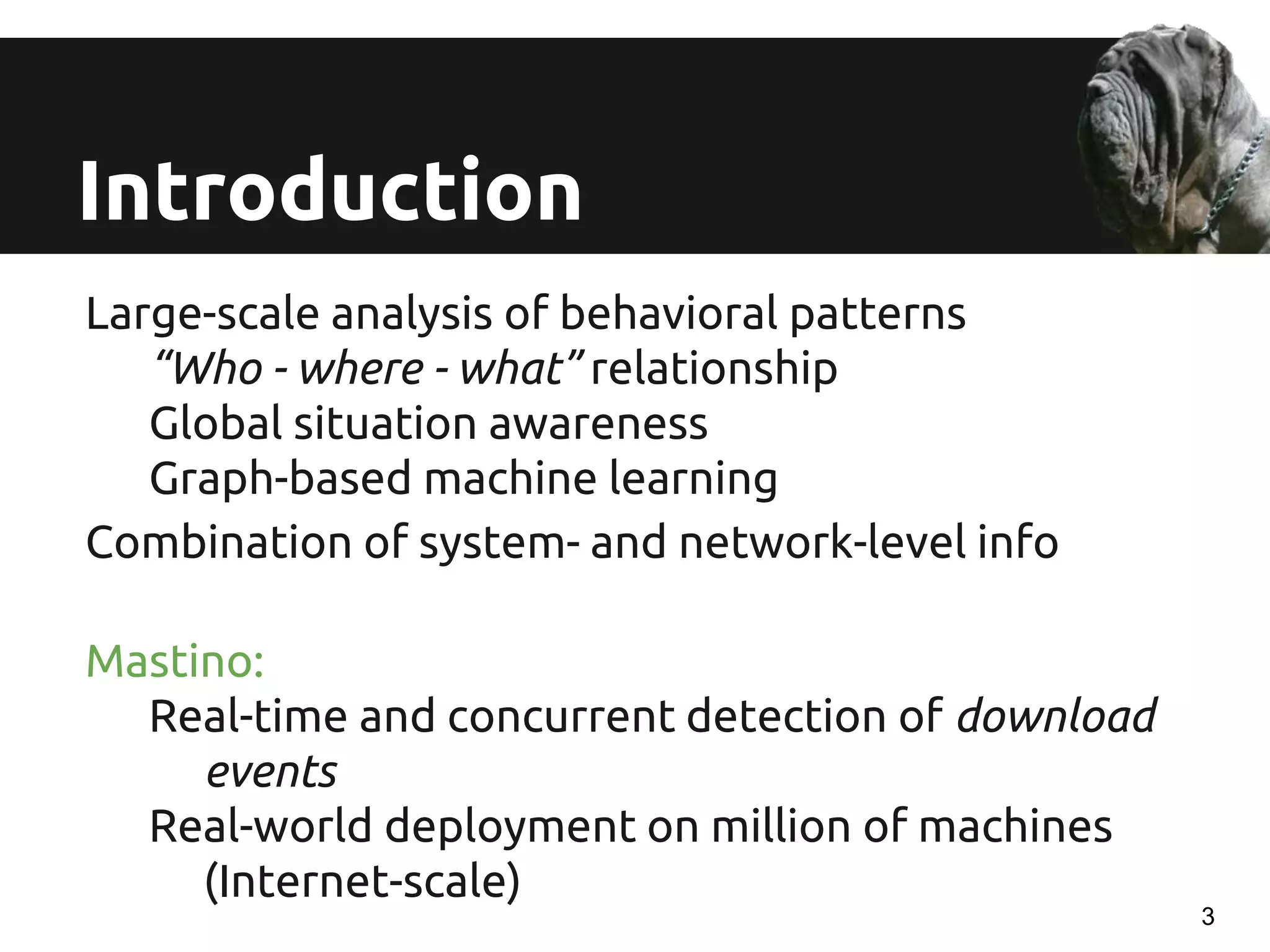
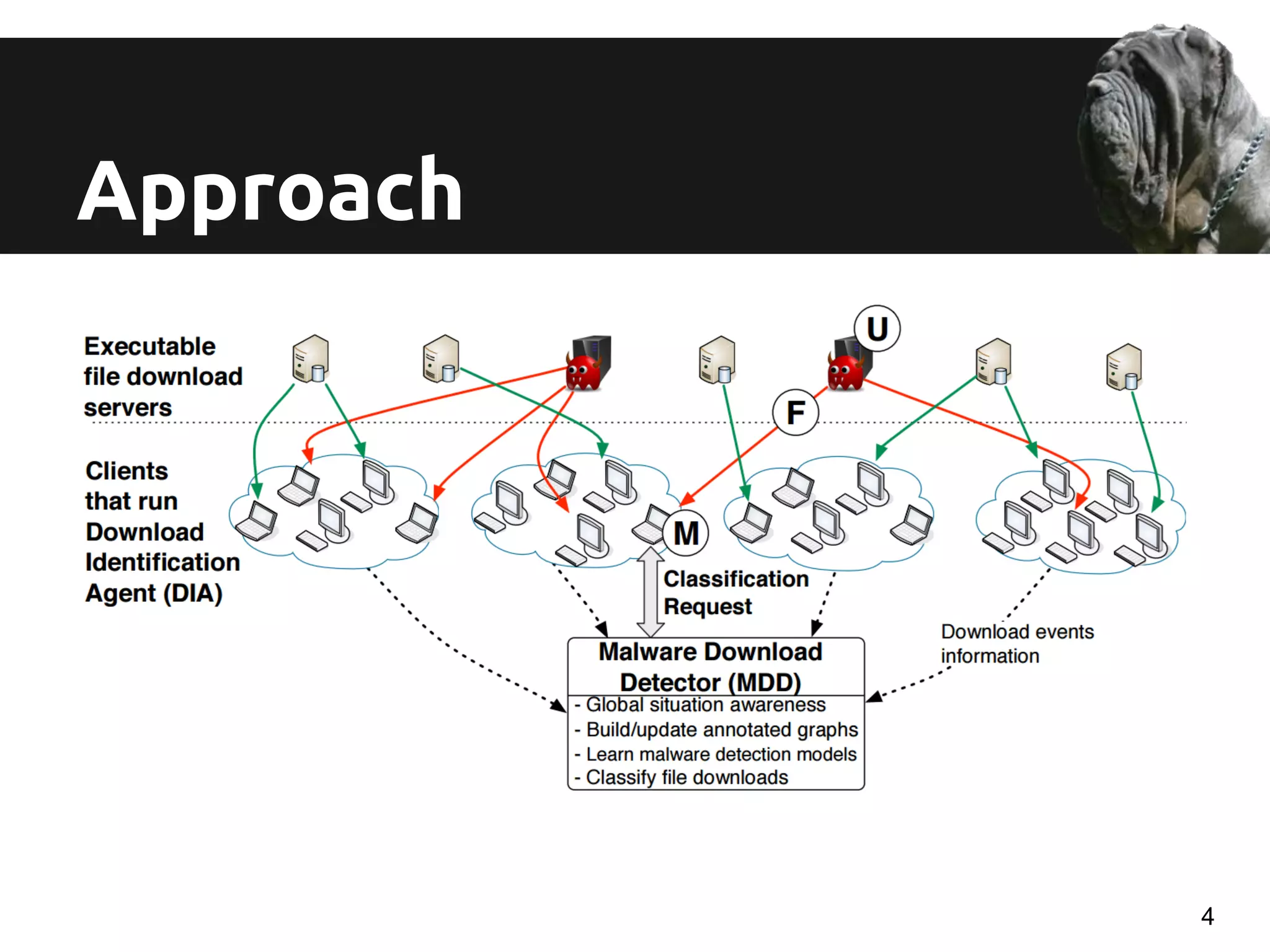
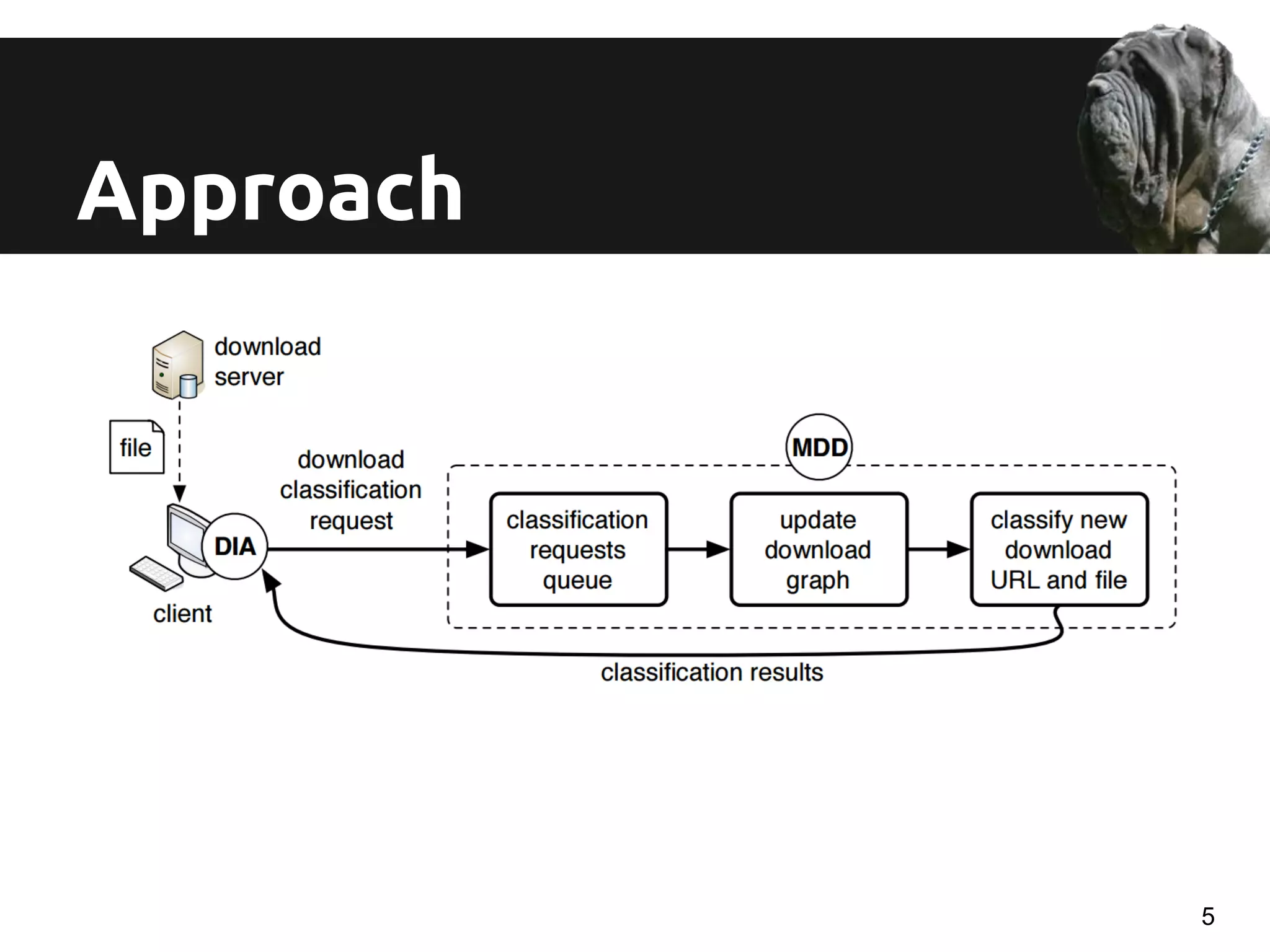
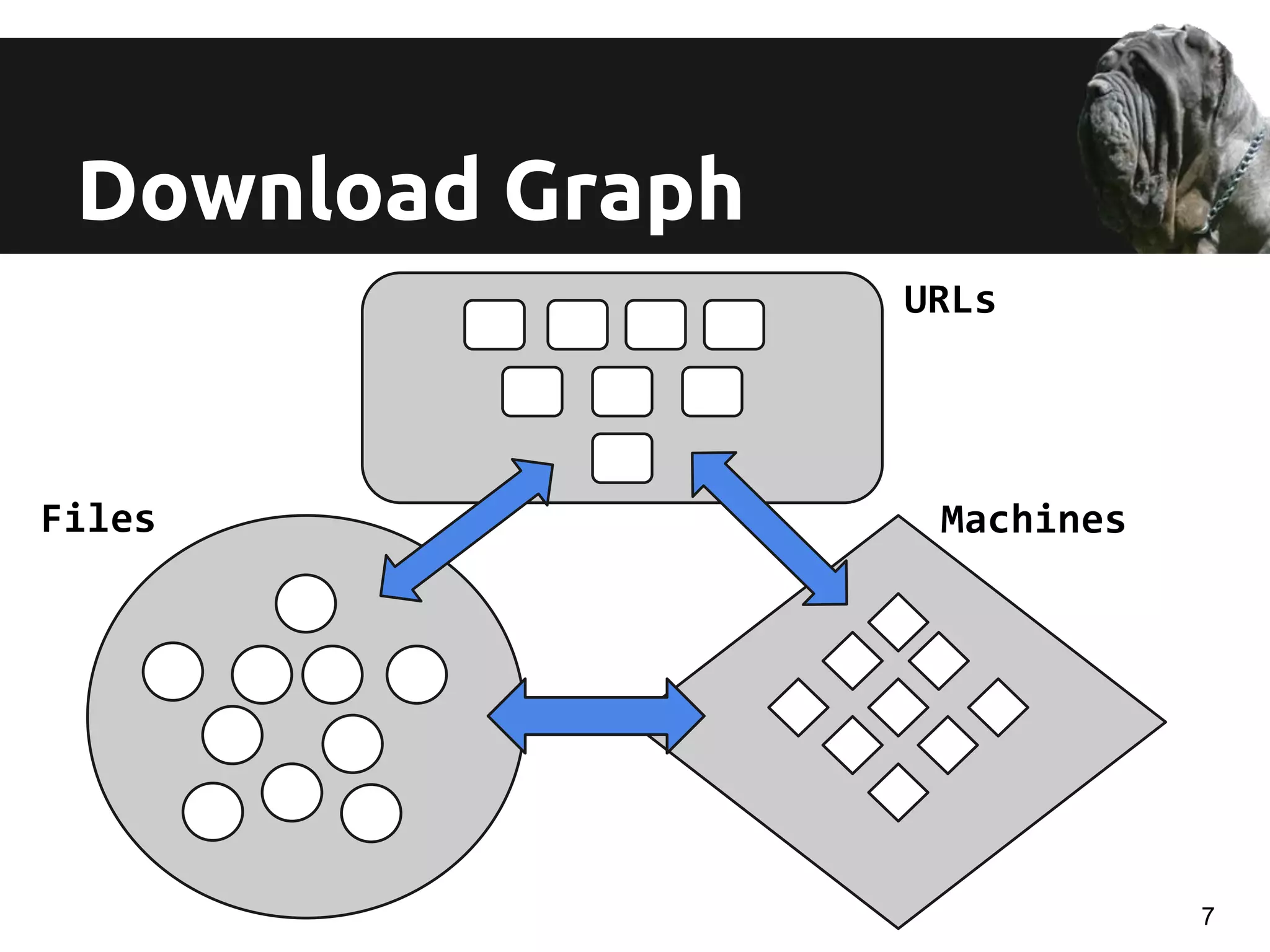
