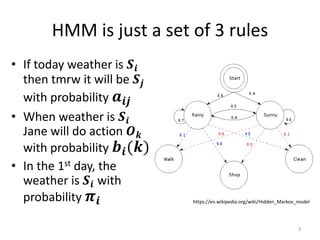
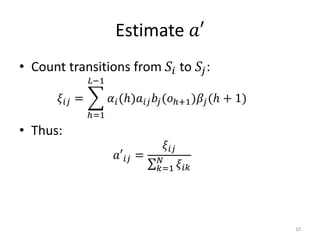
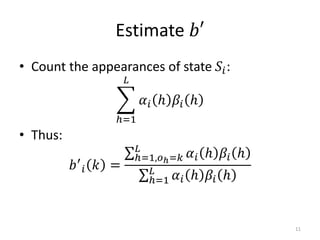
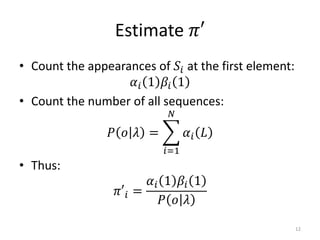
Hidden Markov models (HMMs) are a set of rules used to model probabilistic systems where an underlying process with hidden states influences a series of observable outputs. The document discusses:
1. HMMs involve hidden states that influence observable outputs according to transition and emission probabilities.
2. Two common tasks for HMMs are calculating the probability of a sequence of outputs given a model, and training a model to maximize the probability of an observed sequence.
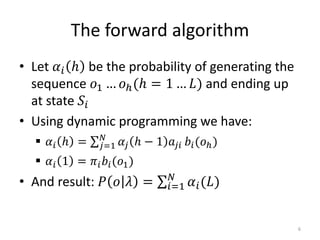
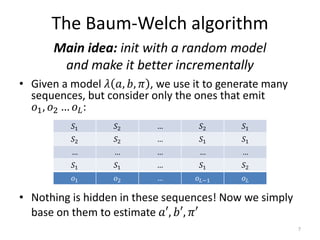
3. The forward and backward algorithms use dynamic programming to efficiently solve these tasks, with the forward algorithm calculating probabilities and the backward algorithm supporting training via the Baum-Welch algorithm.