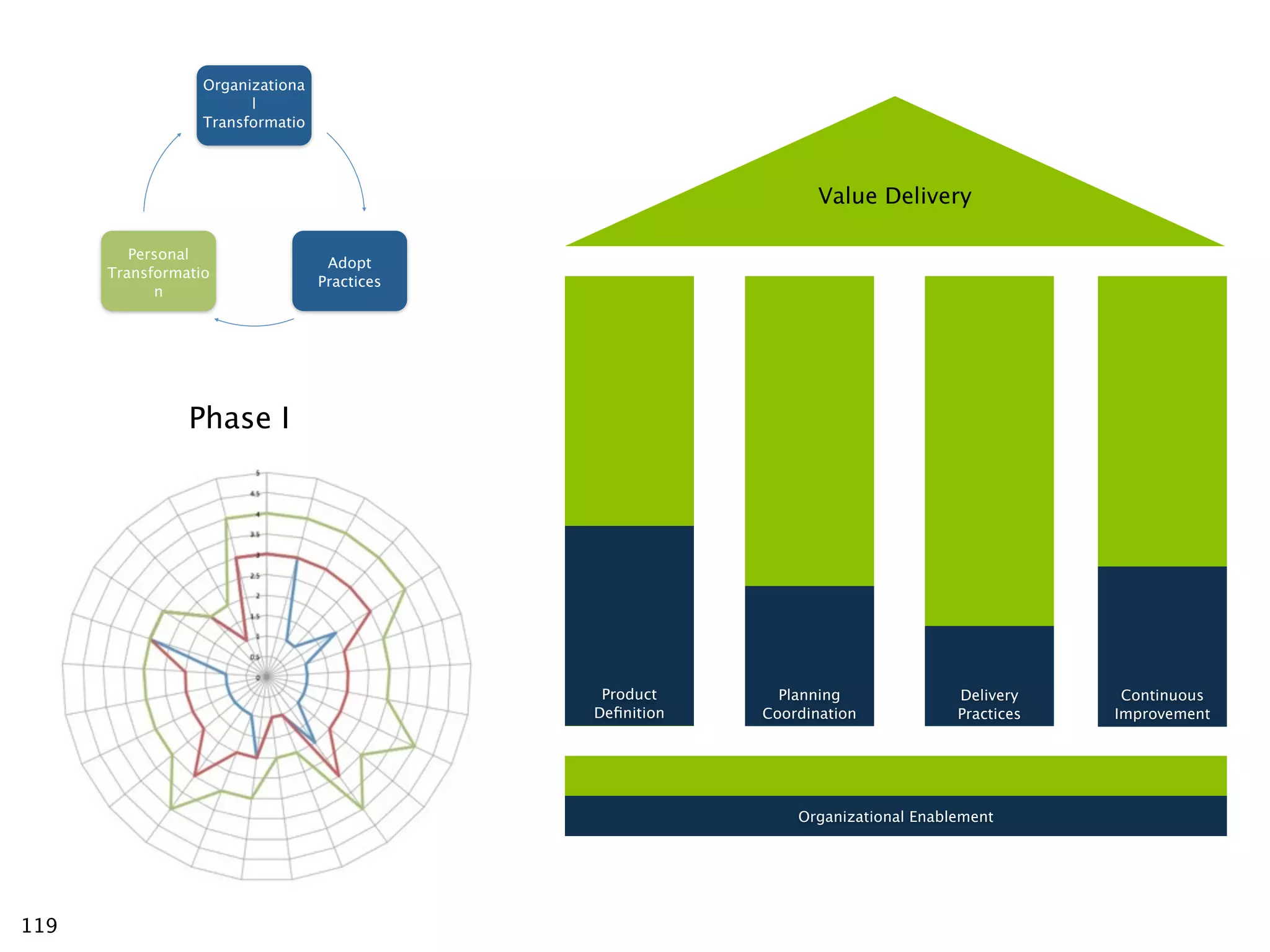
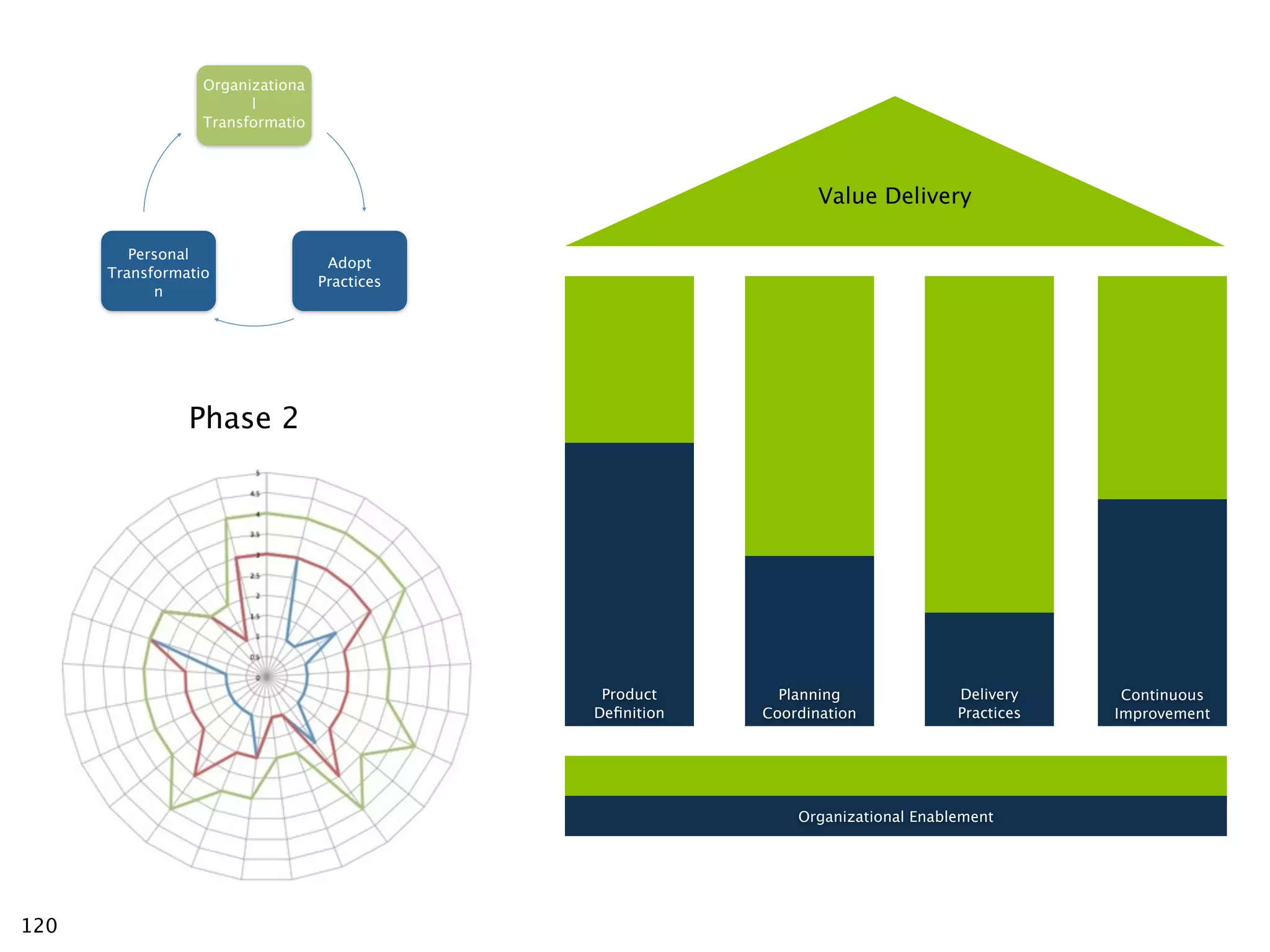
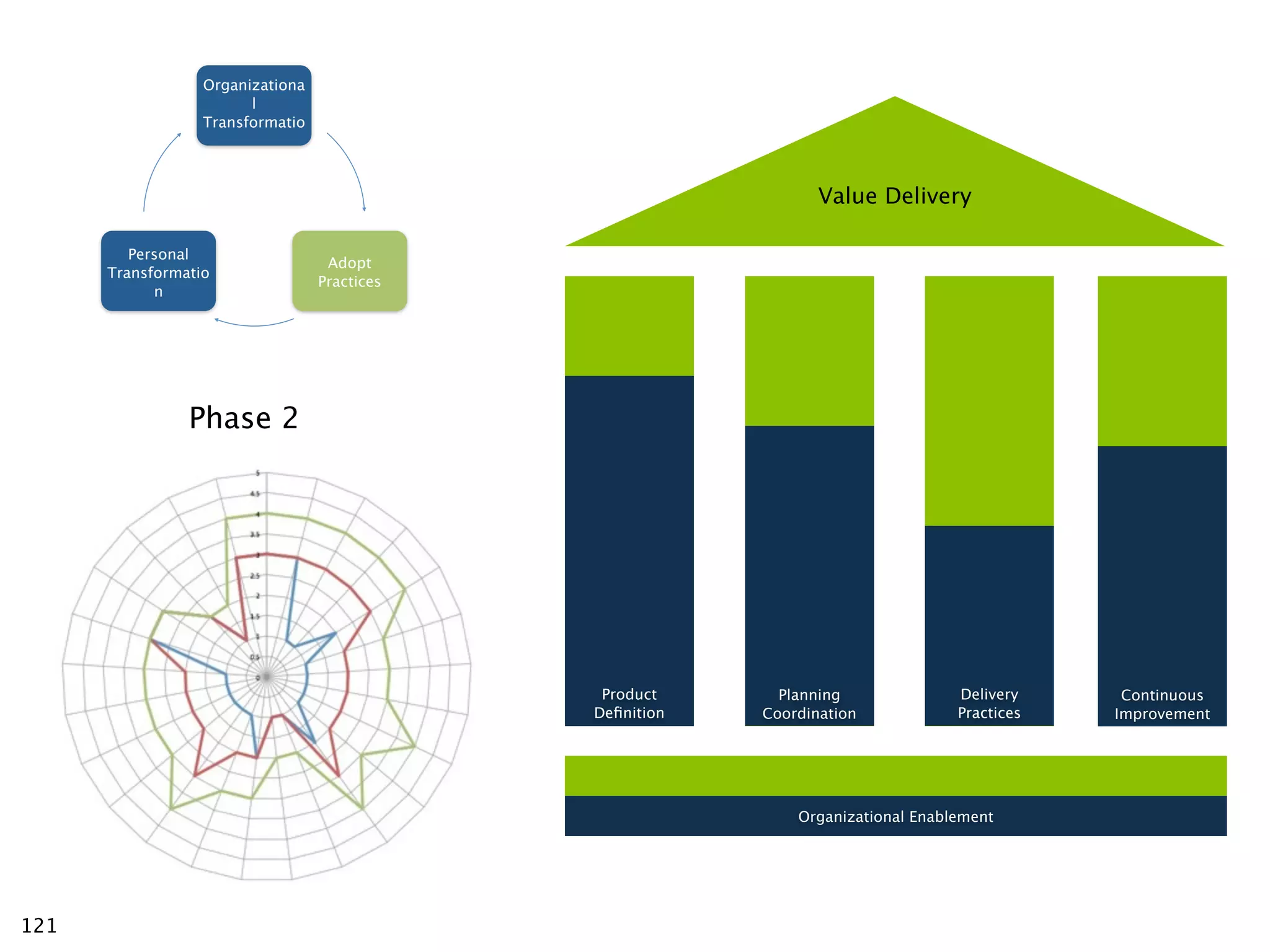
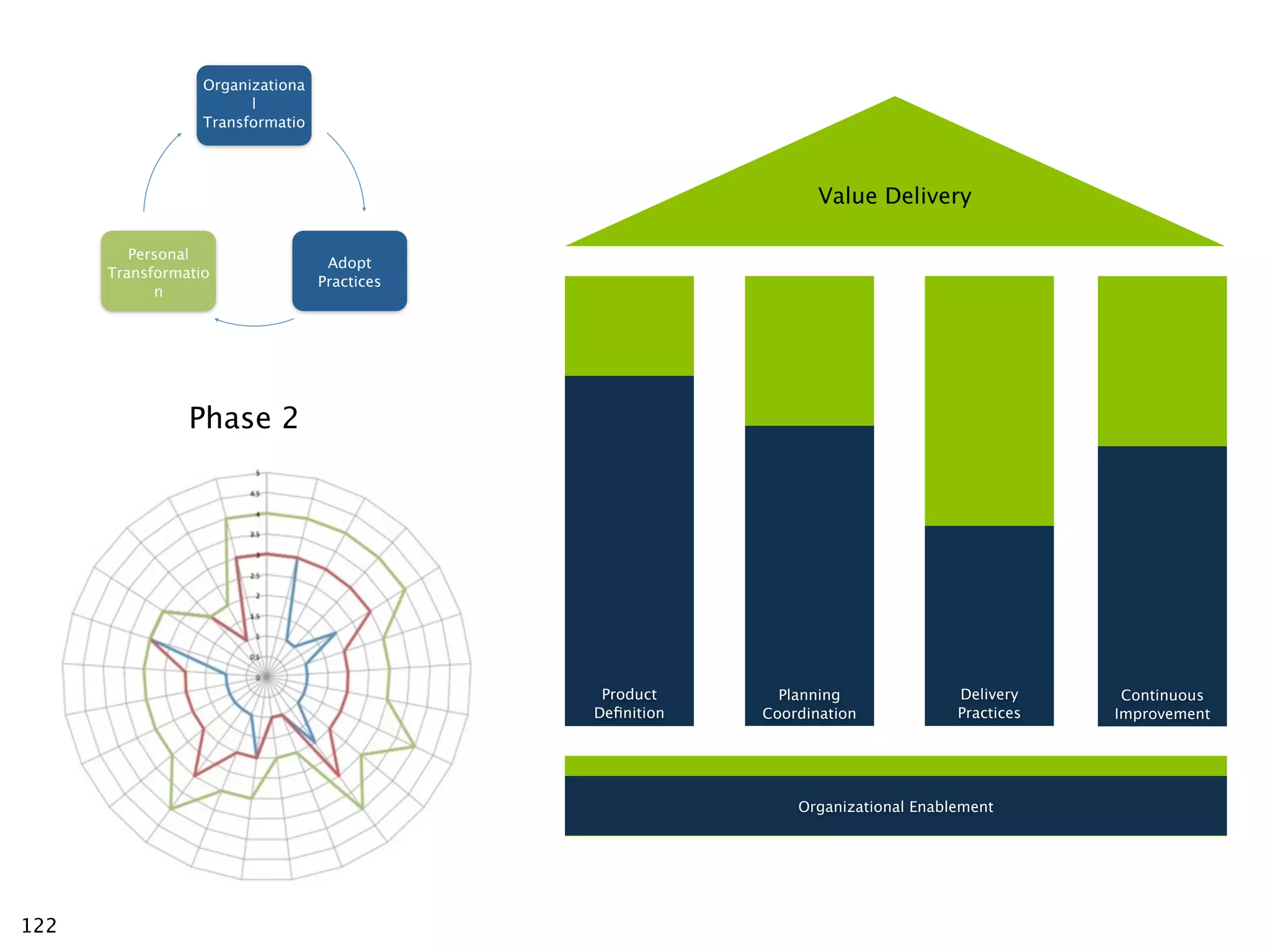