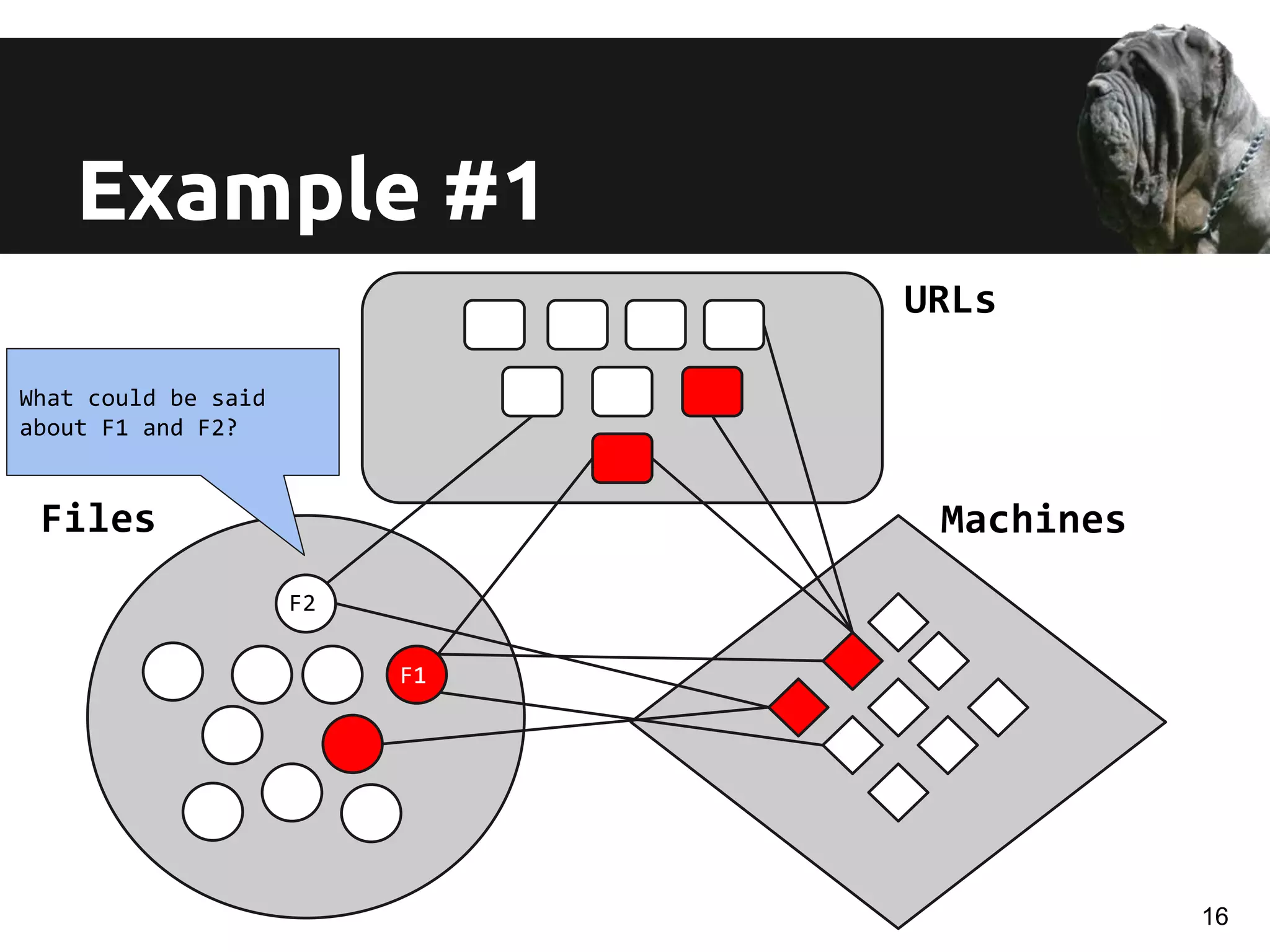
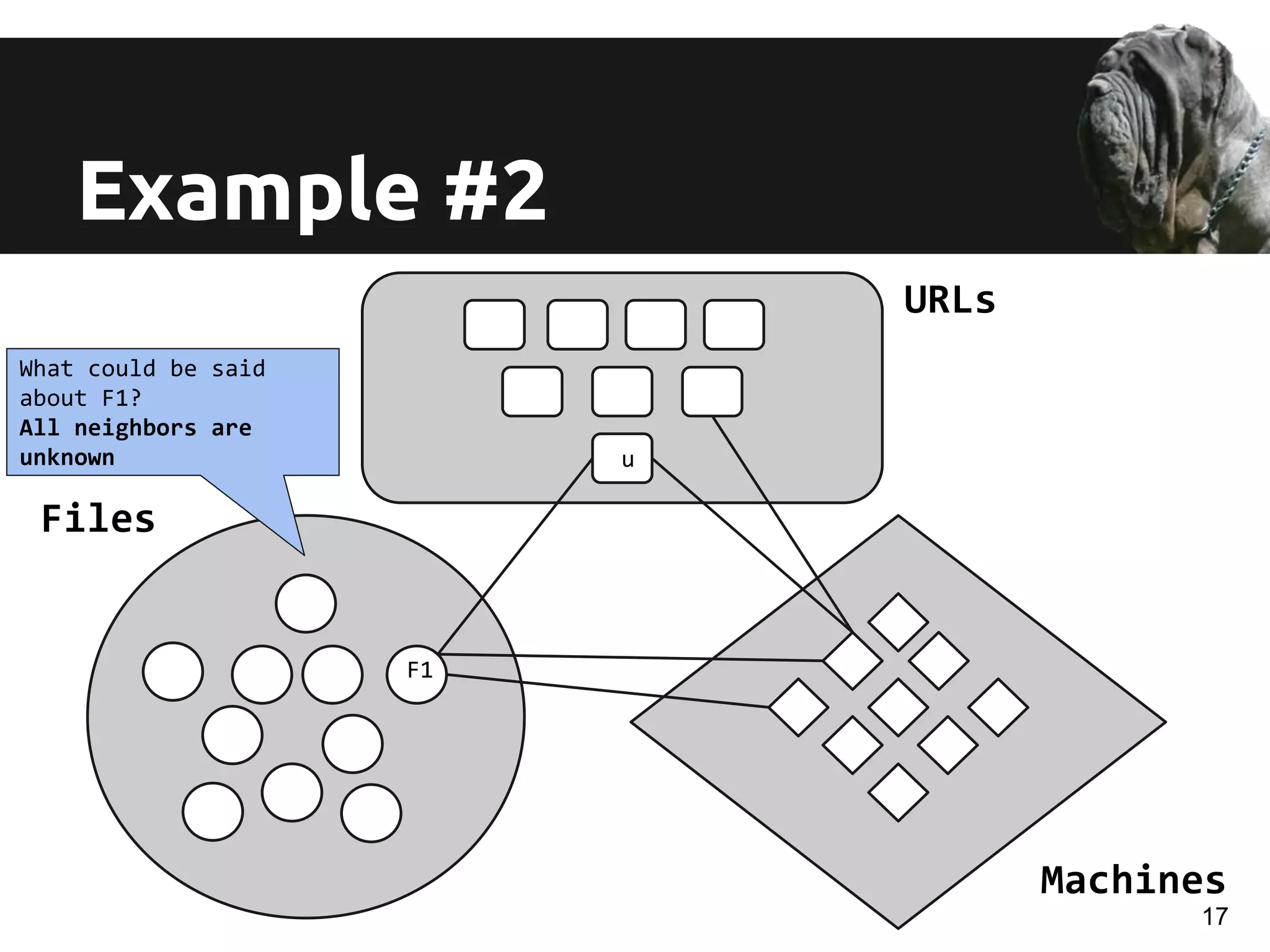
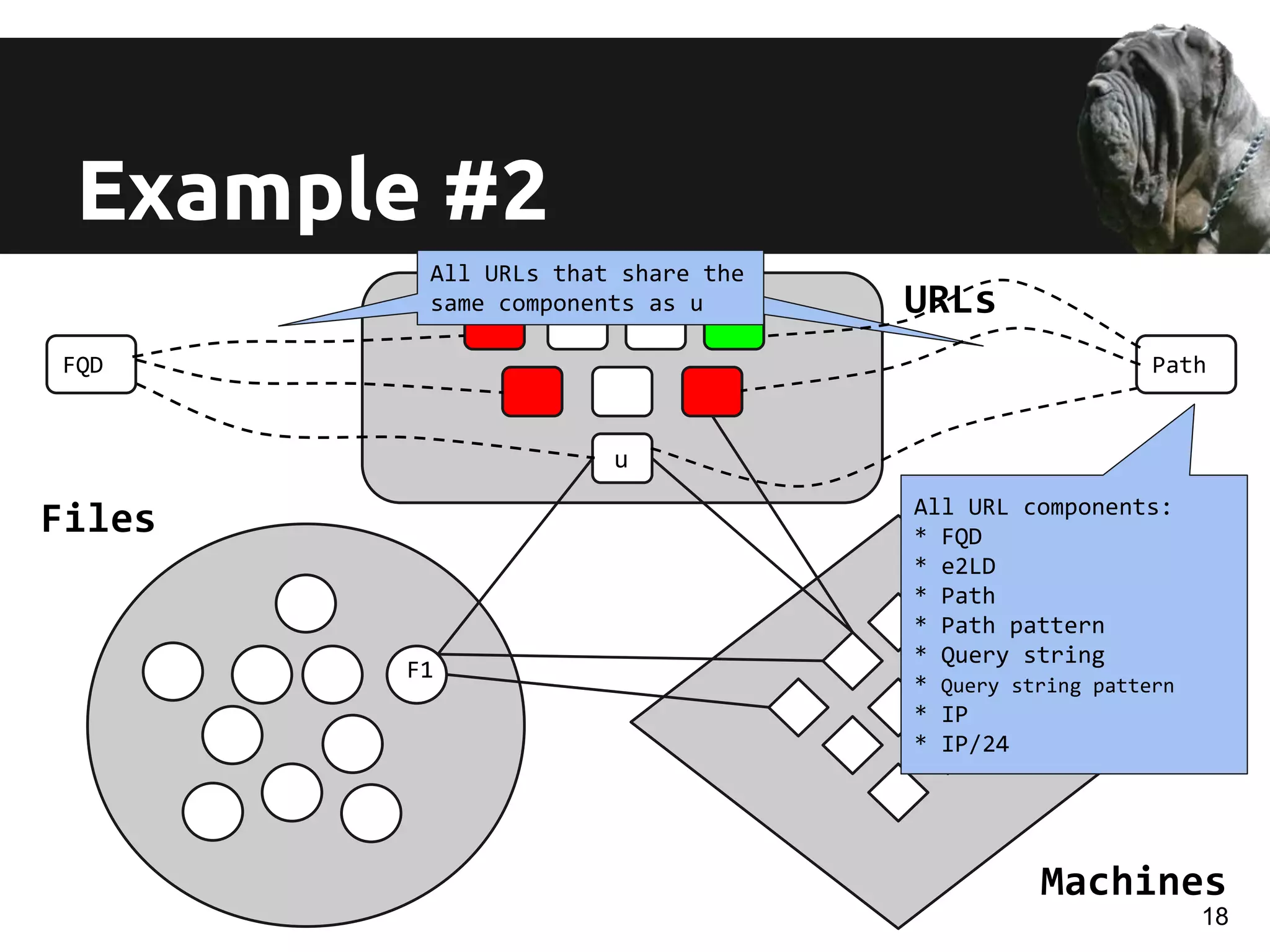
