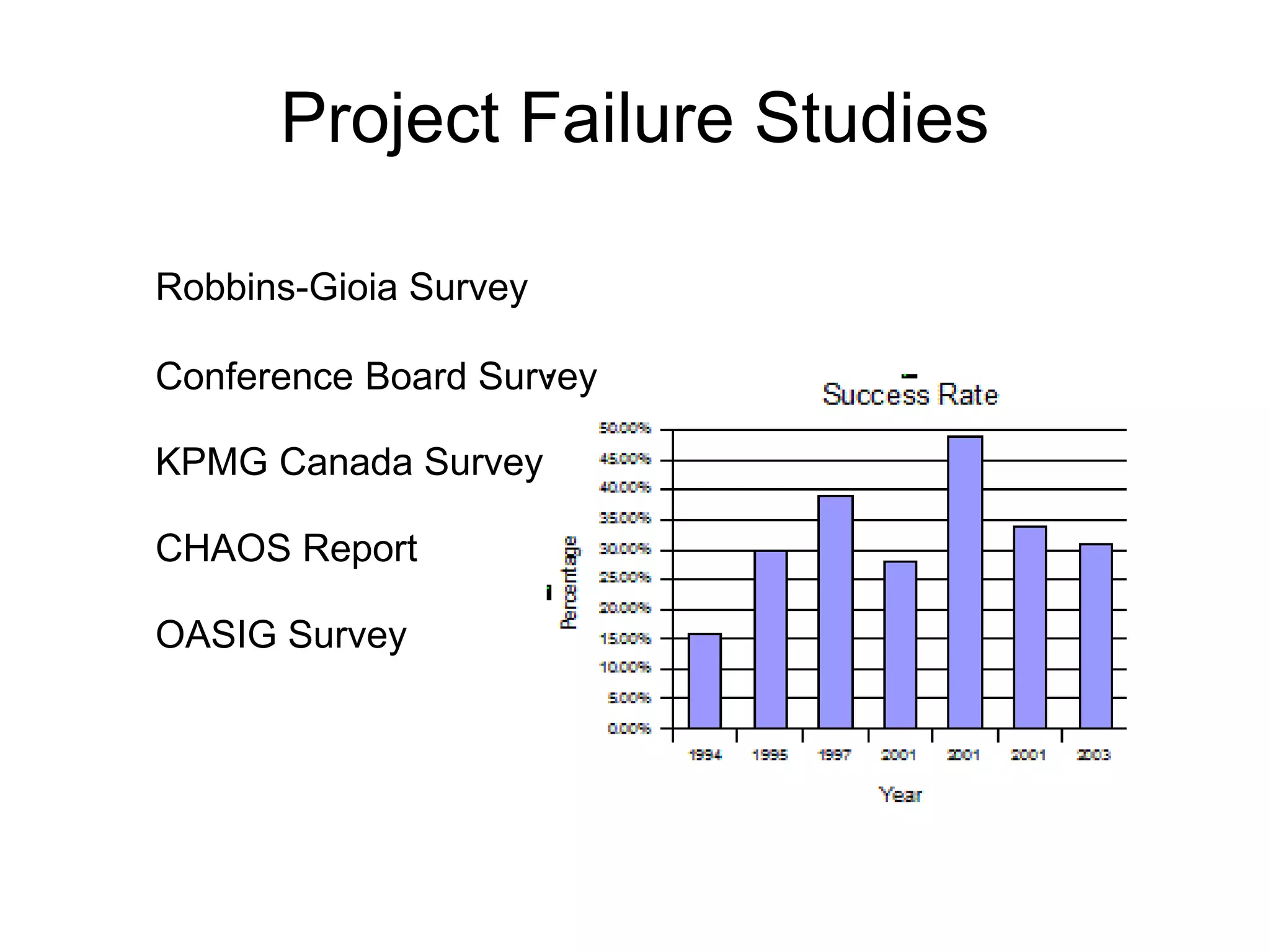
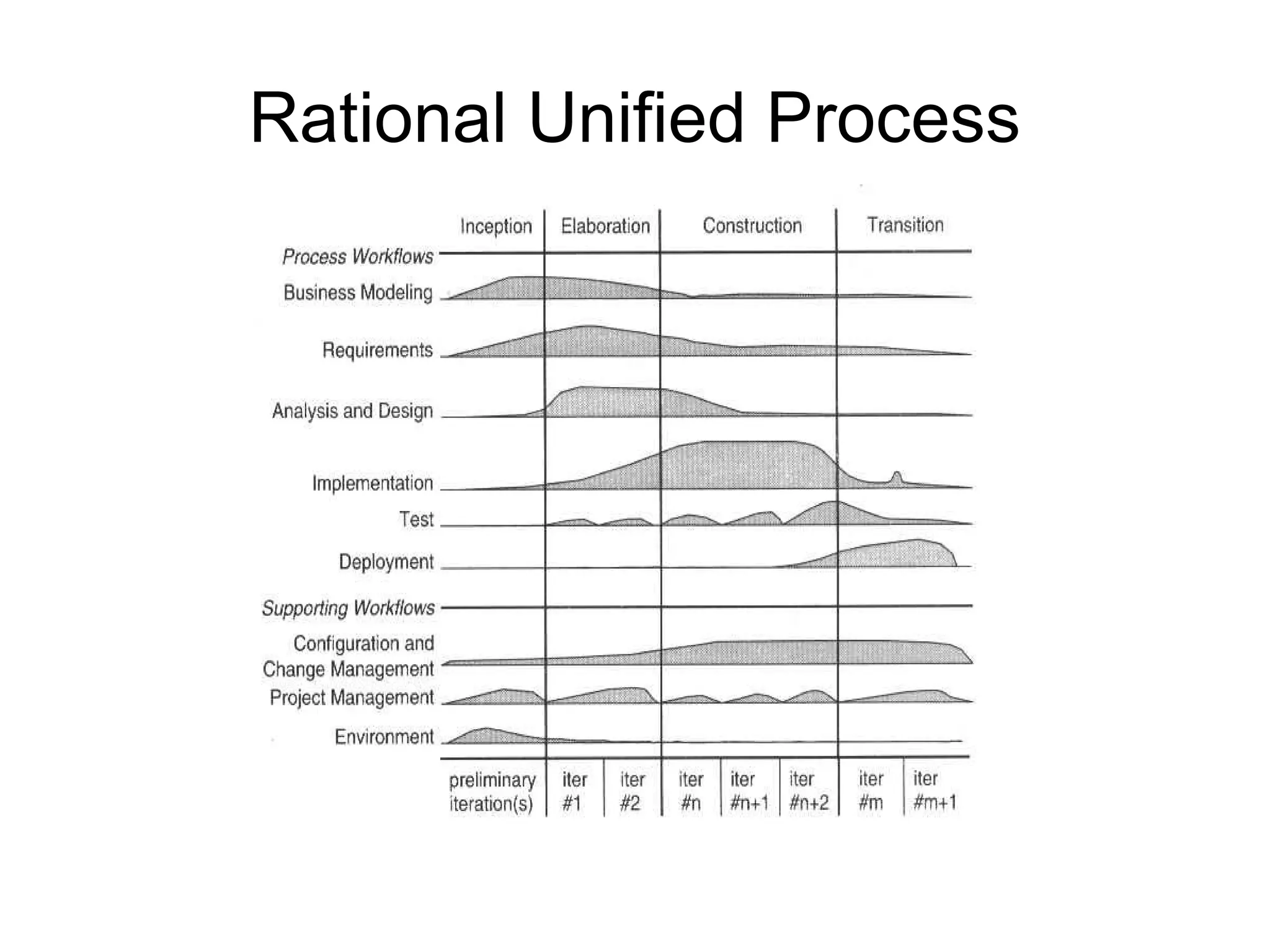
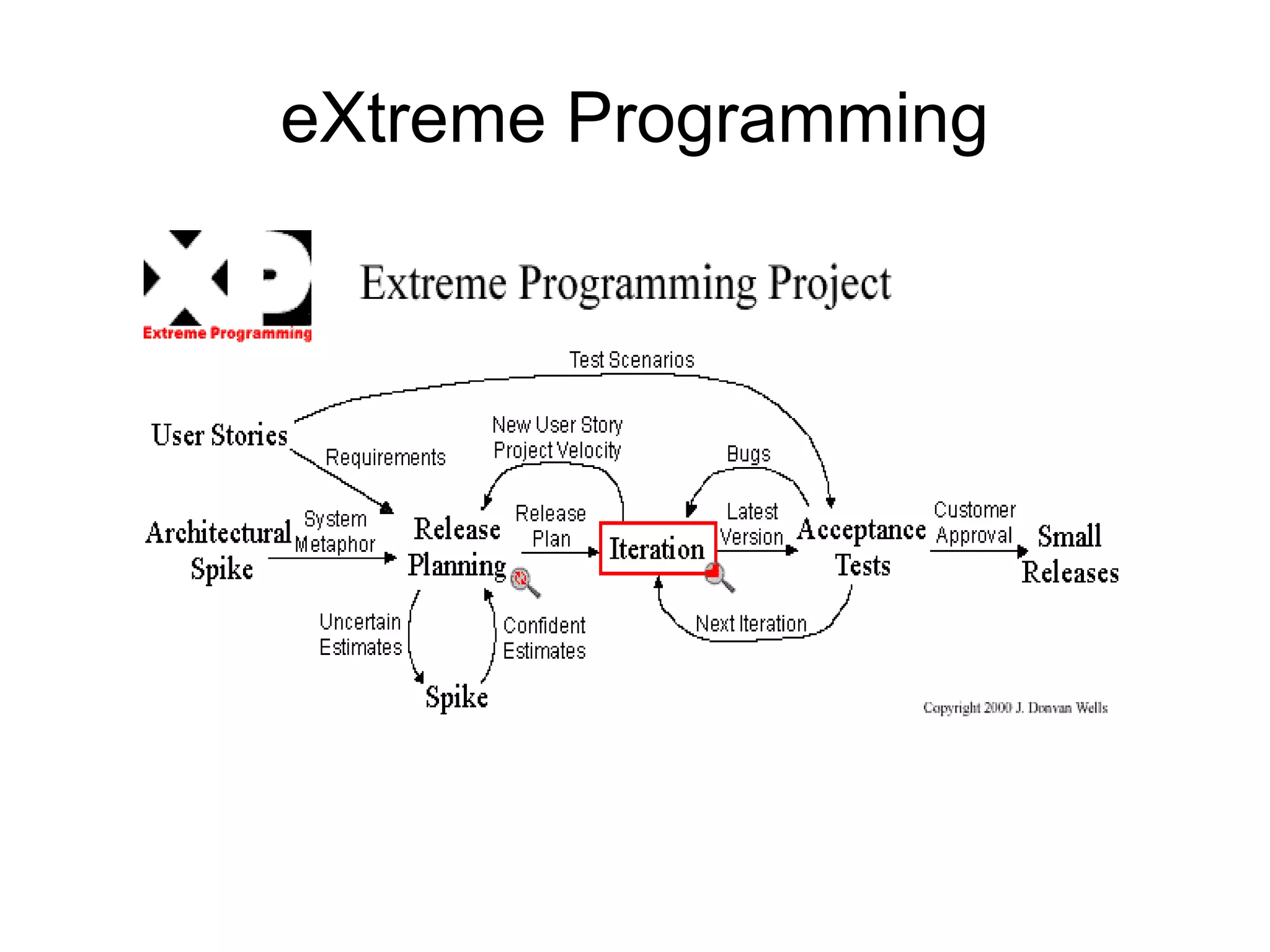
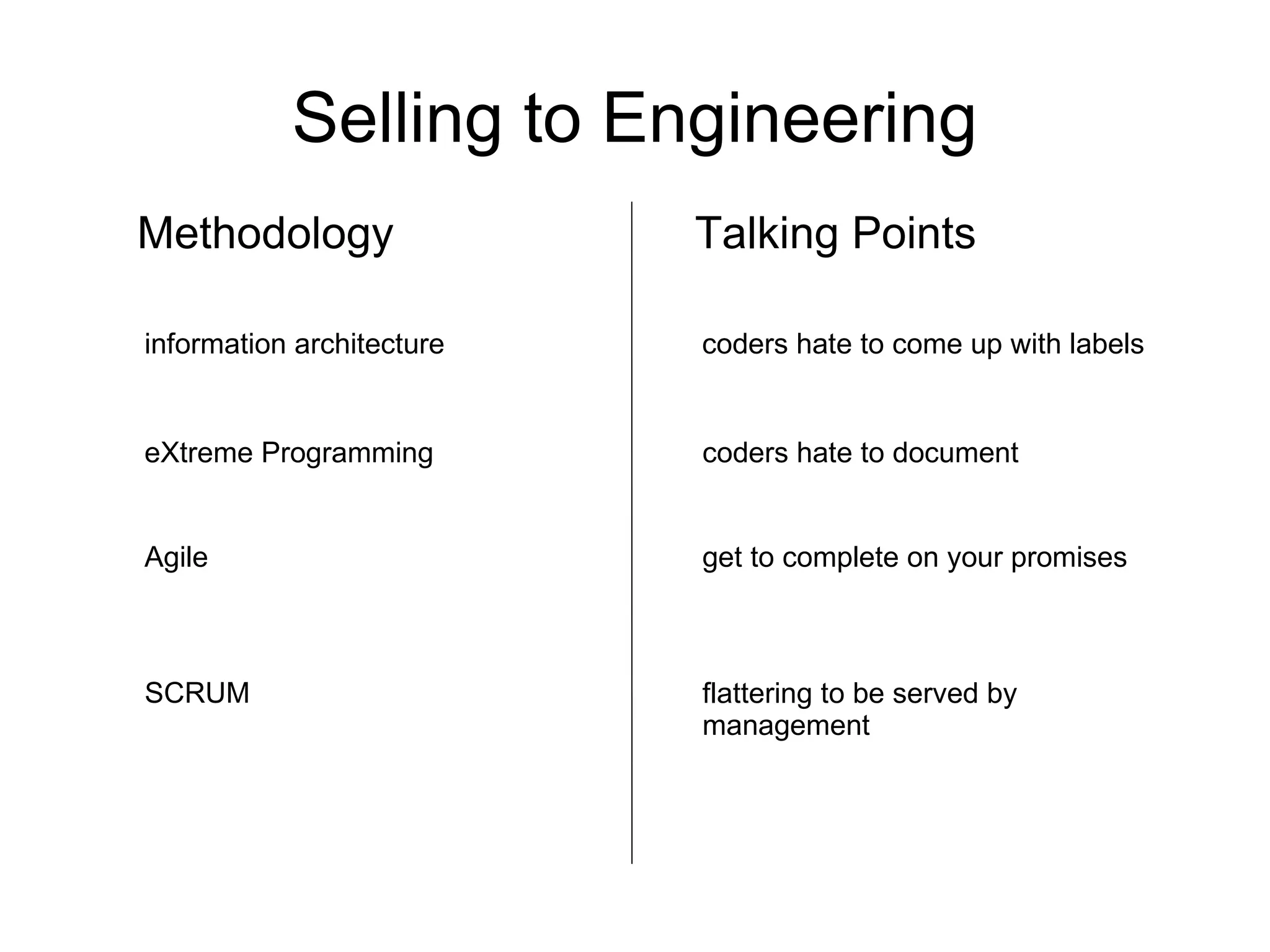
The document discusses the strategic application of software development processes in business projects, highlighting reasons for project failure such as inappropriate methodologies, lack of customer involvement, and technical debt. It emphasizes the need for proper management practices and understanding of software engineering principles to improve project outcomes, alongside the importance of customer engagement and realistic expectations. Additionally, it advocates for adopting methodologies that suit particular team dynamics and project needs, rather than applying every trend indiscriminately.