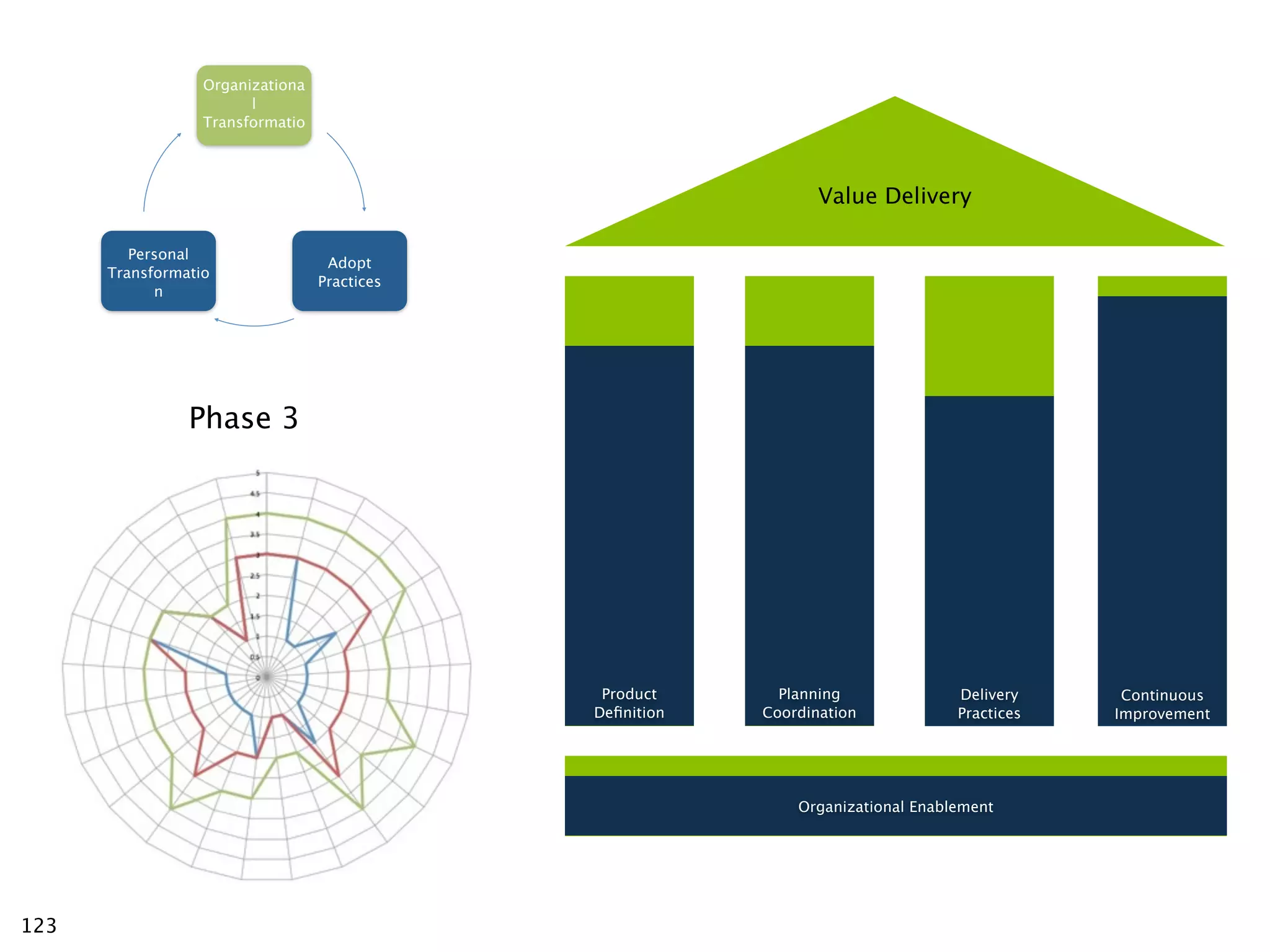
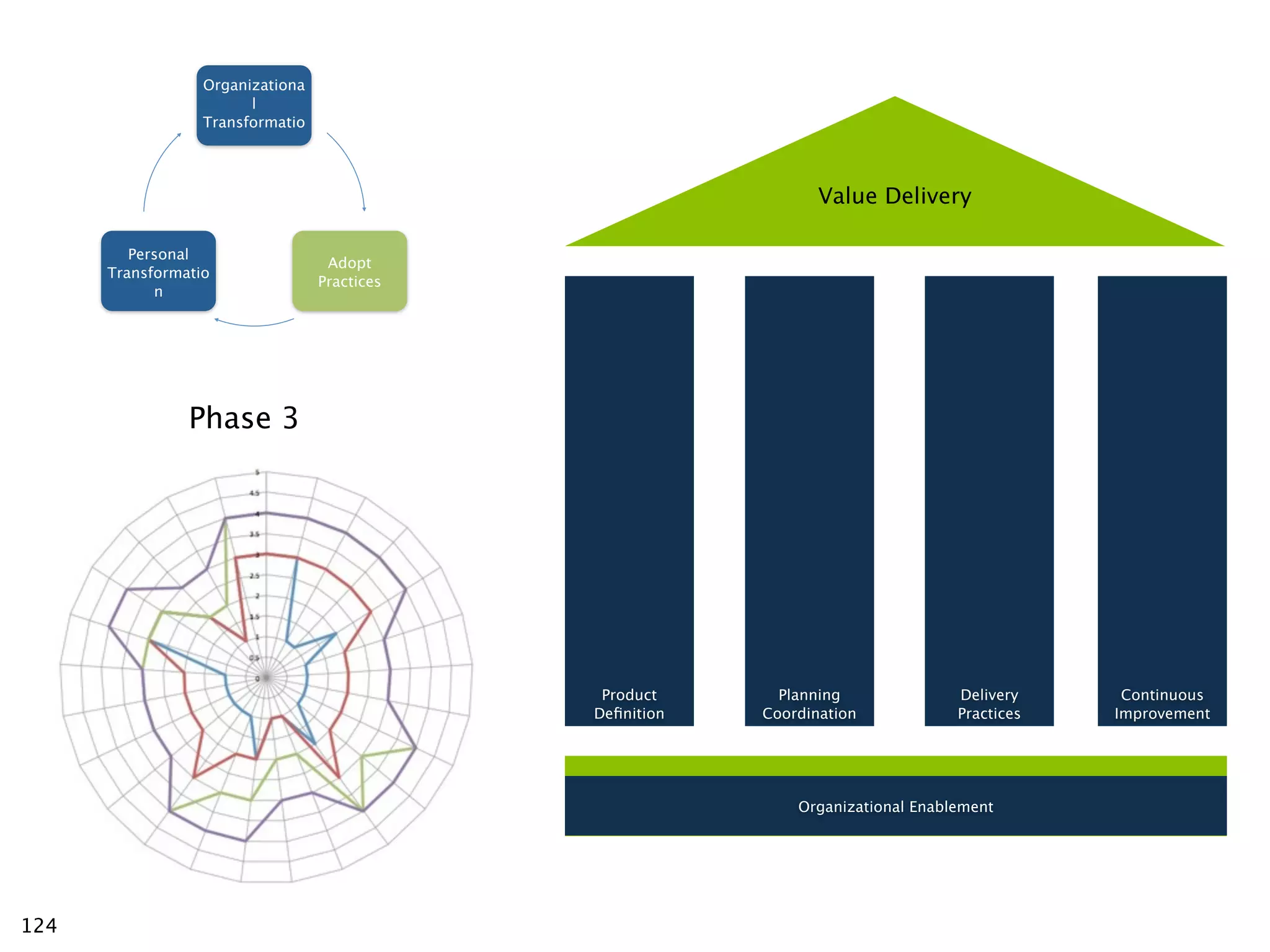
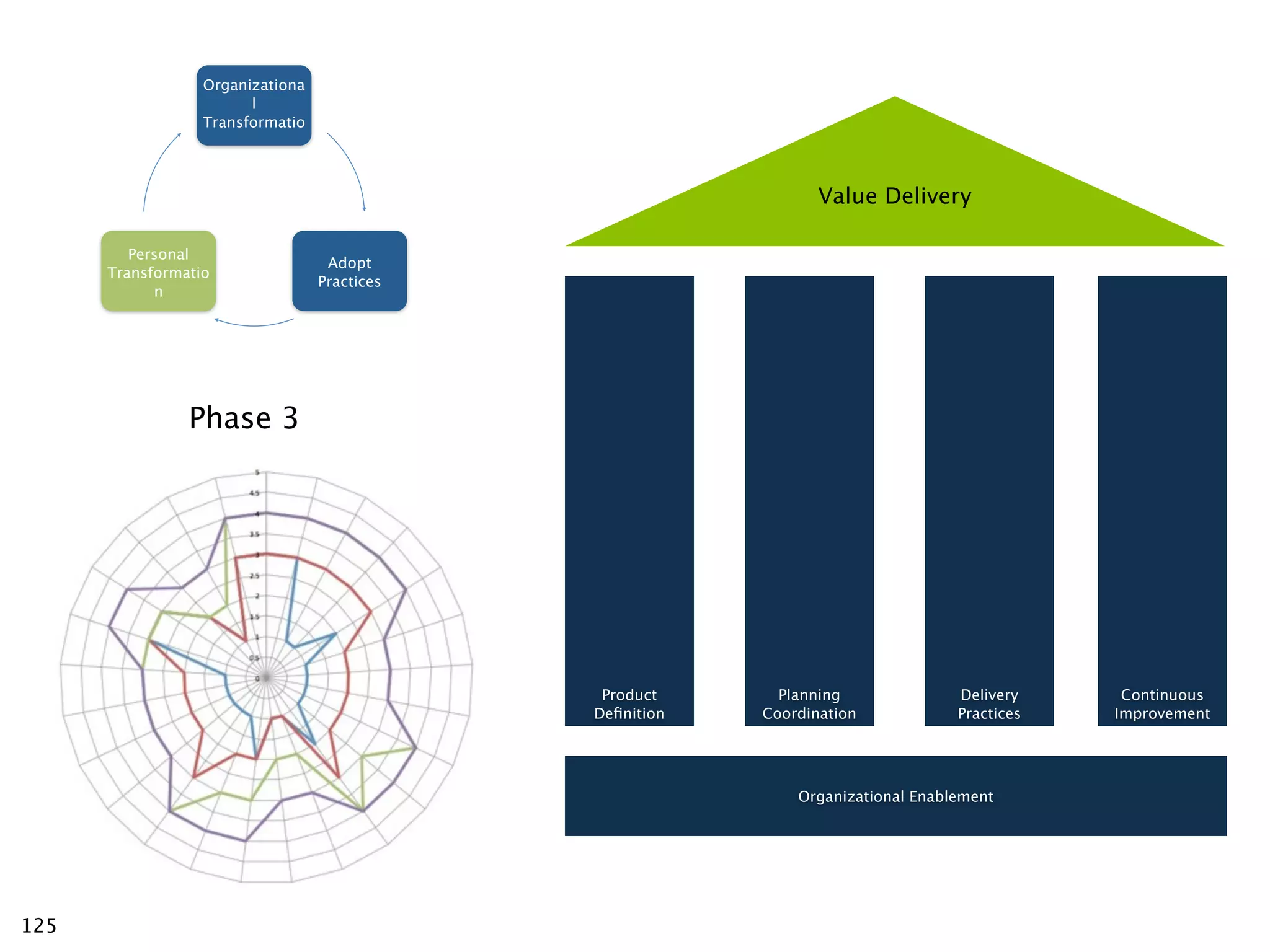
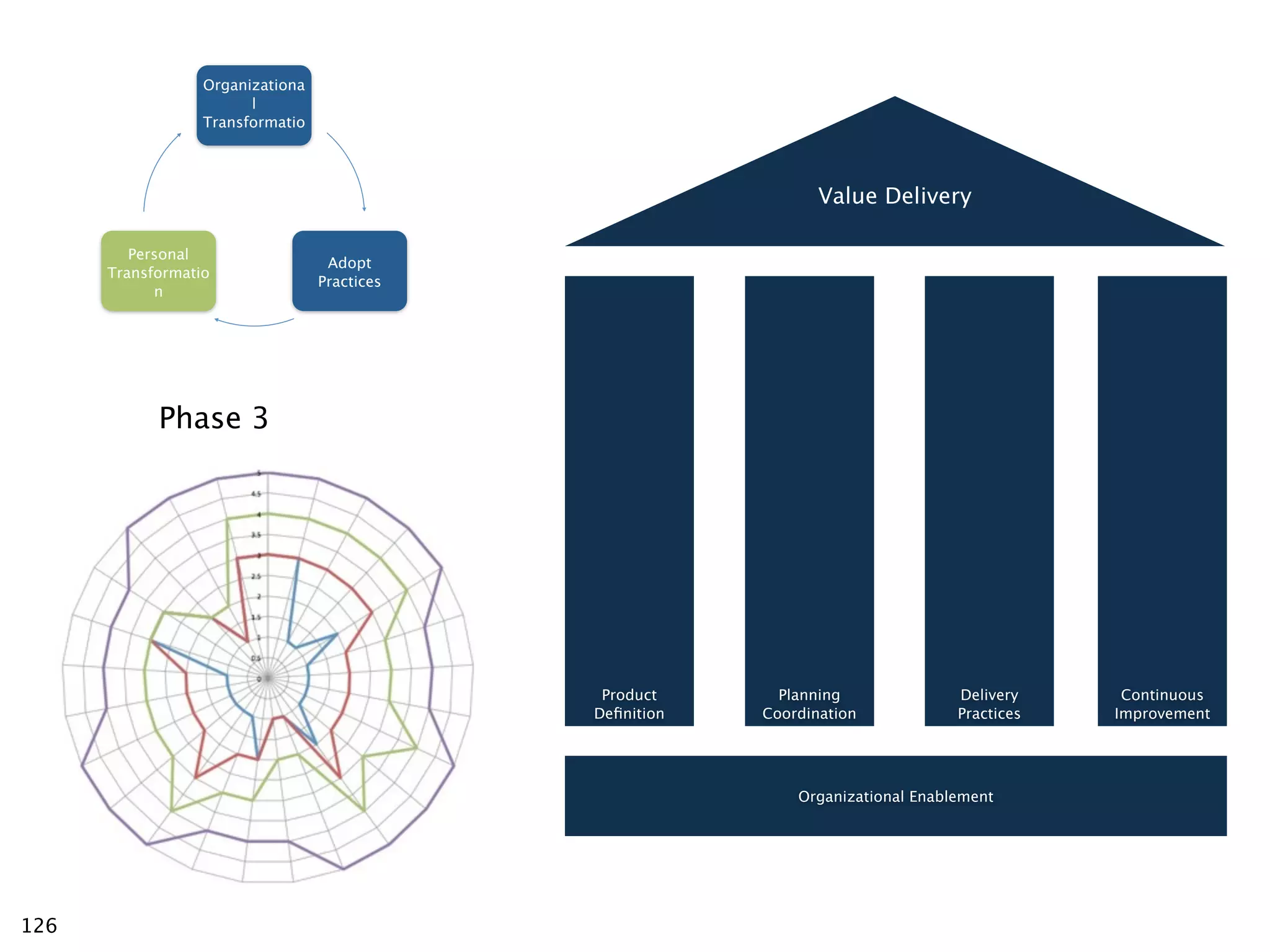
