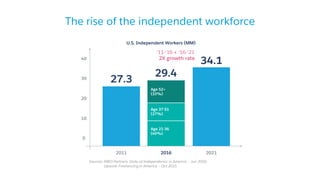
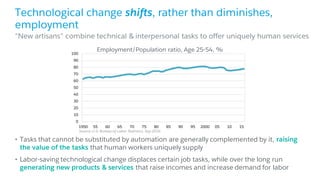
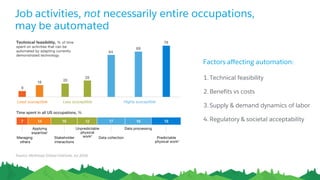
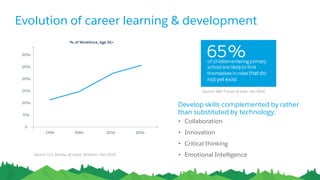
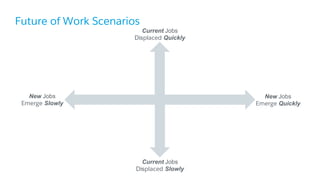
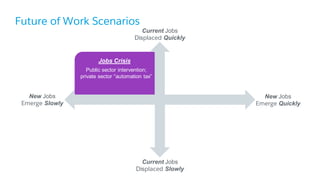
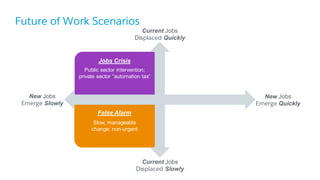
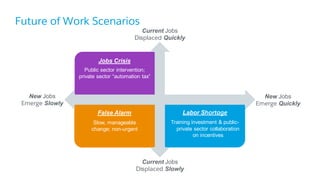
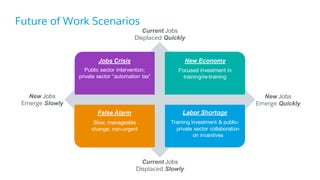
The document discusses the evolution of work, highlighting the rise of the independent workforce driven by economic shifts, increased automation, and the need for flexibility in jobs. It emphasizes the importance of developing uniquely human skills in an era where machines are capable of automating various tasks, and suggests that adaptation through continuous learning is crucial for future job market survival. Additionally, it outlines various future work scenarios and the implications of automation on employment, advocating for strategic investment in training and public-private sector collaboration.