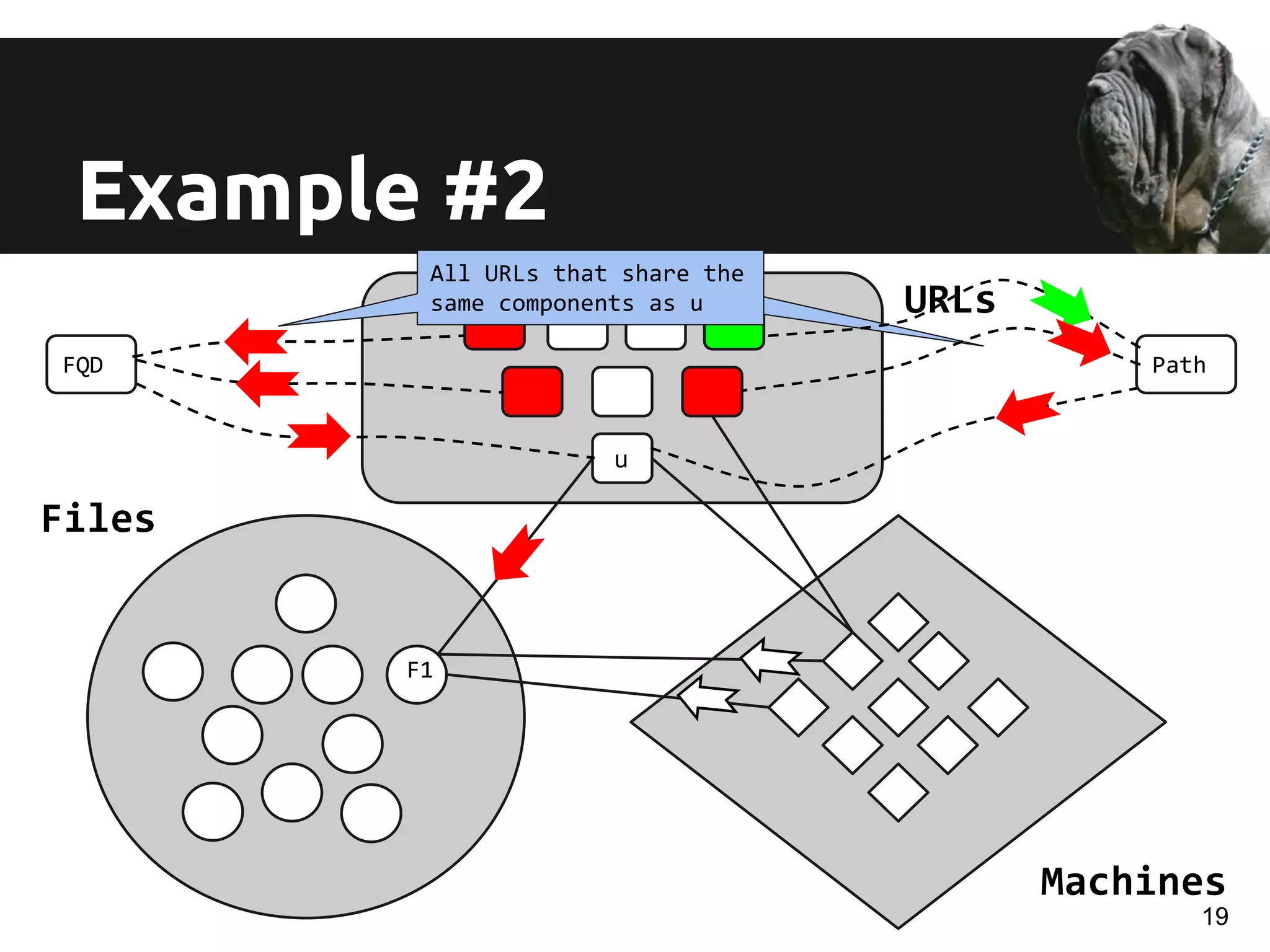
The document discusses a novel approach for real-time detection of malware downloads through large-scale URL to file to machine graph mining, emphasizing the limitations of traditional antivirus methods. It details a system called Mastino, which utilizes behavioral patterns and global situational awareness to identify malicious download events across millions of machines. The paper presents methodologies for classification and detection as well as case studies demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach in real-world scenarios.