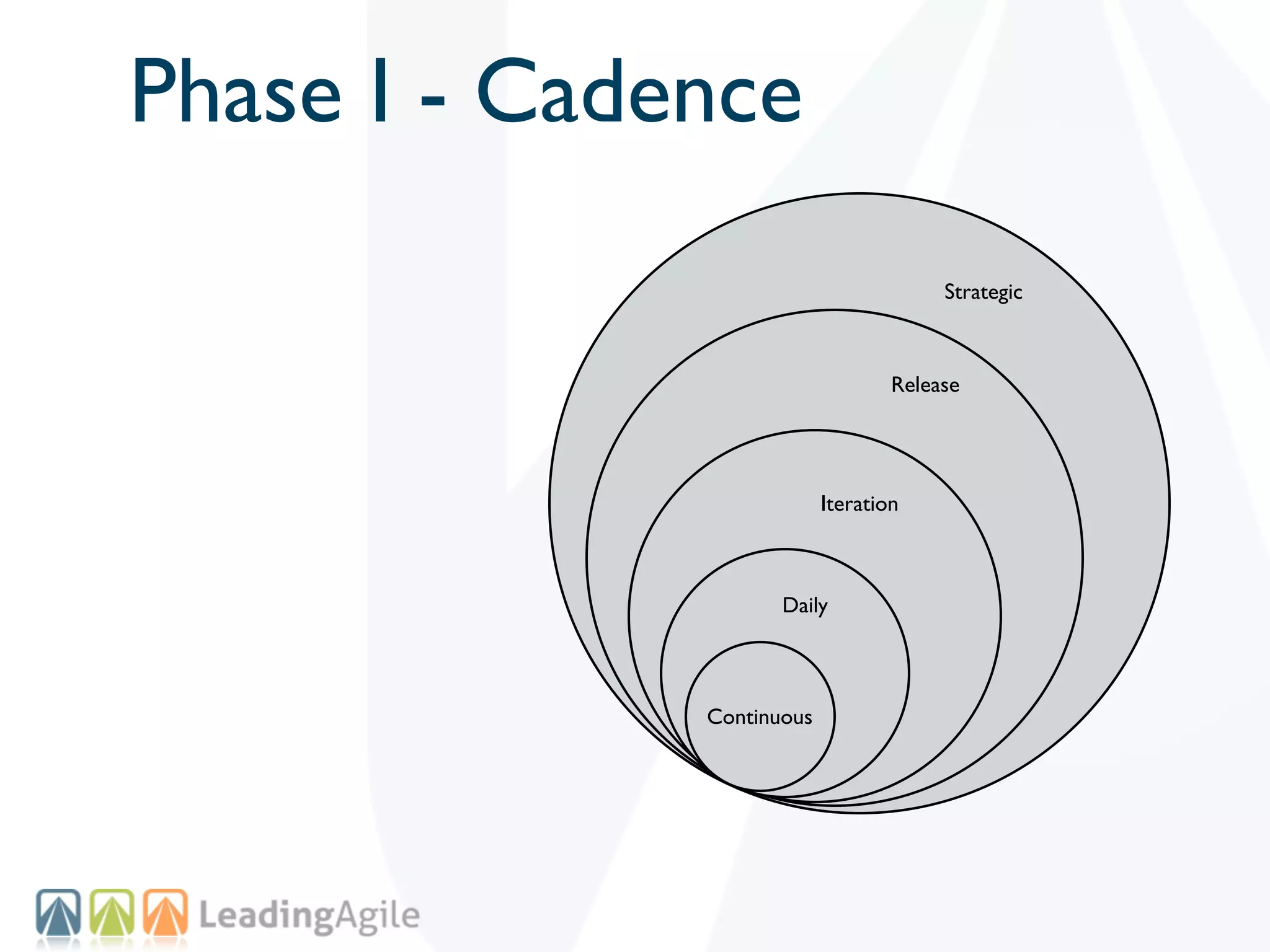
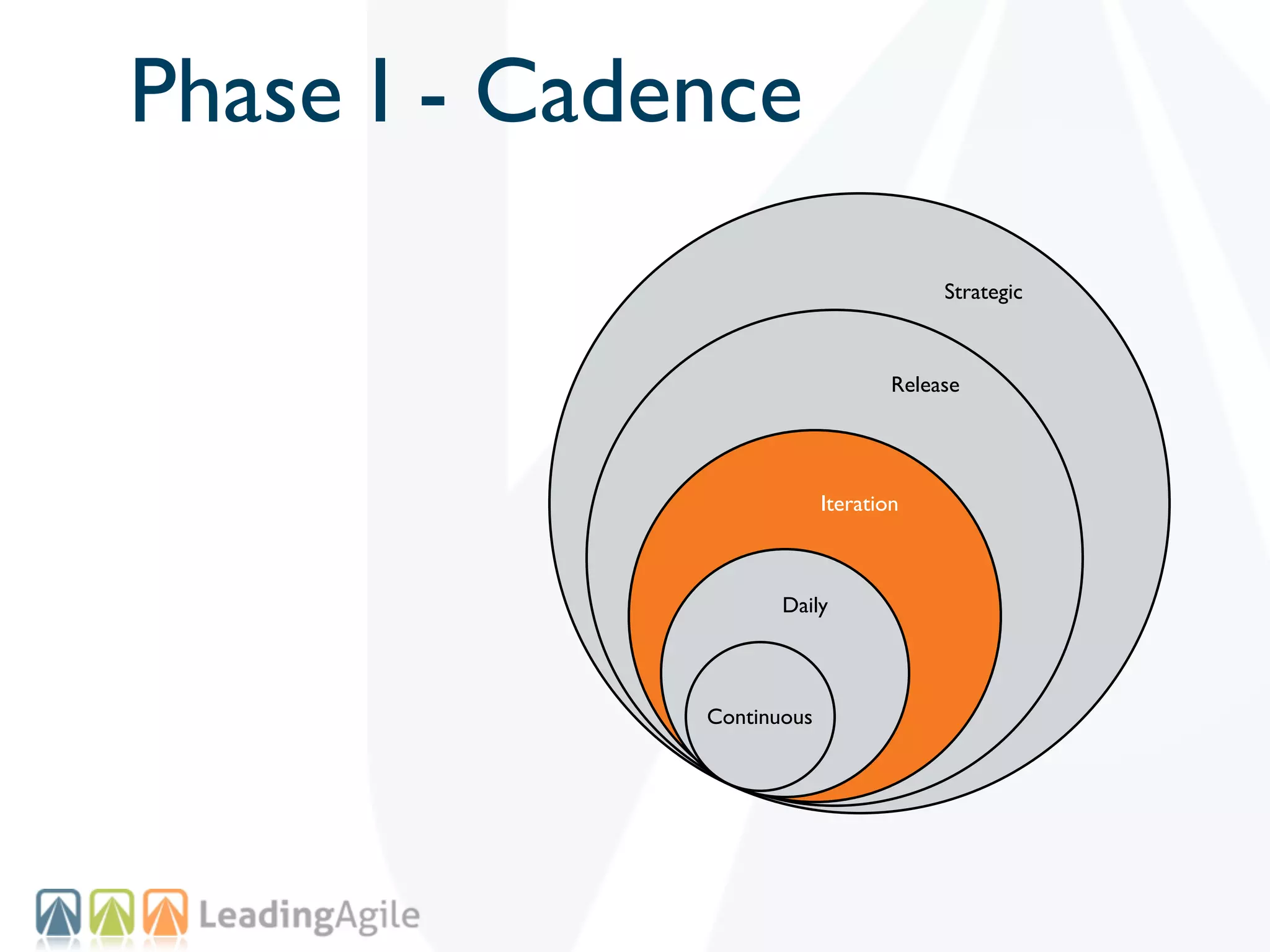
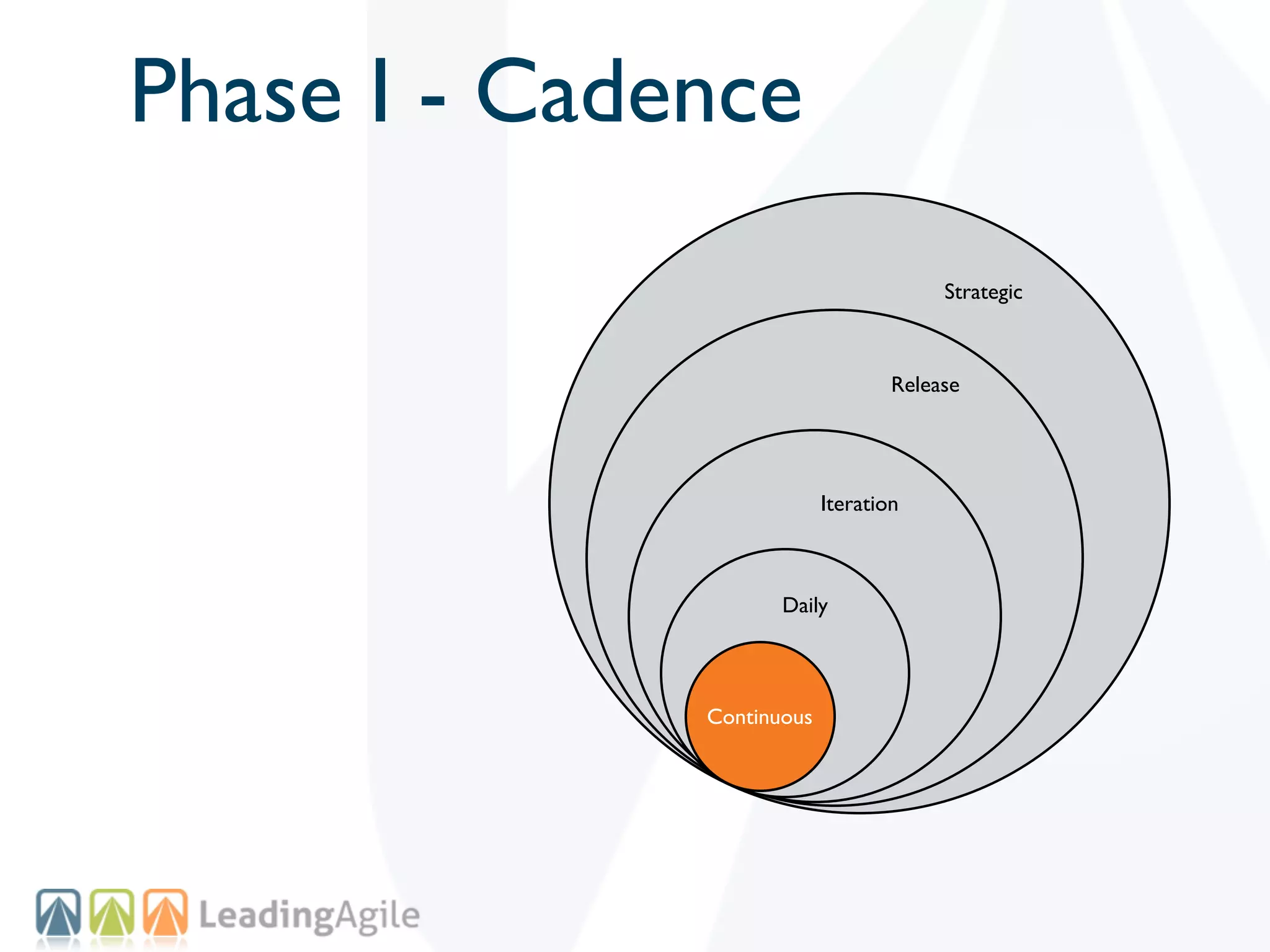
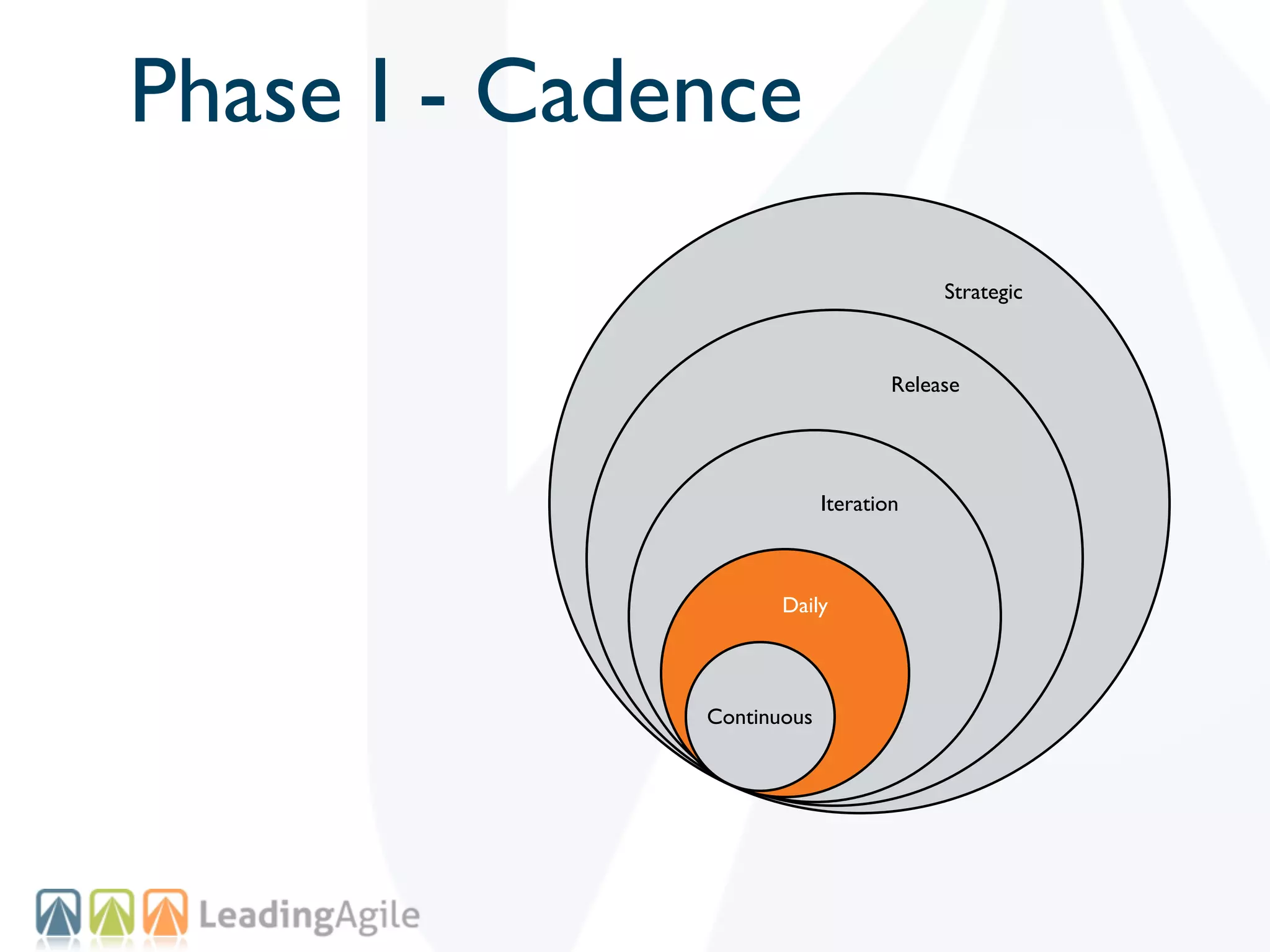
