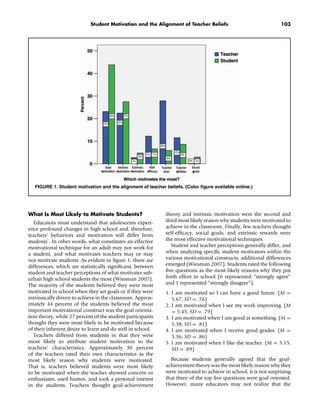
This document discusses differences between student and teacher perceptions of effective student motivation techniques. It finds that students are more likely to attribute their own motivation to intrinsic desires to learn or goals they adopt, while teachers believe students are more motivated by teachers' actions. The document examines factors that may contribute to these differing perceptions, such as adolescents experiencing changes in self-esteem and social influences during high school that impact their motivation differently than adults. It concludes teachers should understand these developmental differences to effectively motivate students.