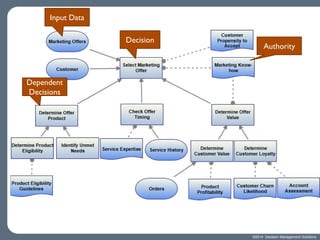
The document outlines the essentials of decision management, emphasizing the importance of identifying, scoping, and automating key business decisions to improve operational efficiency. It discusses methods for modeling decisions, understanding their context, and preparing them for automation while highlighting various types of decisions and their impacts. Additionally, it provides guidance on how to foster a closed loop between operations and analytics for continuous improvement.

























![Specify Logic with Decision Tables Most common rule format A set of rules in a tabular layout Look up tables, comparing attribute values Various formats
Applicant Risk
U
Applicant Age
Medical History
Applicant Risk Rating
1
> 60
good
Medium
2
bad
High
3
[25..60]
-
Medium
4
< 25
good
Low
5
bad
Medium
Special Discount
Type of Order
Web
-
Customer Location
US
-
Type of Customer
Wholesaler
Retailer
-
Special Discount %
10
5
0
F
1
2
3
Credit Limit Assignment
Credit Limit
Income
< $40,000
>= $40,000
Card Type
Standard
$1,000
$2,000
Gold
$1,500
$2,500
©2014 Decision Management Solutions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gettingstartedwithdecisiondiscovery-140909174925-phpapp02/85/Getting-started-with-decision-discovery-27-320.jpg)