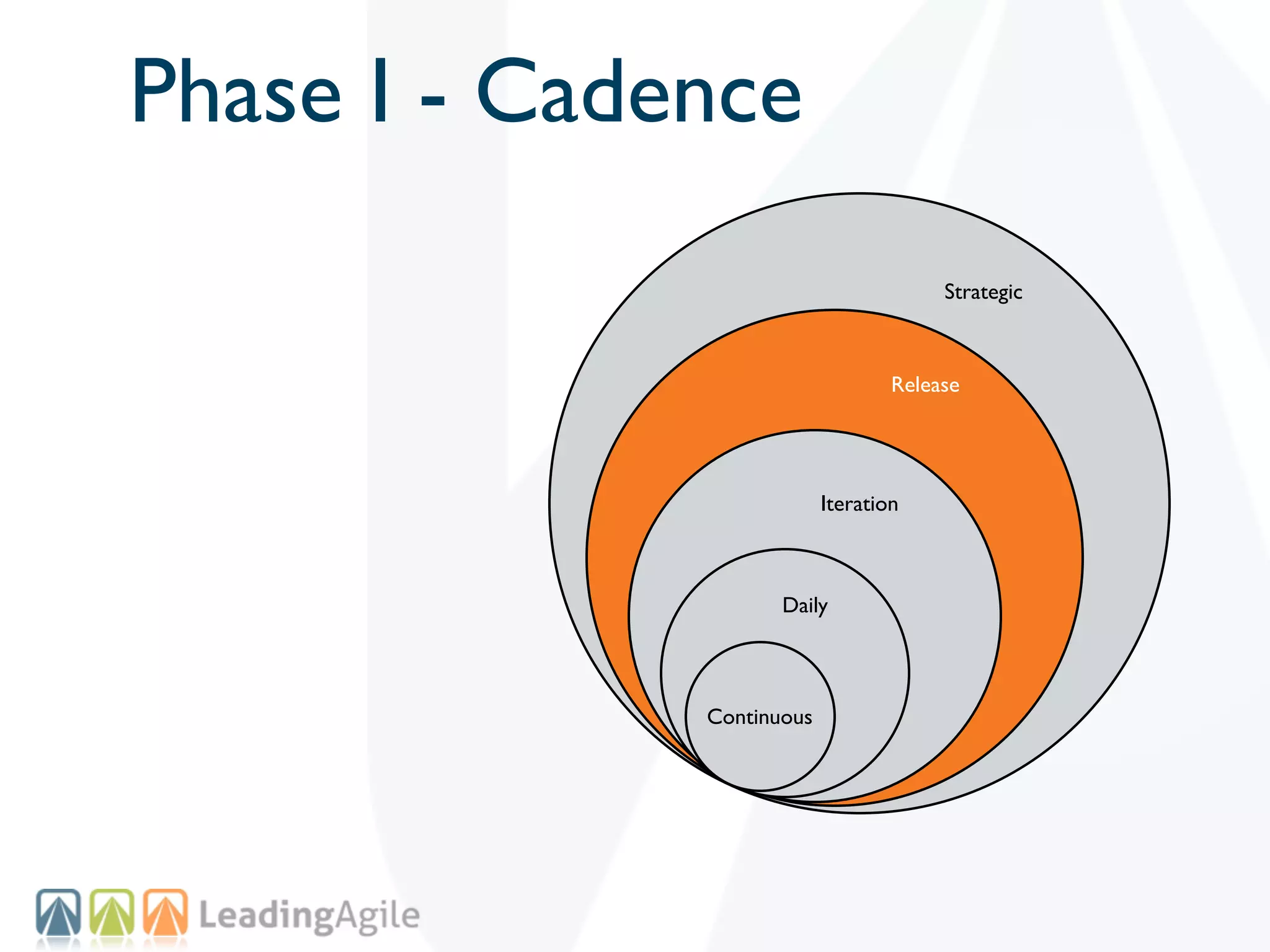
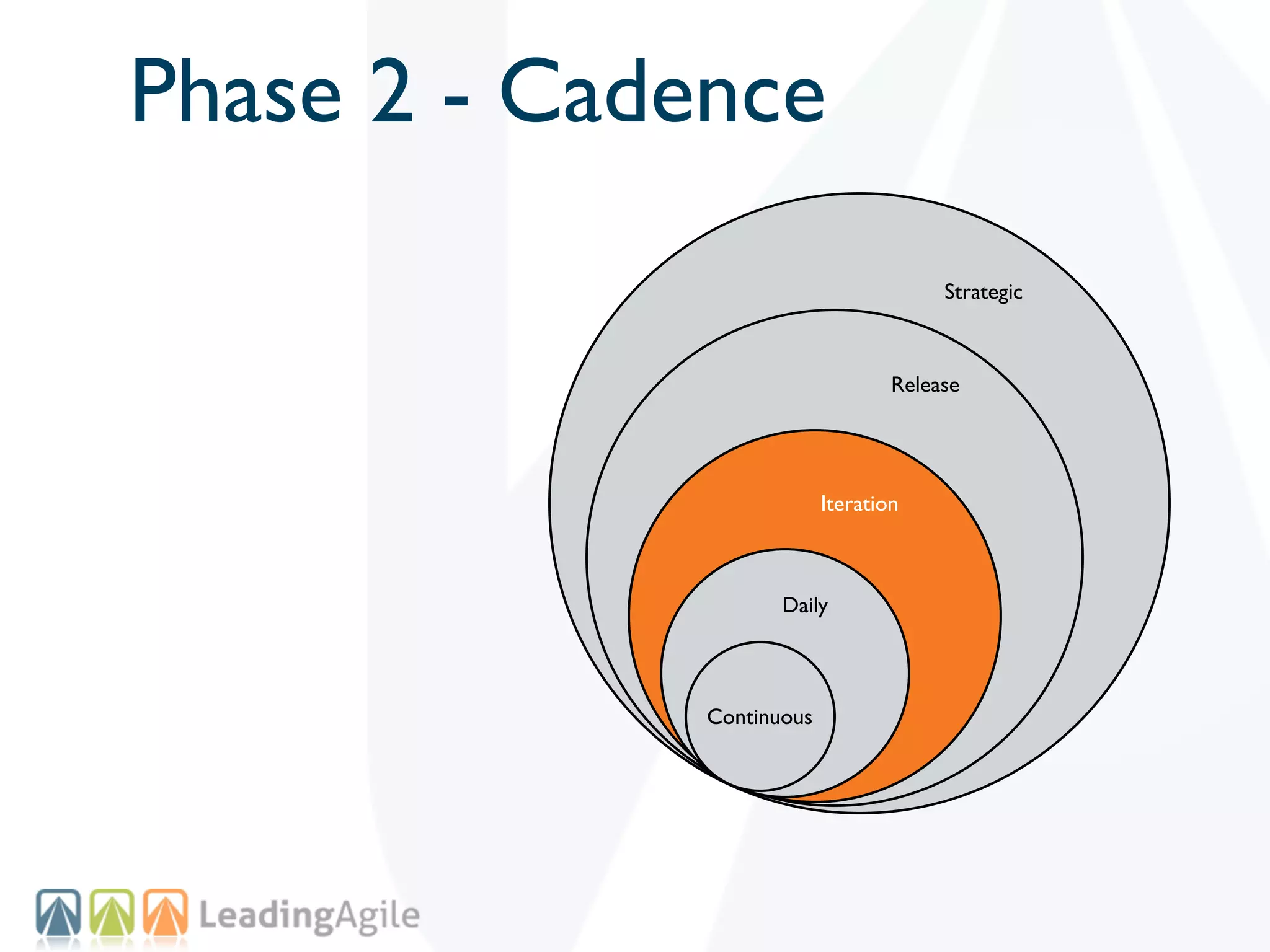
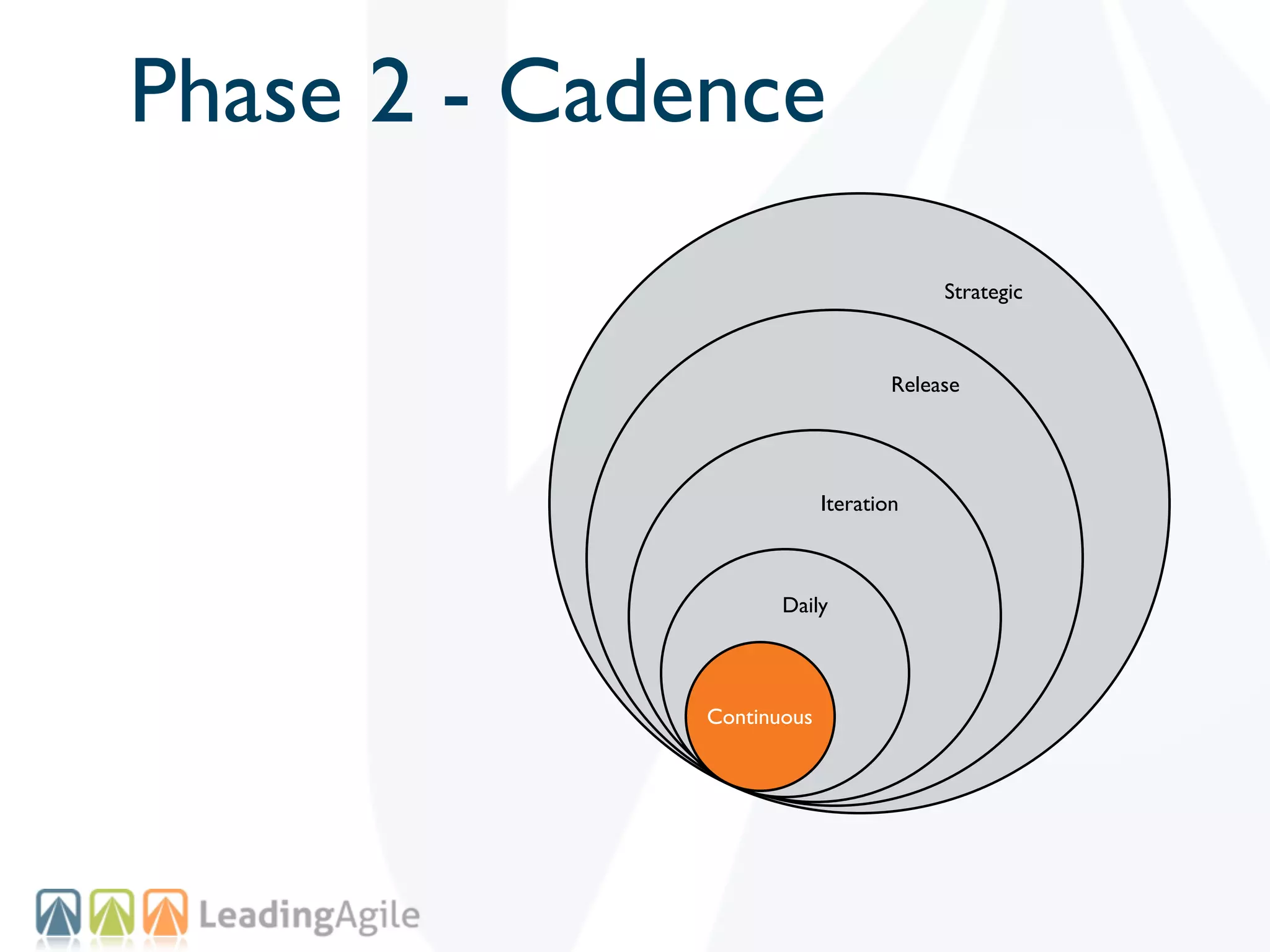
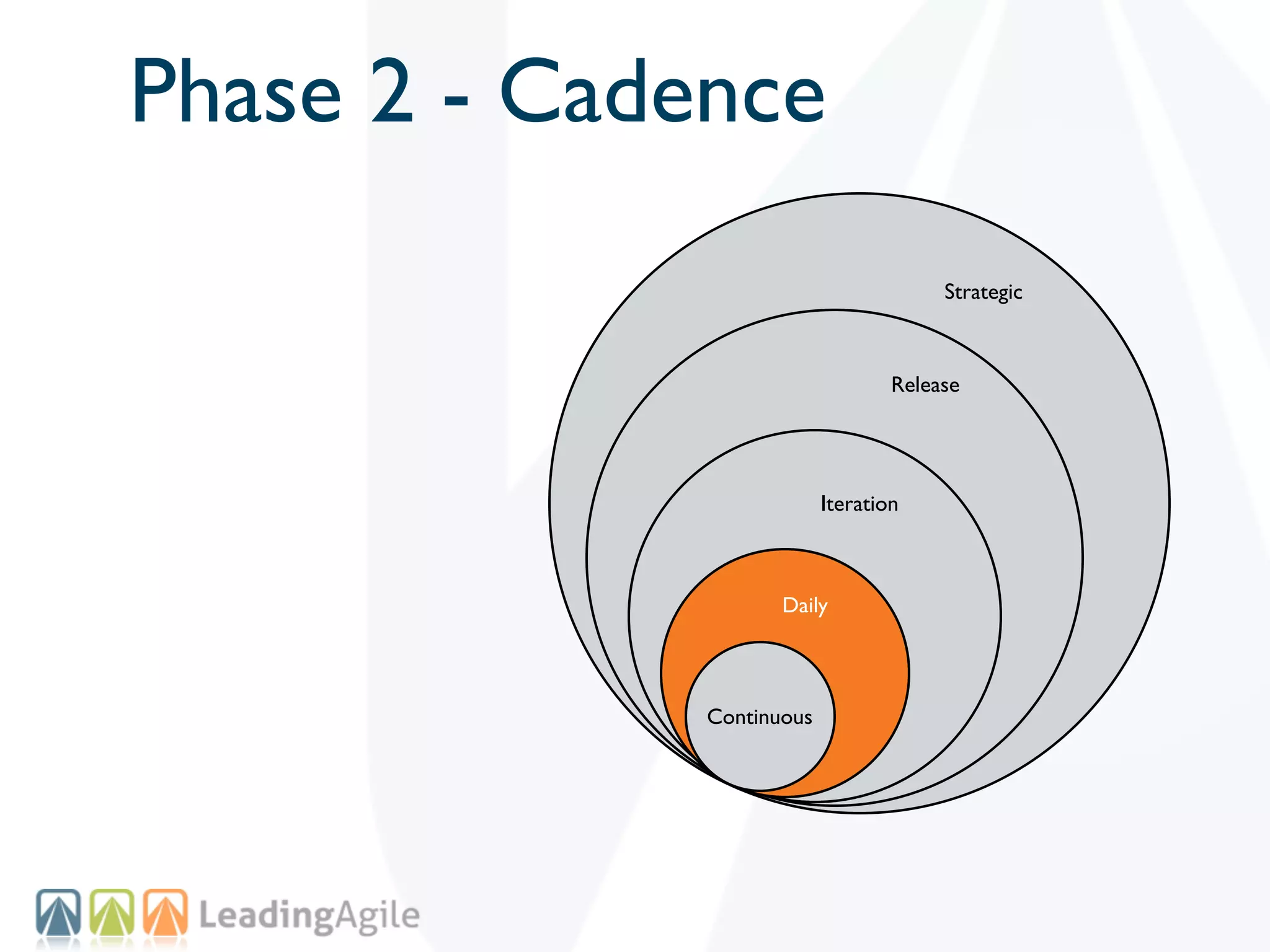