![Static+dynamic detection [Many]
Graph mining detection: Polonium [KDD10]
Offline approach VS real-time
Only files classification VS + URLs (download event)
Bipartite VS tripartite graph
Proprietary reputation function VS open
AMICO [Esorics13]
HTTP-centric VS protocol-independent
Only works in LANs VS “move across networks”
Google’s CAMP [NDSS13]
Browser-centric VS system-centric
(Quick) Related Work
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-6-2048.jpg)
![Features and classifier
f
url1 url2 url3
f behavior-based
features = {URL stats, machine stats}
url4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
URL’s R + R of [FQD, e2LD, path, path
pattern, query string, query pattern]
Machine’s R
Files Features
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-10-2048.jpg)
![Features and classifier
f
url1 url2 url3
f behavior-based
features = {URL stats, machine stats}
url4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
URL’s R + R of [FQD, e2LD, path, path
pattern, query string, query pattern]
Machine’s R
f intrinsic
features = {file size, prevalence,
packed, signed, ...}
+
Files Features
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-11-2048.jpg)
![Features and classifier
f
url1 url2 url3
f behavior-based
features = {URL stats, machine stats}
url4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
URL’s R + R of [FQD, e2LD, path, path
pattern, query string, query pattern]
Machine’s R
f intrinsic
features = {file size, prevalence,
packed, signed, ...}
Files Features
URLs Features
u + {all URLs sharing
a component with u}
file1 file2 file3
u behavior-based
features = {files stats, machine stats}
file4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
File’s R
Machine’s R
+
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-12-2048.jpg)
![Features and classifier
URLs Features