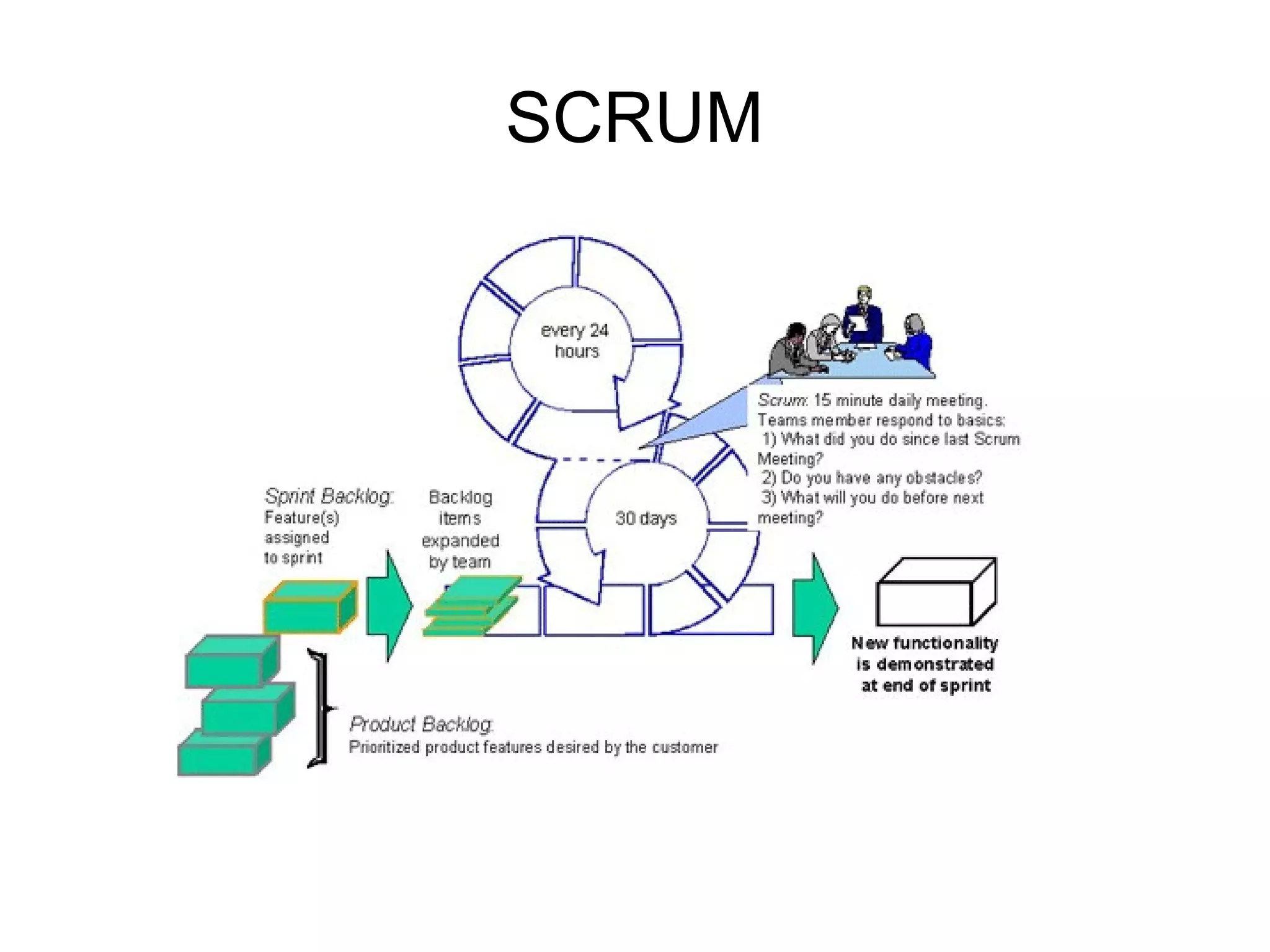




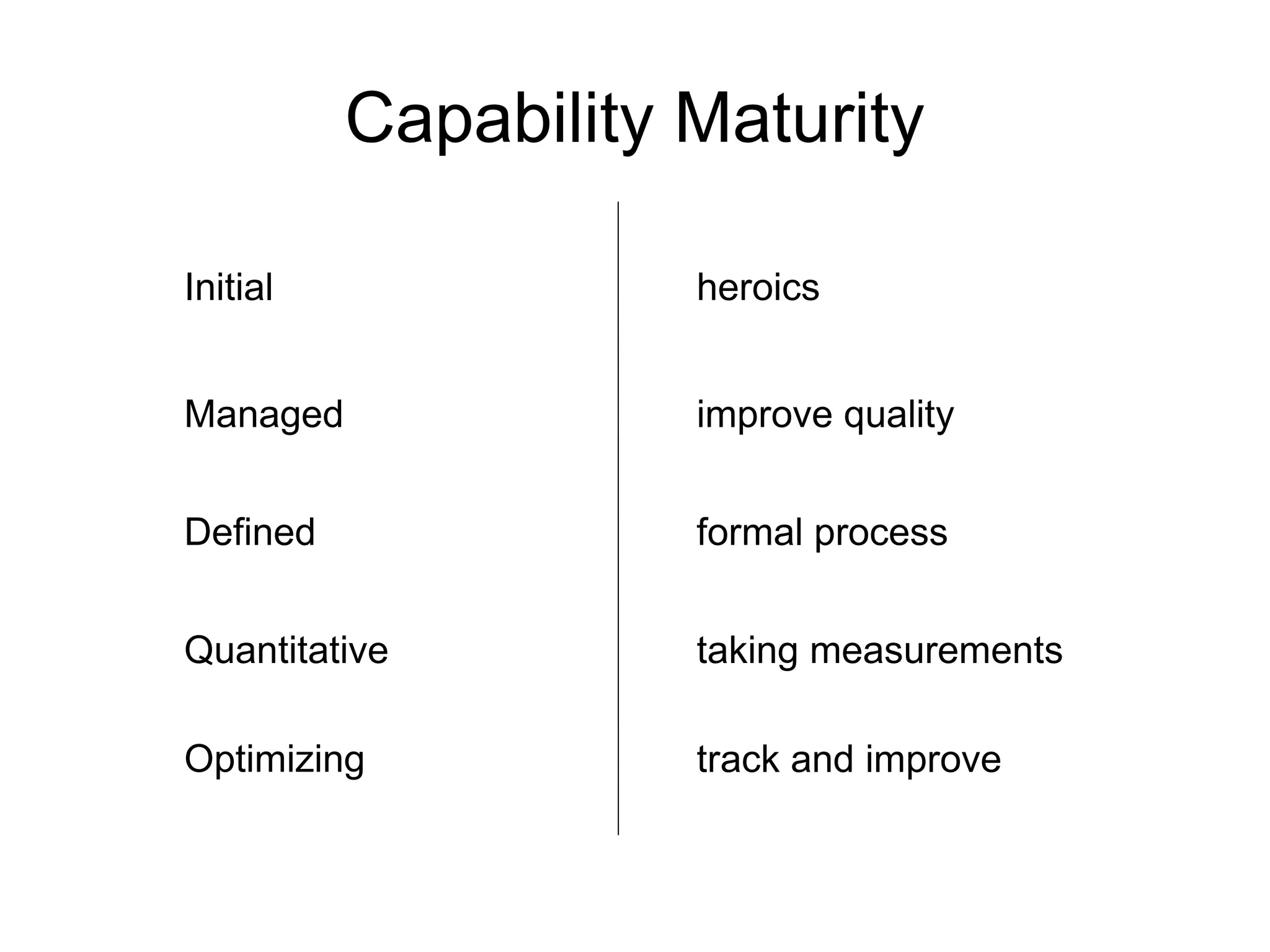


