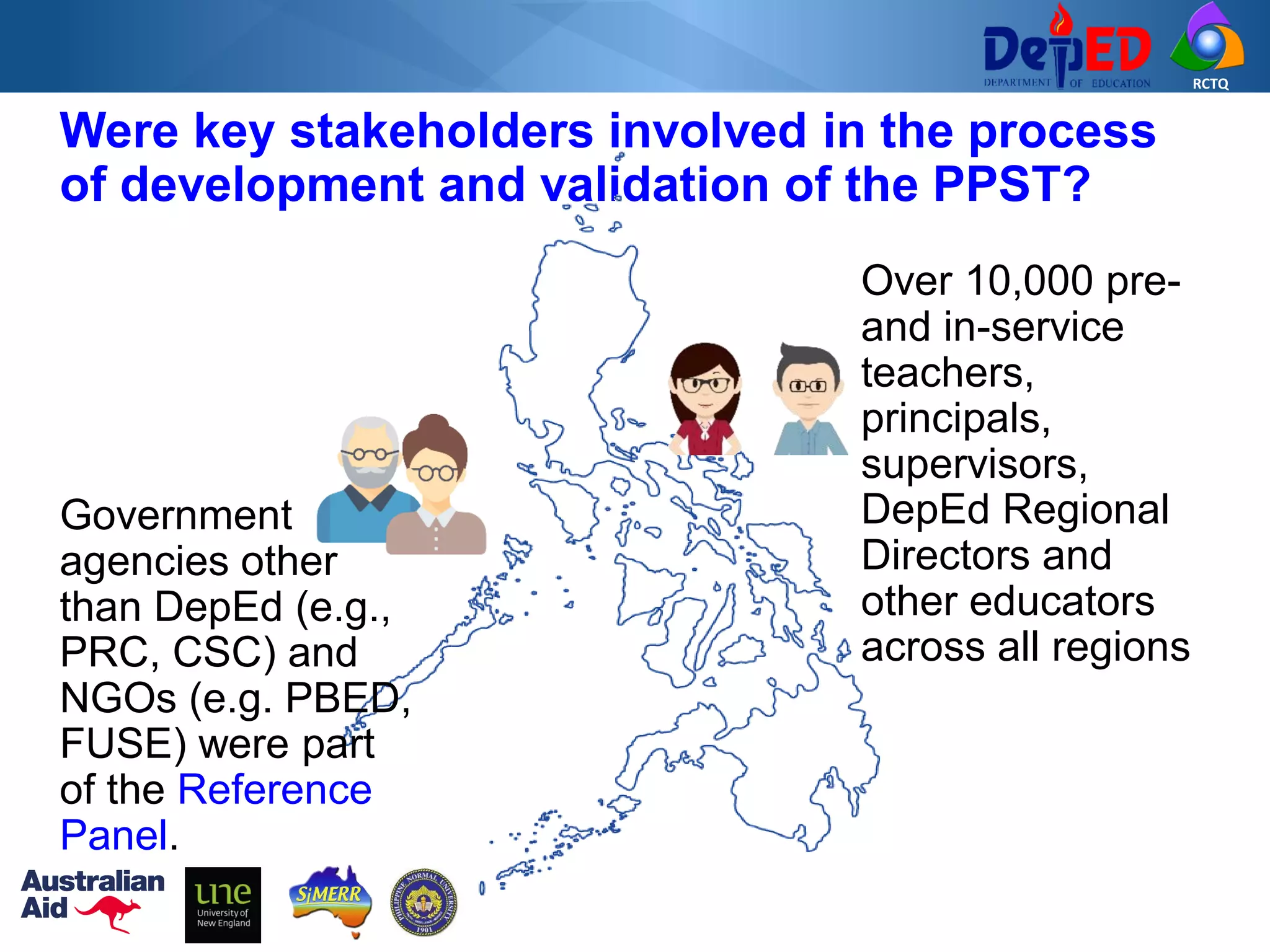
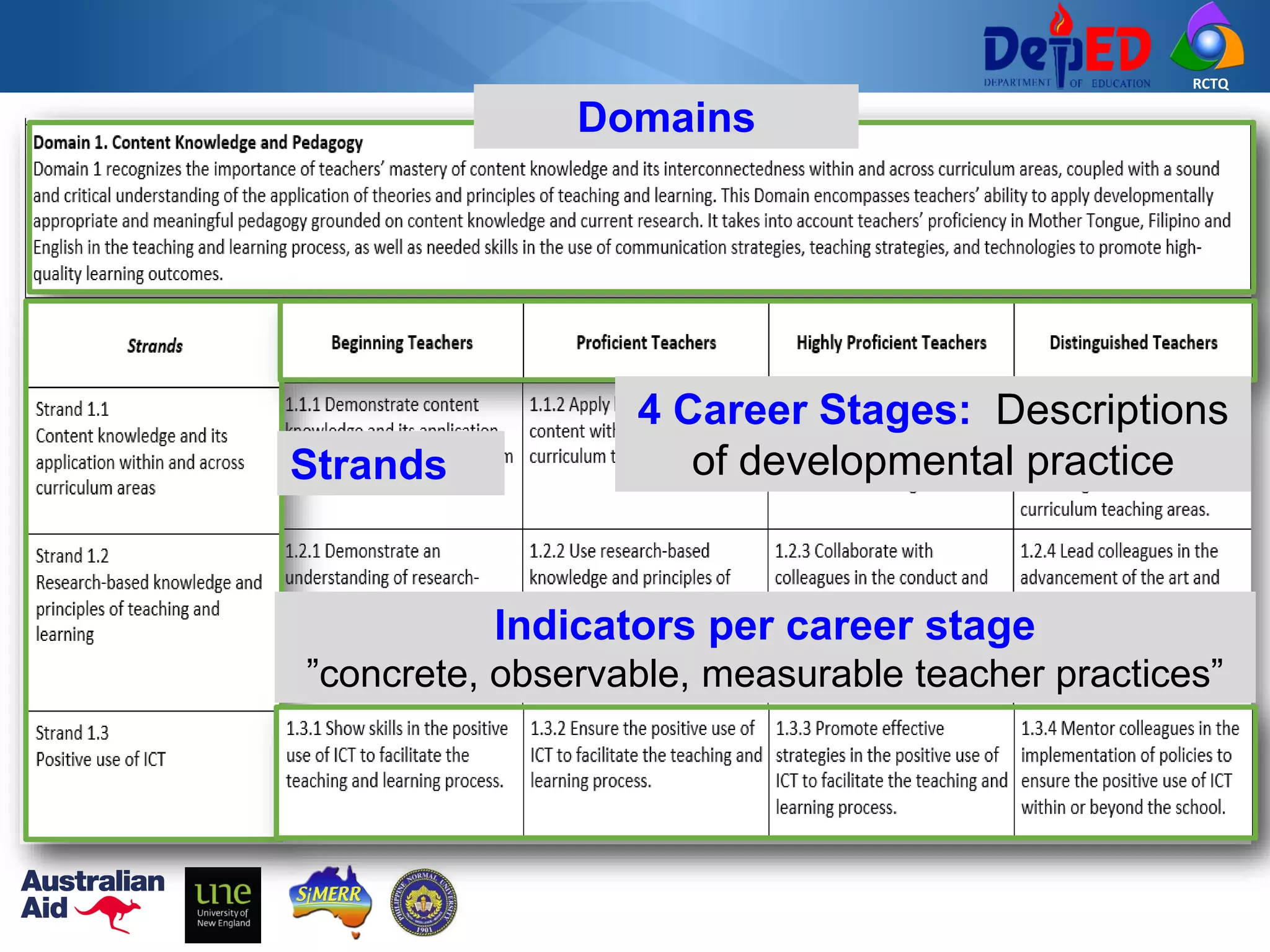
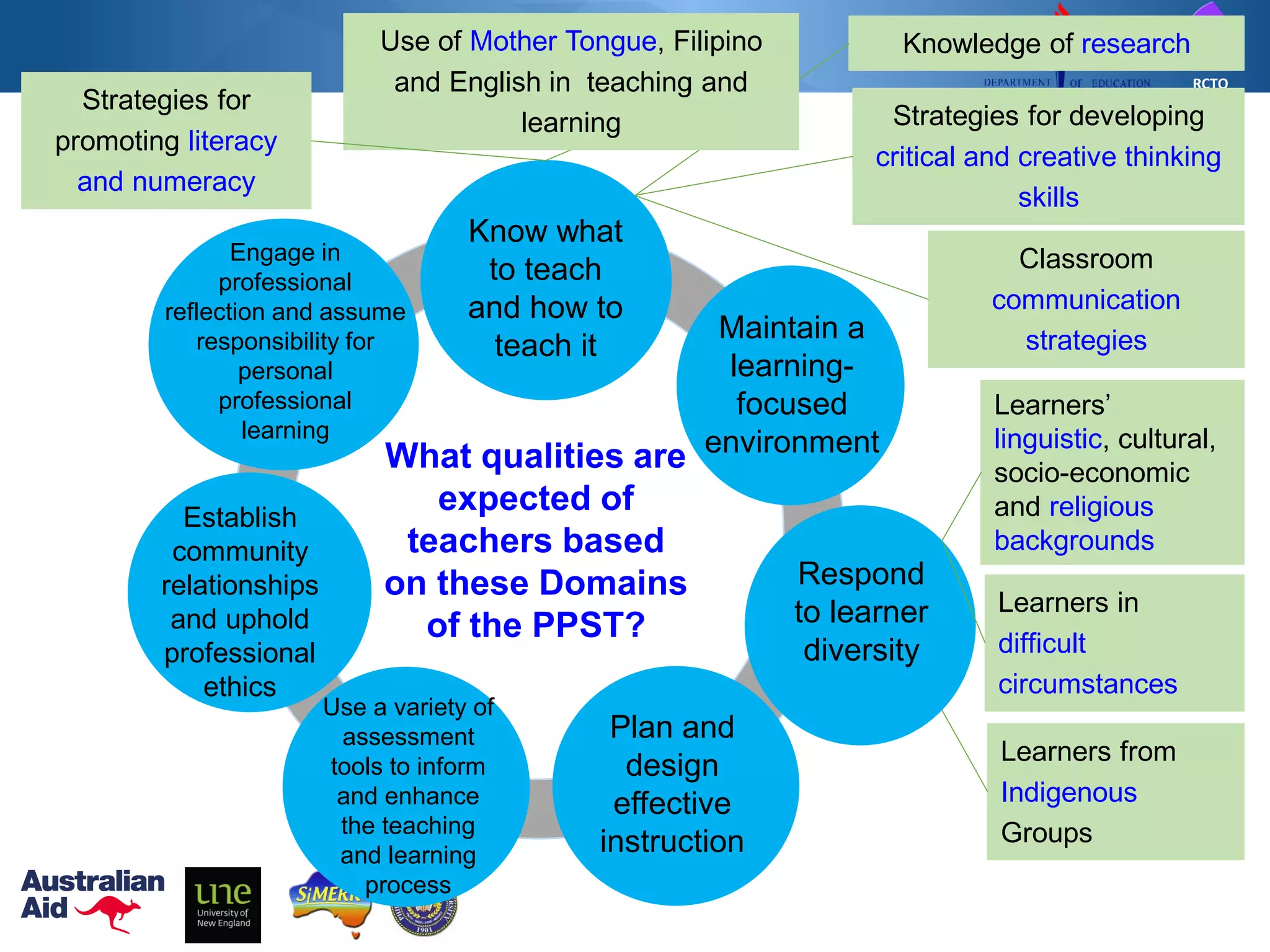
