Bacterial-Cell-Structure-Function.pptx
- 1. Bacterial Cell Structure & Function Dr.Qurat-Ul-Ain Department Of Microbiology KEMU,Lahore
- 3. 1 m = 100 cm = 1,000mm = 1,000,000 µm = 1,000,000,000nm 1mm = 1000 µm = 1000000nm 1 µm = 1000nm
- 4. Average bacteria 0.5 - 2.0 um in diam. ◦ RBC is 7.5 um in diam. Surface Area ~12 um^2 Volume is ~4 um Surface Area to Volume is 3:1 Typical Eukaryote Cell SA/Vol is 0.3:1 Food enters through SA, quickly reaches all parts of bacteria Eukaroytes need structures & organelles
- 5. Coccus ◦ Chain = Streptoccus ◦ Cluster = Staphylococcus Bacillus ◦ Chain = Streptobacillus Coccobacillus Vibrio = curved Spirillum Spirochete
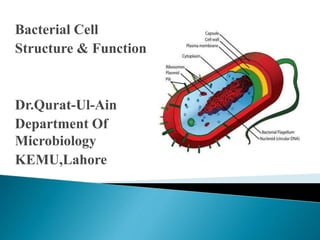
- 6. Flagella Pili Capsule Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Cell Wall Lipopolysaccharid es Teichoic Acids Inclusions Spores
- 7. Cytoplasm: Also known as proto-plasm. Gel-like matrix of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, (organic n inorganic solutes) and gases and contains cell structures like numerous ribosomes and polysomes. No ER n memb.bound organelles. Shows signs of internal mobility like cytoplasmic streaming , amoeboid movement and formation and disappearance of vacoules. Location of growth, metabolism, and replication. Granules or inclusions: Bacteria’s way of storing nutrients. Staining of some granules aids in identification.
- 8. Ribosomes: Small electron dense particles Involved in prt.synthesis 70 S(30 S + 50S) Different from host cell ribosomes in SR. Streptomycin interferes with bacterial metabolism sparing the host cell ribosomes. 3 types of RNAs: Ribosomal, transfer , mRNA Found within cytoplasm or attached to plasma membrane.
- 9. Separates the cell from its environment. Limits the protoplast Thin n elastic , can be only seen with electron microscope With the exception of mycoplasma , bacterial cytoplasmic memb.lacks sterol. Phospholipid molecules oriented so that hydrophilic,water-loving heads directed outward and hydrophobic ,water-hating tails directed inward. Proteins embedded in two layers of lipids (lipid bilayayer) FUNCTIONS: Semipermeable membrane Housing enzymes for cell wall, outer membrane synthesis, assembly n secretion of extractoplasmic n extracellular substances Generation of ATP Cell motility Mediation of chromosomal segragation during replication
- 10. Peptido-glycan Polymer (amino acids + sugars) Unique to bacteria Sugars; NAG & NAM ◦ N-acetylglucosamine ◦ N-acetymuramic acid D form of Amino acids used not L form ◦ Hard to break down D form Amino acids cross link NAG & NAM
- 12. Peptidoglycan is a huge polymer of interlocking chains of identical peptidoglycan monomers. Provides rigid support while freely permeable to solutes. Backbone of peptidoglycan molecule composed of two derivatives of glucose: - N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) - N-acetlymuramic acid (NAM) NAG / NAM strands are connected by inter- peptide bridges. Prokaryotes – Cell Wall
- 13. From the peptidoglycan inwards all bacteria are very similar. Going further out, the bacterial world divides into two major classes (plus a couple of odd types). These are: Gram Positive Gram Negative Prokaryotes - Cell Wall
- 16. Gram + only Glycerol, Phosphates, & Ribitol Attachment for Phages Participate in MG supply to the cell Antigenic determinant
- 17. Endotoxin or Pyrogen ◦ Fever causing ◦ Toxin nomenclature Endo- part of bacteria Exo- excreted into environment Structure ◦ Lipid A ◦ Polysaccharide O Antigen of E. coli, Salmonella G- bacteria only ◦ Alcohol/Acetone removes primary stain durind gram’s staining.
- 18. Chapter 4
- 19. Appearance of Colonies ◦ Mucoid = Smooth (lots of LPS or capsule) ◦ Dry = Rough (little LPS or capsule) O Antigen of Salmonella and E. coli ◦ 2,000 different O Ags of Salmonella ◦ 100’s different O Ags of E. coli E. coli O157 O Ags differ in Sugars, not Lipid A
- 20. 80% Water {20% Salts-Proteins) ◦ Osmotic Shock important DNA is circular, Haploid ◦ Advantages of 1N DNA over 2N DNA ◦ More efficient; grows quicker ◦ Mutations allow adaptation to environment quicker Plasmids; extra circular DNA ◦ Antibiotic Resistance No organelles (Mitochondria, Golgi, etc.)
- 21. Some bacteria have an additional layer outside of the cell wall called the glycocalyx. This additional layer can come in one of two forms: 1- Glycoproteins loosely associated with the cell wall. - Slime layer causes bacteria to adhere to solid surfaces and helps prevent the cell from drying out. - Streptococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Streptococcus mutans allows it to accumulate on tooth enamel (yuck mouth and one of the causes of cavities). Other bacteria in the mouth become trapped in the slime and form a biofilm & eventually a buildup of plaque.
- 22. 2.Polysaccharides firmly attached to the cell wall. Capsules adhere to solid surfaces and to nutrients in the environment. Adhesive power of capsules is a major factor in the initiation of some bacterial diseases. Capsule also protect bacteria from being phagocitized by cells of the hosts immune system.
- 23. Some prokaryotes have distinct appendages that allow them to move about or adhere to solid surfaces. Consist of delicate strands of proteins. Flagella: Long, thin extensions that allow some bacteria to move about freely in aqueous environments. Endoflagella: Wind around bacteria, causing movement in waves.
- 24. Motility - movement Swarming occurs with some bacteria ◦ Spread across Petri Dish ◦ Proteus species most evident Arrangement basis for classification ◦ Monotrichous; 1 flagella ◦ Lophotrichous; tuft at one end ◦ Amphitrichous; both ends ◦ Peritrichous; all around bacteria
- 25. Short protein appendages ◦ smaller than flagella Adhere bacteria to surfaces ◦ E. coli has numerous types K88, K99, F41, etc. ◦ Antibodies to it will block adherence. F-pilus; used in conjugation ◦ Exchange of genetic information
- 26. Resistant structure ◦ Heat, irradiation, cold ◦ Boiling >1 hr still viable ◦ Takes time and energy to destroy spores Location important in classification ◦ Central, Subterminal, Terminal Bacillus stearothermophilus -spores ◦ Used for quality control of heat sterilization equipment Bacillus anthracis - spores ◦ Used in biological warfare
- 27. Spore Formation This is what happens ………….. Cell
- 33. Now see as, in suitable conditions, the cell begins to divide (binary fission)………………………….
- 35. Bacteria sometimes occur in groups, rather than singly. _________ divide along a single axis, seen in pairs or chains. _________ divide on one or more planes, producing cells in: - pairs (diplococci) - chains (streptococci) - packets (sarcinae) - clusters (staphylococci). Size, shape and arrangement of cells often first clues in identification of a bacterium. Many “look-alikes”, so shape and arrangement not enough for id of genus and species.