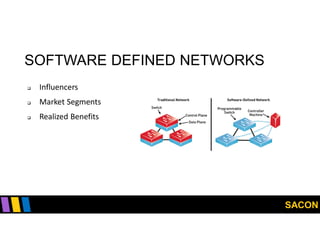
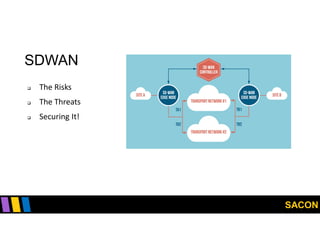
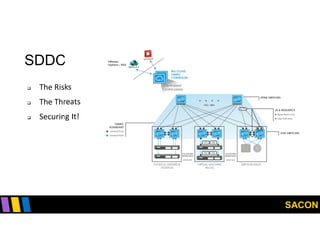
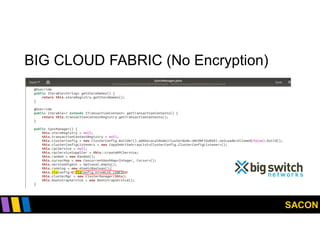
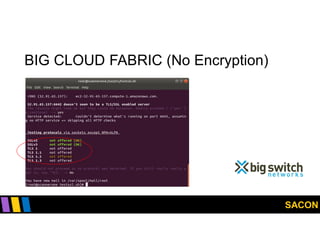
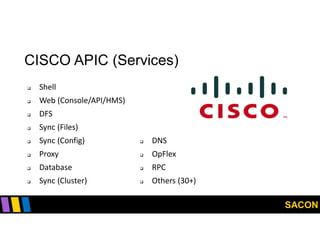
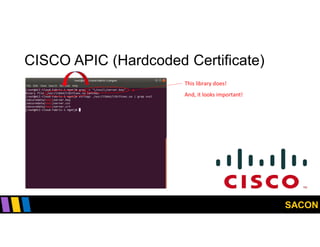
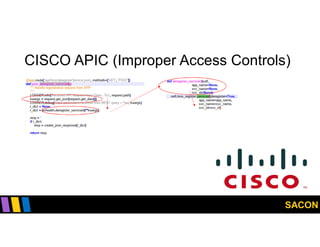
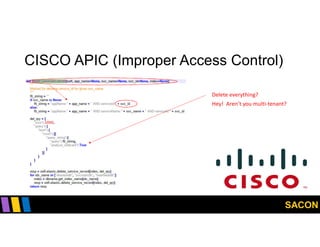
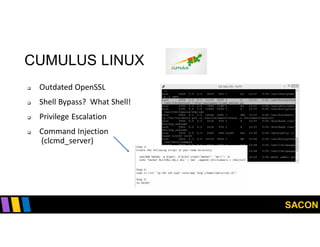
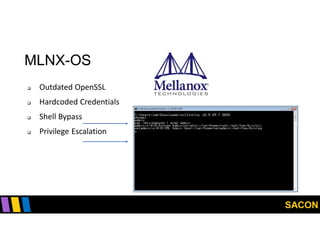
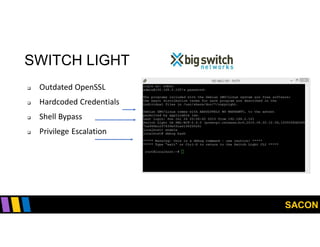
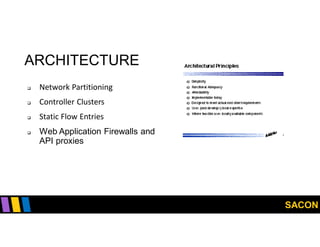
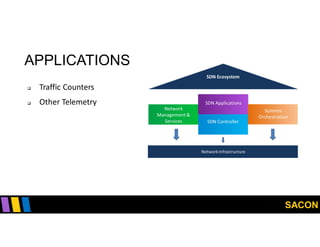
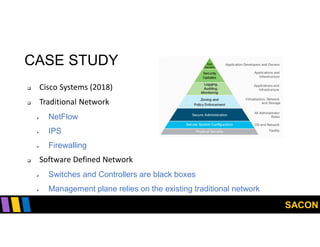
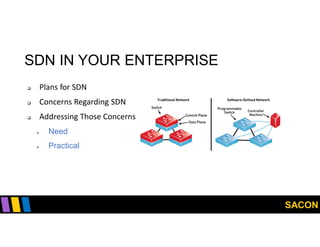
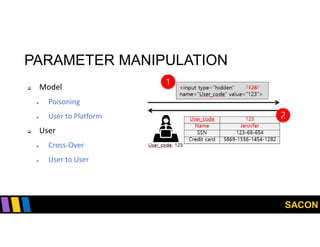
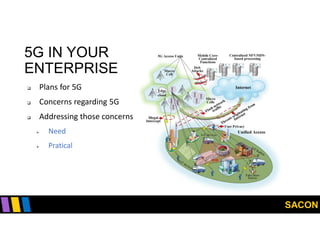
This document summarizes Gregory Pickett's presentation on SDN security at SACON International 2020. It discusses current SDN trends like SDN, SD-WAN and SDDC. It then covers vulnerabilities in SDN components like switches, controllers and applications. Examples of vulnerabilities in vendors like Cisco APIC, Floodlight and Big Cloud Fabric are provided. Finally, it discusses general approaches to securing SDN through techniques like encryption, authentication, hardening, architecture and operations. A case study of Cisco's approach to SDN security is also summarized.