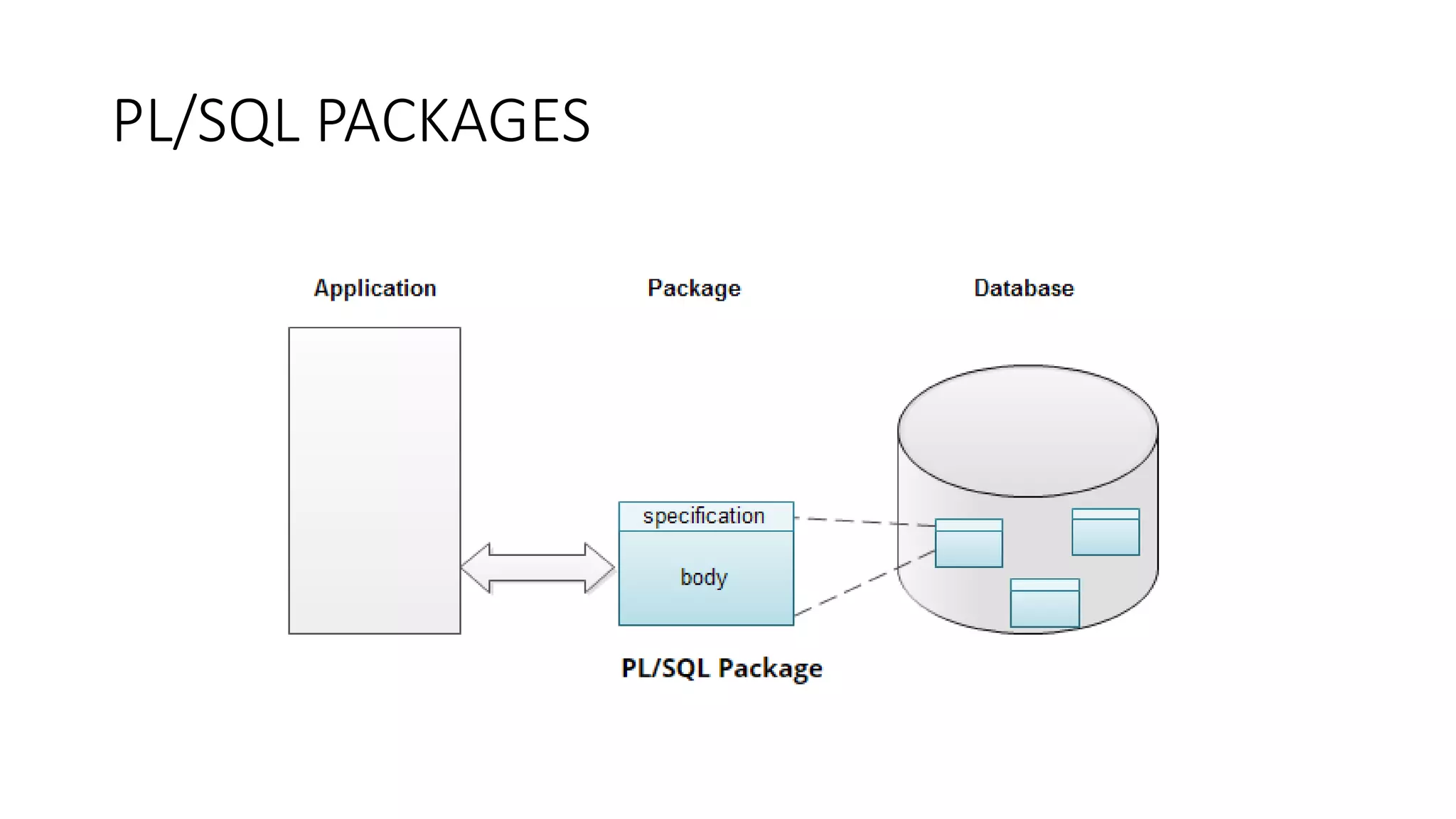
Packages in PL/SQL group logically related types, variables, and subprograms. A package has a specification and body. The specification declares public objects available outside the package. The body defines private objects and code for methods in the specification. Public package elements can be called using package_name.element_name. Packages allow organizing program logic and controlling access.