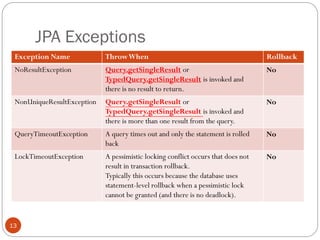
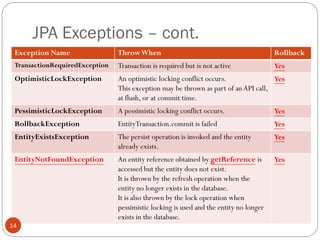
The document discusses various JPA and EJB concepts related to entity relationships, locking, exceptions, and the entity manager. It provides annotations for mapping entity relationships and collections. It defines different lock types in JPA and exceptions that can occur at the JPA, EJB, and transaction levels and whether they cause rollbacks. It also describes how the persistence context is propagated for local EJBs and when the transaction scoped persistence context is created.