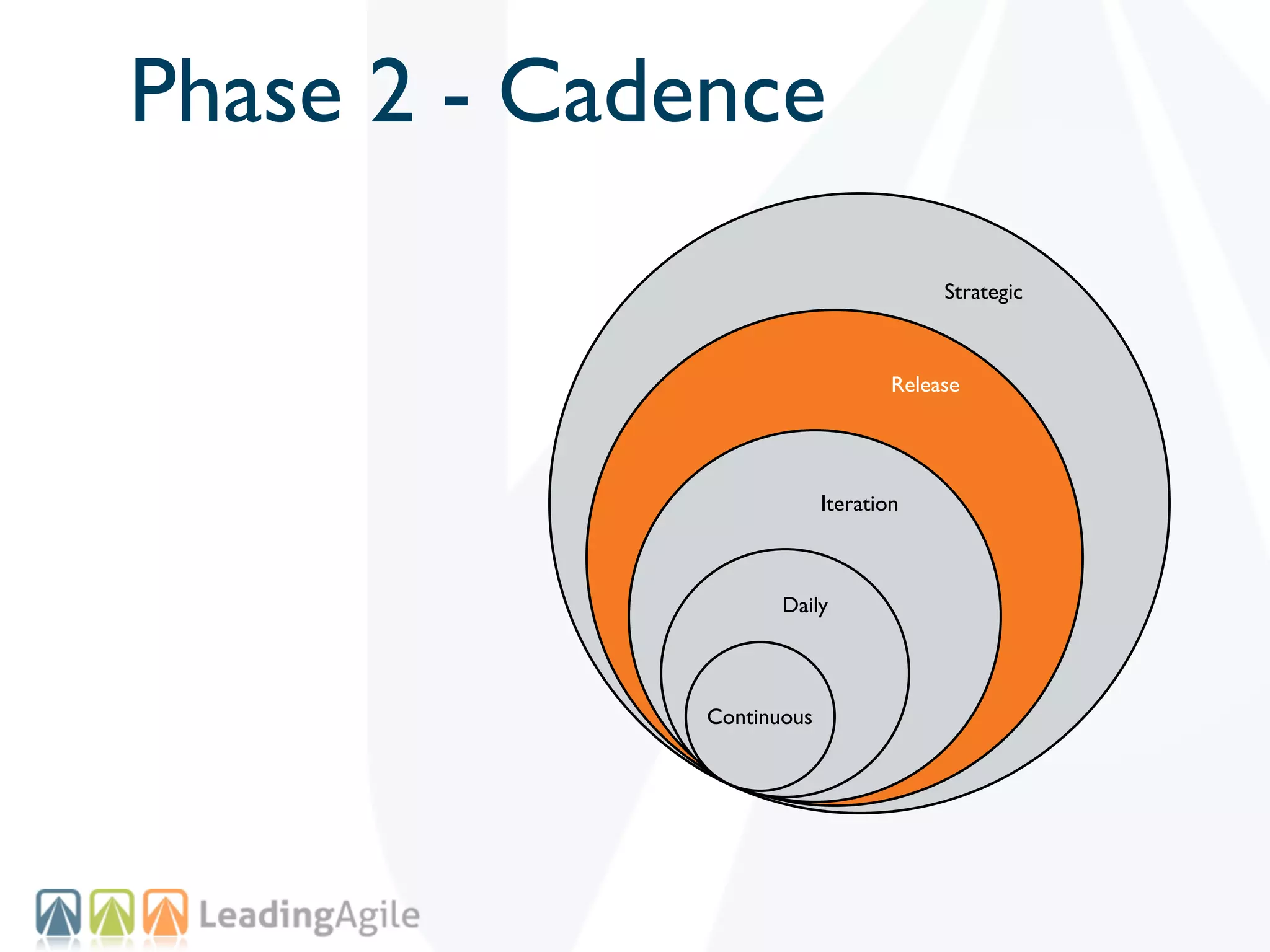
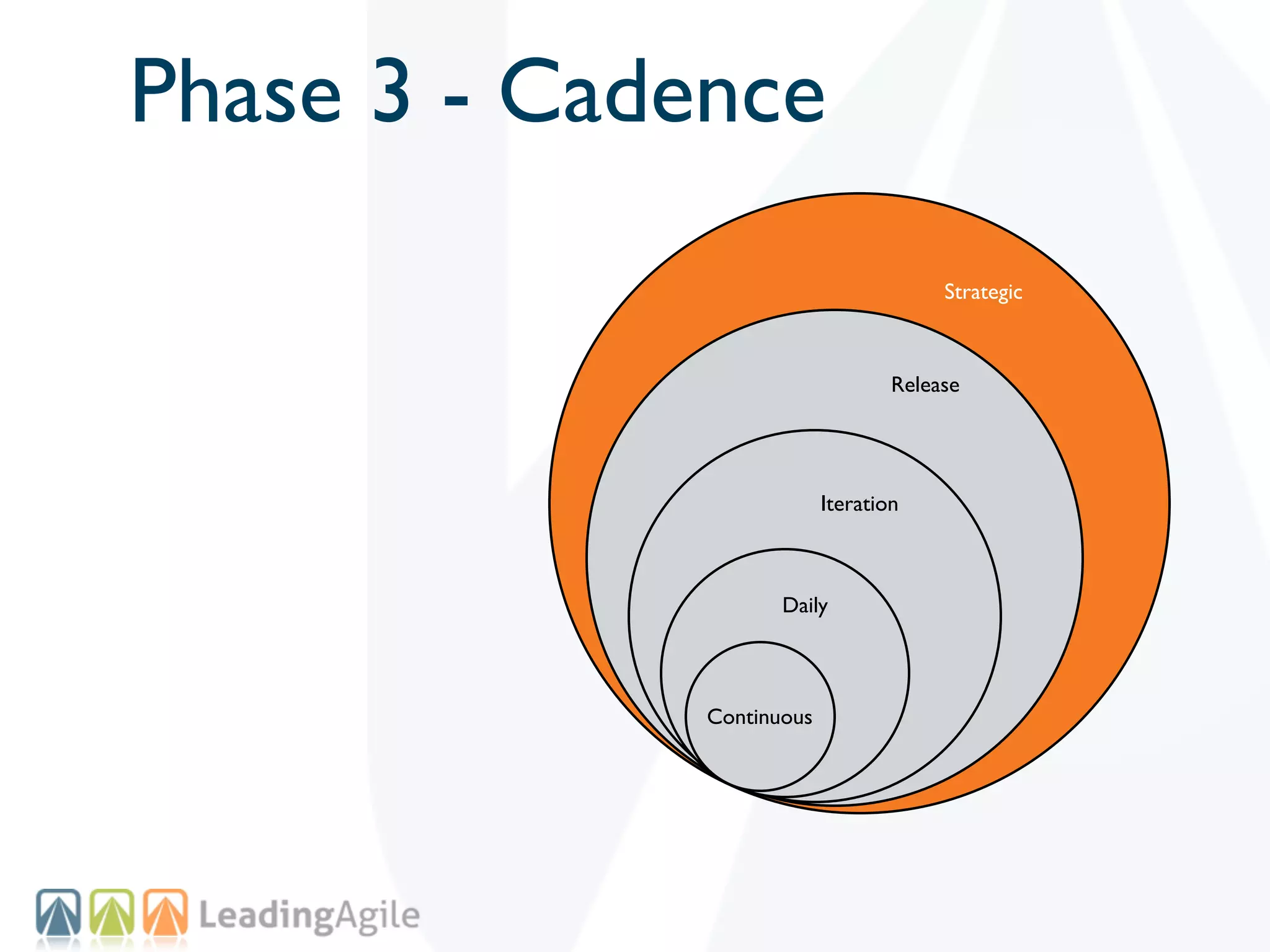
The document discusses challenges with enterprise agile transformations and proposes solutions. It notes that while having agile teams is good, true enterprise agility requires alignment across the organization. Focusing only on teams can cause problems if other areas are not adapted. True agile practices require changes at all levels from teams to portfolio. The solution involves establishing the right competencies at each level, adapting practices for scale and cadence, and addressing organizational structure, processes, and culture changes together.