Session ID: SFO17-314
Session Name: Optimizing GoLang for High Performance with ARM64 Assembly - SFO17-314
Speaker: Wei Xiao - Fannie Zhang
Track: LEG
★ Session Summary ★
It is a guide to ARM64 GoLang assembly. It introduces how to write a ARM64 GoLang assembly program and some descriptions of key Go-specific details for ARM64. When we get to know the go assembly, we can do some optimization to improve performance. We will also show case with an example of SHA optimization.
---------------------------------------------------
★ Resources ★
Event Page: http://connect.linaro.org/resource/sfo17/sfo17-314/
Presentation:
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q_pmdO7sFC4
---------------------------------------------------
★ Event Details ★
Linaro Connect San Francisco 2017 (SFO17)
25-29 September 2017
Hyatt Regency San Francisco Airport
---------------------------------------------------
Keyword:
'http://www.linaro.org'
'http://connect.linaro.org'
---------------------------------------------------
Follow us on Social Media
https://www.facebook.com/LinaroOrg
https://twitter.com/linaroorg
https://www.youtube.com/user/linaroorg?sub_confirmation=1
https://www.linkedin.com/company/1026961




![© 2017 Arm Limited8
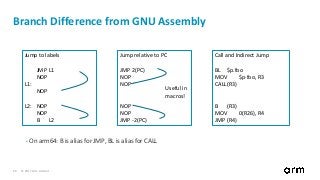
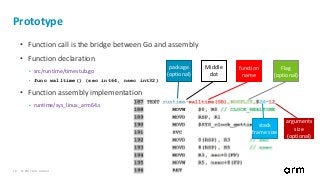
Go Assembly Extension for arm64
• Extended register, e.g.: ADD Rm.<ext>[<<amount], Rn, Rd
• Arrangement for SIMD instructions, e.g.: VADDP Vm.<T>, Vn.<T>, Vd.<T>
• Width specifier and element index for SIMD instructions, e.g.: VMOV Vn.<T>[index], Rd
• Register List, e.g.: VLD1 (Rn), [Vt1.<T>, Vt2.<T>, Vt3.<T>]
• Register offset variant, e.g.: VLD1.P (Rn)(Rm), [Vt1.<T>, Vt2.<T>]
• Go assembly for ARM64 reference manual: src/cmd/internal/obj/arm64/doc.go
• Full details
• https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/41654](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfo17-314optimizinggolangforhighperformancewitharm64assembly-171010155339/85/Optimizing-GoLang-for-High-Performance-with-ARM64-Assembly-SFO17-314-8-320.jpg?cb=1507650874)



![© 2017 Arm Limited14
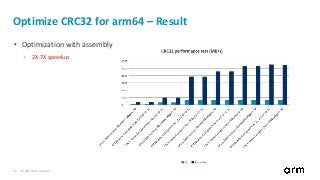
Optimize CRC32 for arm64 – Before
• Pure Go table-driven implementation
src/hash/crc32/crc32_generic.go
42 func simpleUpdate(crc uint32, tab *Table, p []byte) uint32 {
43 crc = ^crc
44 for _, v := range p {
45 crc = tab[byte(crc)^v] ^ (crc >> 8)
46 }
47 return ^crc
48 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfo17-314optimizinggolangforhighperformancewitharm64assembly-171010155339/85/Optimizing-GoLang-for-High-Performance-with-ARM64-Assembly-SFO17-314-14-320.jpg?cb=1507650874)
![© 2017 Arm Limited15
Optimize CRC32 for arm64 – After
• Assembly for arm64
src/hash/crc32/crc32_arm64.s
9 // func castagnoliUpdate(crc uint32, p []byte) uint32
10 TEXT ·castagnoliUpdate(SB),NOSPLIT,$0-36
11 MOVWU crc+0(FP), R9 // CRC value
12 MOVD p+8(FP), R13 // data pointer
13 MOVD p_len+16(FP), R11 // len(p)
14
15 CMP $8, R11
16 BLT less_than_8
17
18 update:
19 MOVD.P 8(R13), R10
20 CRC32CX R10, R9
21 SUB $8, R11
22
23 CMP $8, R11
24 BLT less_than_8
25
26 JMP update
…
46 done:
47 MOVWU R9, ret+32(FP)
48 RET
0(FP)
ret
p.cap
p.len
p.base
crc
32(FP)
8(FP)
16(FP)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfo17-314optimizinggolangforhighperformancewitharm64assembly-171010155339/85/Optimizing-GoLang-for-High-Performance-with-ARM64-Assembly-SFO17-314-15-320.jpg?cb=1507650874)
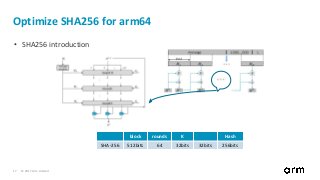
![© 2017 Arm Limited18
Optimize SHA256 for arm64 – Message schedule
src/crypto/sha256/sha256block.go
84 for i := 0; i < 16; i++ {
85 j := i * 4
86 w[i] = uint32(p[j])<<24 | uint32(p[j+1])<<16 | uint32(p[j+2])<<8 | uint32(p[j+3])
87 }
88 for i := 16; i < 64; i++ {
89 v1 := w[i-2]
90 t1 := (v1>>17 | v1<<(32-17)) ^ (v1>>19 | v1<<(32-19)) ^ (v1 >> 10)
91 v2 := w[i-15]
92 t2 := (v2>>7 | v2<<(32-7)) ^ (v2>>18 | v2<<(32-18)) ^ (v2 >> 3)
93 w[i] = t1 + w[i-7] + t2 + w[i-16]
94 }
for i := 16; i < 64; i+=4 {
SHA256SU0 Vn.S4, Vd.S4
SHA256SU1 Vm.S4, Vn.S4, Vd.S4
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfo17-314optimizinggolangforhighperformancewitharm64assembly-171010155339/85/Optimizing-GoLang-for-High-Performance-with-ARM64-Assembly-SFO17-314-18-320.jpg?cb=1507650874)
![© 2017 Arm Limited19
Optimize SHA256 for arm64 – Hash Computation
src/crypto/sha256/sha256block.go
98 for i := 0; i < 64; i++ {
99 t1 := h + ((e>>6 | e<<(32-6)) ^ (e>>11 | e<<(32-11)) ^ (e>>25 | e<<(32-25))) + ((e & f) ^ (^e & g)) + _K[i] + w[i]
100
101 t2 := ((a>>2 | a<<(32-2)) ^ (a>>13 | a<<(32-13)) ^ (a>>22 | a<<(32-22))) + ((a & b) ^ (a & c) ^ (b & c))
102
103 h = g
104 g = f
105 f = e
106 e = d + t1
107 d = c
108 c = b
109 b = a
110 a = t1 + t2
111 }
for i := 0; i < 64; i+=4 {
SHA256H Vm, Vn, Vd.4S
SHA256H2 Vm, Vn, Vd.4S
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sfo17-314optimizinggolangforhighperformancewitharm64assembly-171010155339/85/Optimizing-GoLang-for-High-Performance-with-ARM64-Assembly-SFO17-314-19-320.jpg?cb=1507650874)