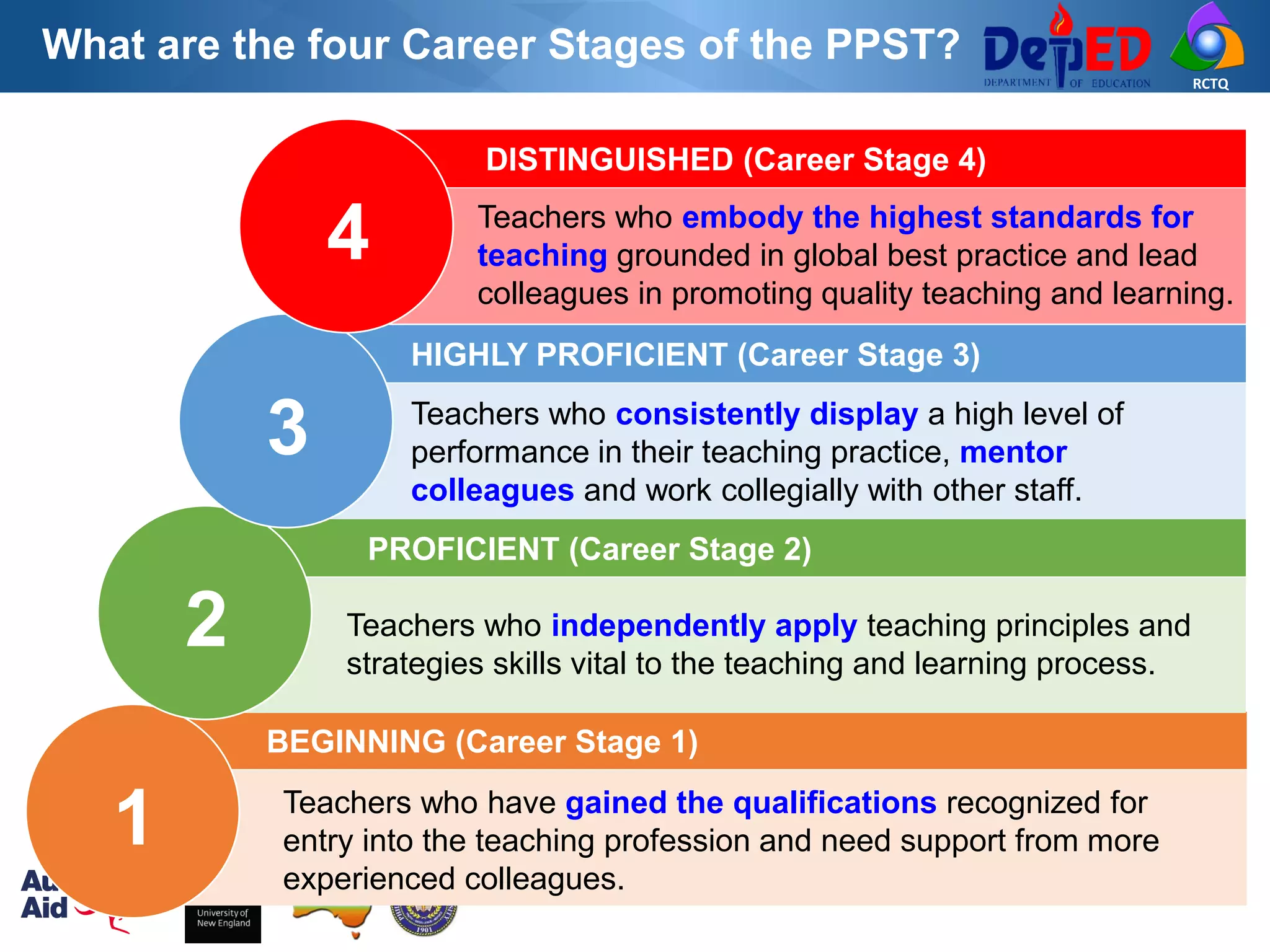
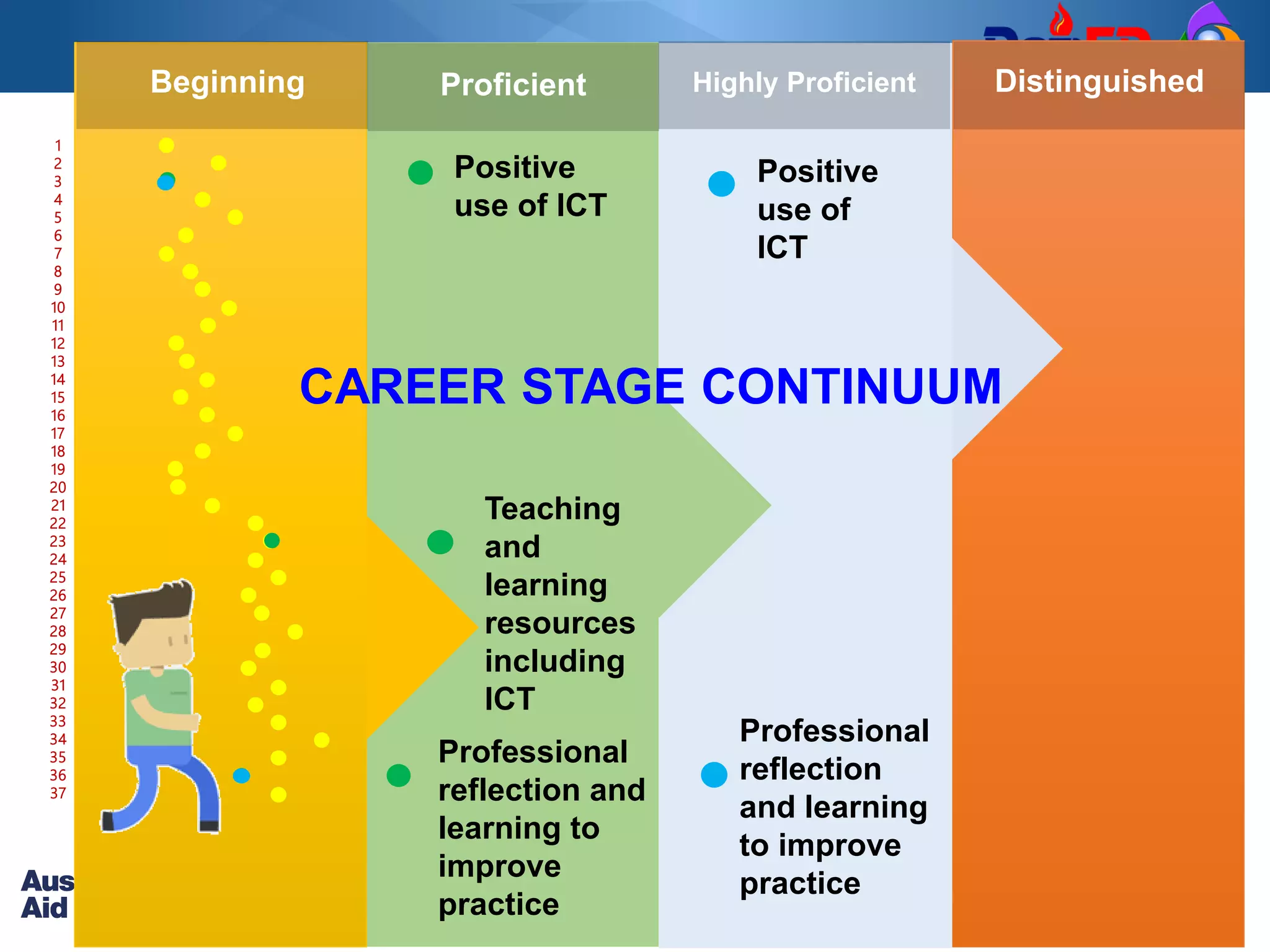
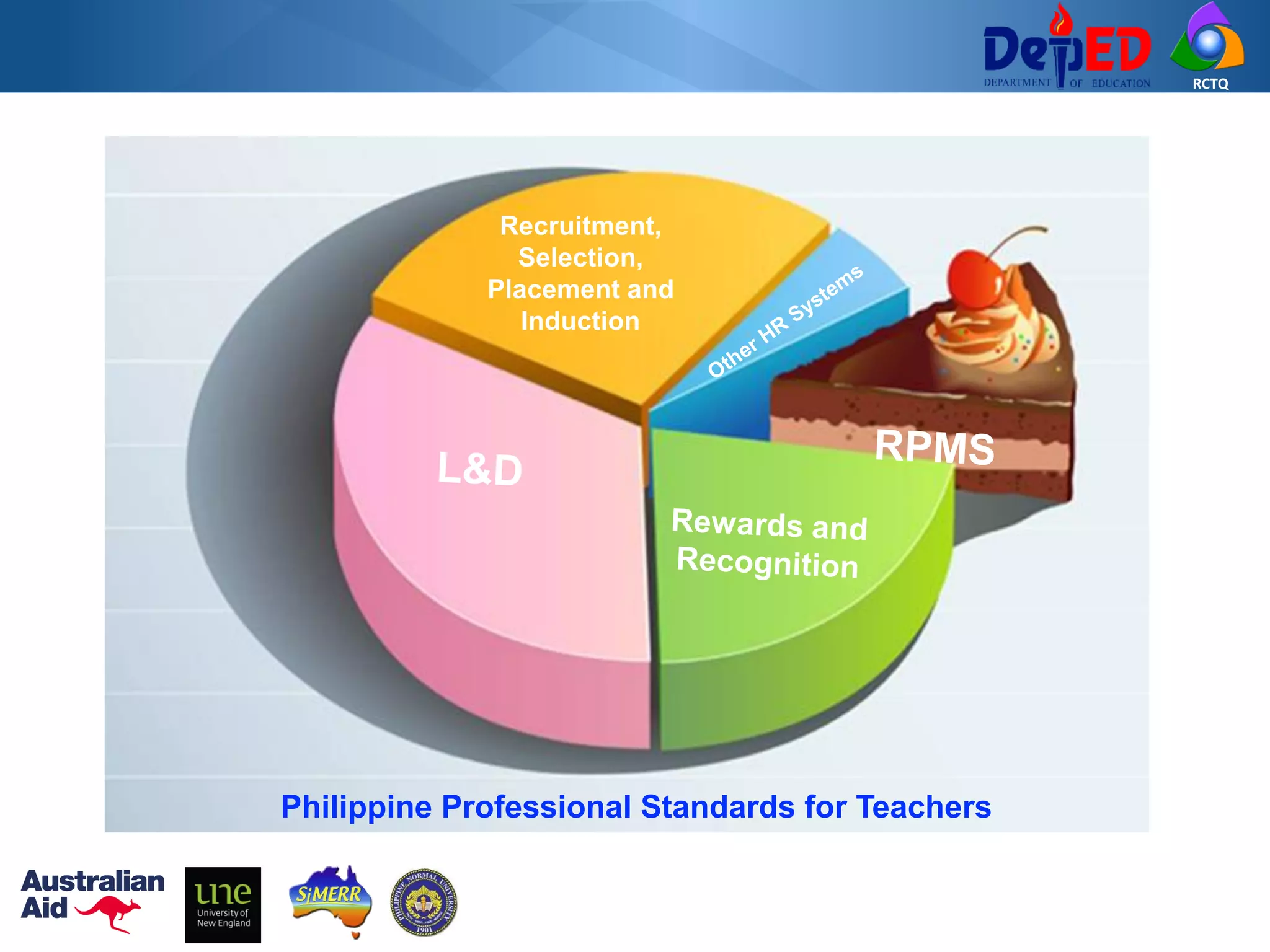
The Philippine Professional Standards for Teachers (PPST) establishes a framework for teacher quality and development with four career stages - beginning, proficient, highly proficient, and distinguished. It was developed over three years through extensive stakeholder consultations and research to align with international standards and support the K to 12 reform. The PPST addresses seven domains of teaching and will be used to guide teacher recruitment, assessment, professional development and other human resource functions to enhance teaching quality.