u + {all URLs sharing
a component with u}
file1 file2 file3
u behavior-based
features = {files stats, machine stats}
file4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
File’s R
Machine’s R
u intrinsic
features = {URL, FQD,
e2LD recency}
+
f
url1 url2 url3
f behavior-based
features = {URL stats, machine stats}
url4
machine1 machine3machine2
compute min, max,
med, avg, and std
compute min, max, med,
avg, and std
URL’s R + R of [FQD, e2LD, path, path
pattern, query string, query pattern]
Machine’s R
f intrinsic
features = {file size, prevalence,
packed, signed, ...}
Files Features
+
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-13-2048.jpg)
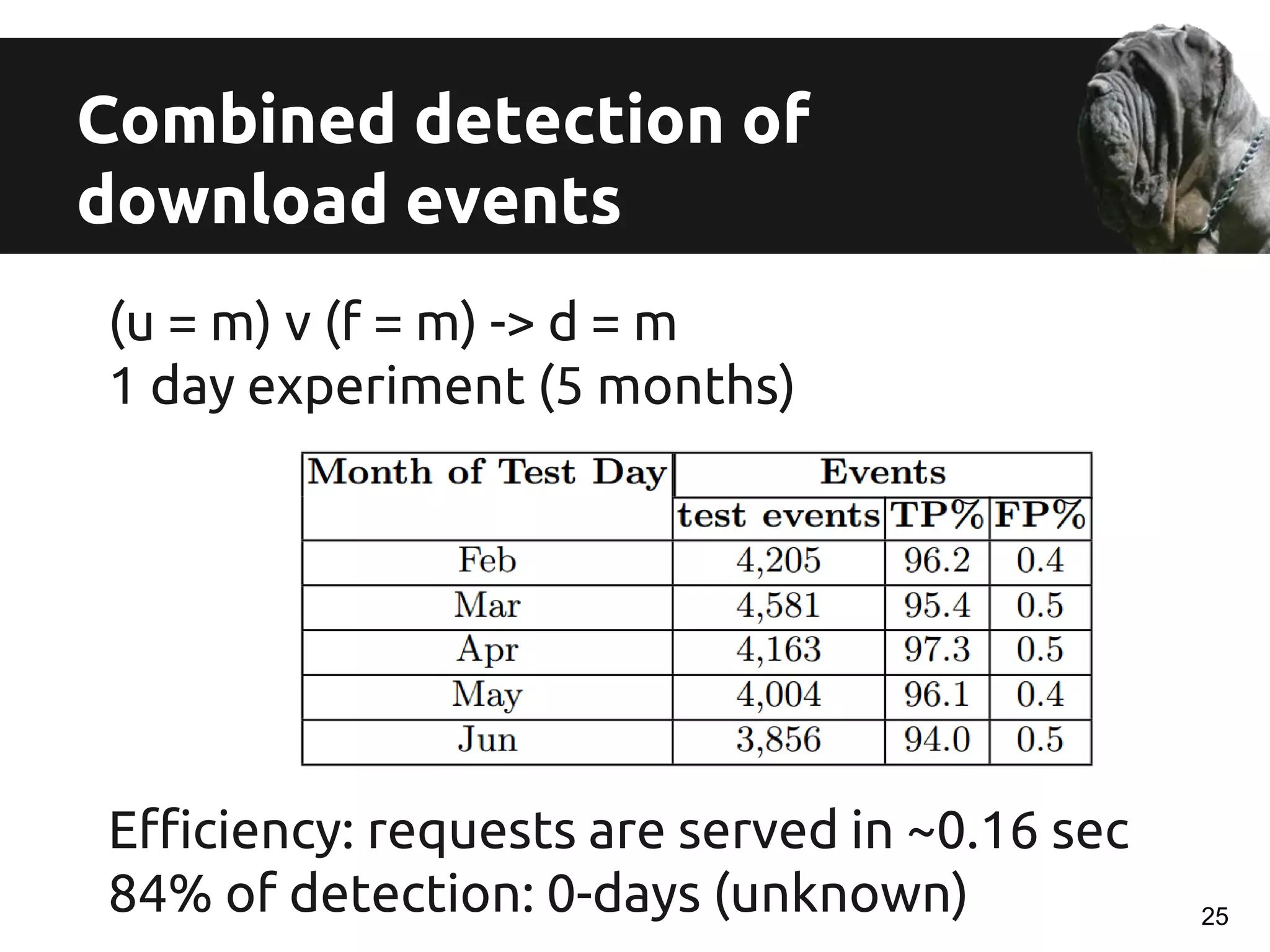
![Data Collection
7 months of data (Jan to Aug 2014)
d = (u; f; m)
Hundreds of thousands of machines, files, urls
Million of nodes
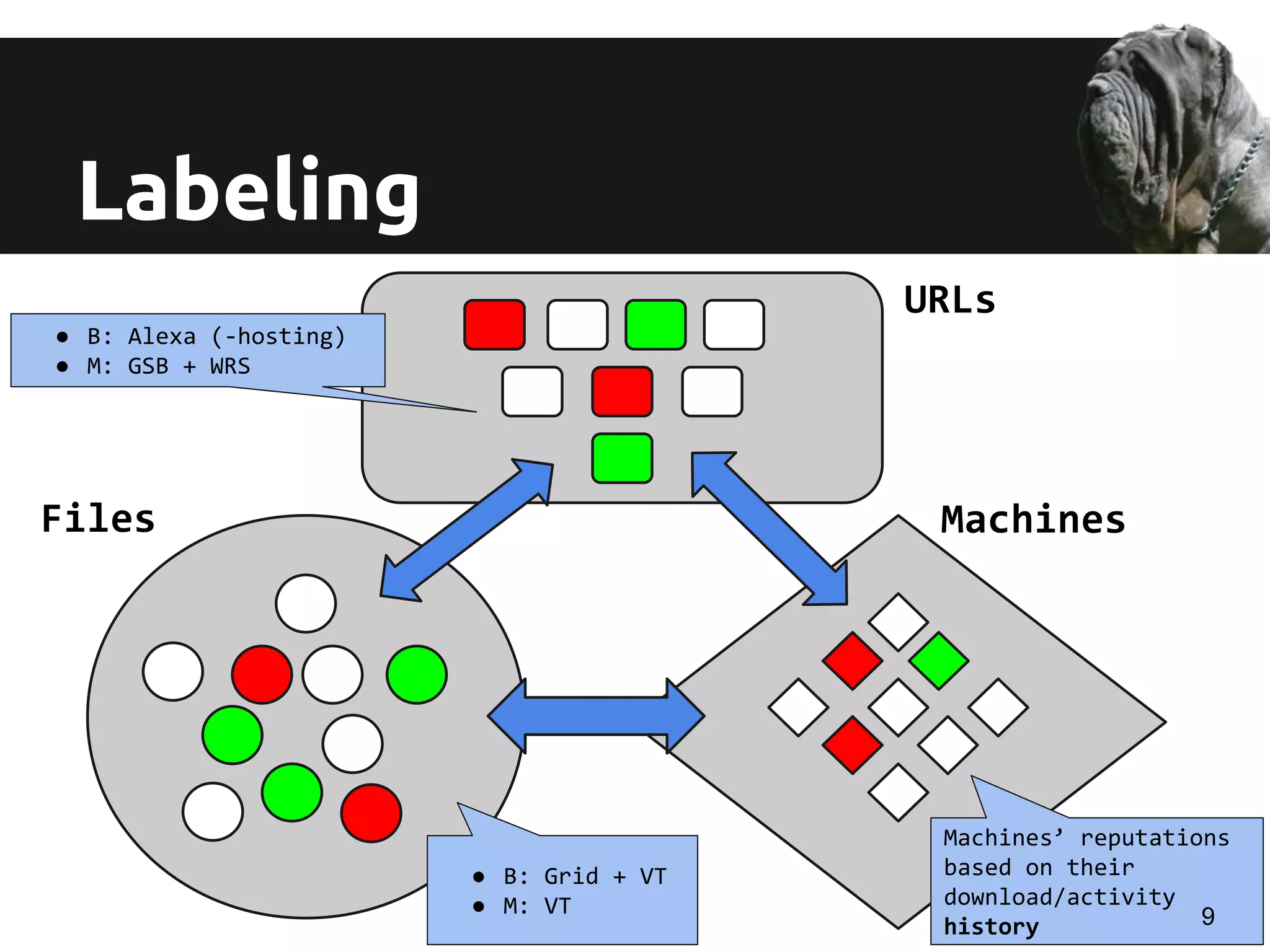
Labeling:
Files: VirusTotal, GRID [Trend]
URLs: Alexa, Google Safe Browsing, WRS [Trend]
Annotations:
File census and GUID census [Trend]
Virus Total (signed..)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-23-2048.jpg)
![Wuachos.A Dropper
Filename file_saw.exe
URLs with _no_ reputation
Low prevalence
Invalid signature
Path pattern with R of 0.72 (malicious) [*]
1,445 URLs serving 182 polymorphic malware
[*] /f/1392240240/1255385580/2 , /f/1392240120/4165299987/2 -> /H1/I10/I10/I1
Case Study #1
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-26-2048.jpg)
![Somoto Adware
Filename FreeZipSetup-[d].exe
Packed, short lifetime, prevalence = 0
1 related machine downloaded 1 known
sample during our time window T=10days
Detected a campaign of 695 samples
616 were unknown to VirusTotal
61 unknown +6 months
Case Study #2
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asiaccs16-160606144201/75/Detection-of-Malware-Downloads-via-Graph-Mining-AsiaCCS-16-27-2048.jpg)