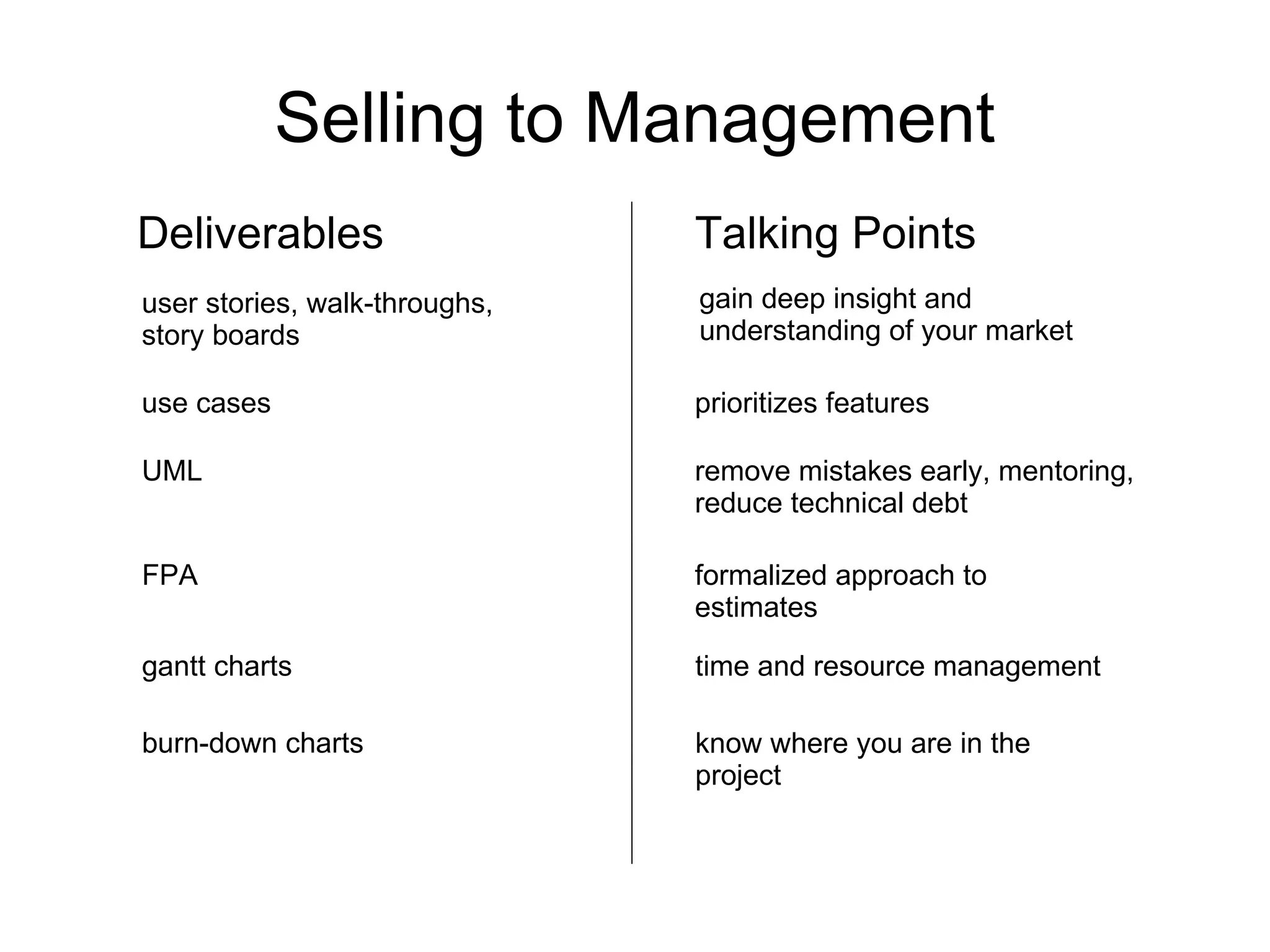

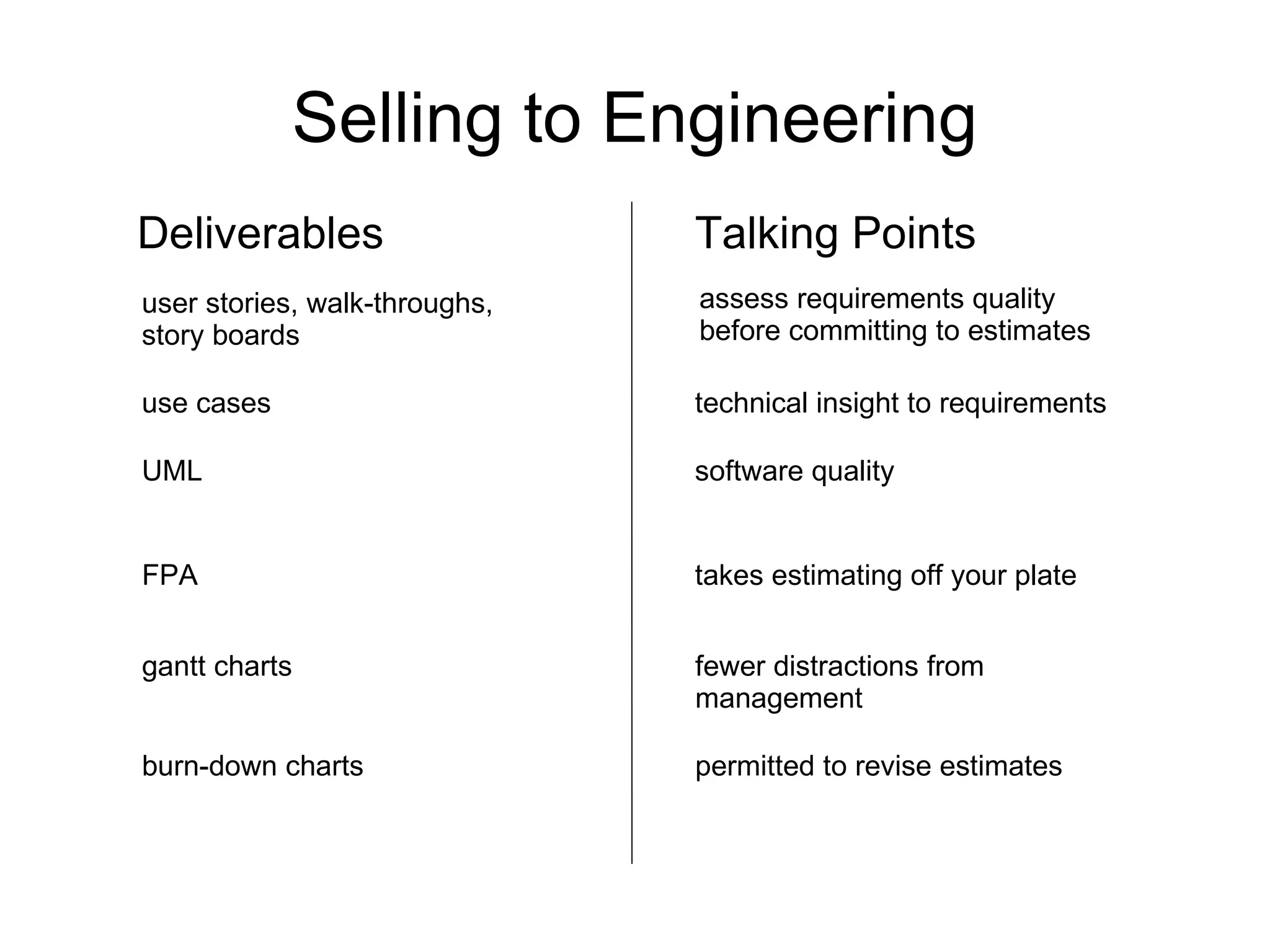

![Thank You http://code-roller.com http://www.dynamicalsoftware.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applyingsdlc4business-090626125704-phpapp01/75/Strategic-Application-of-Software-Development-Process-for-Business-Oriented-Projects-28-2048.jpg)