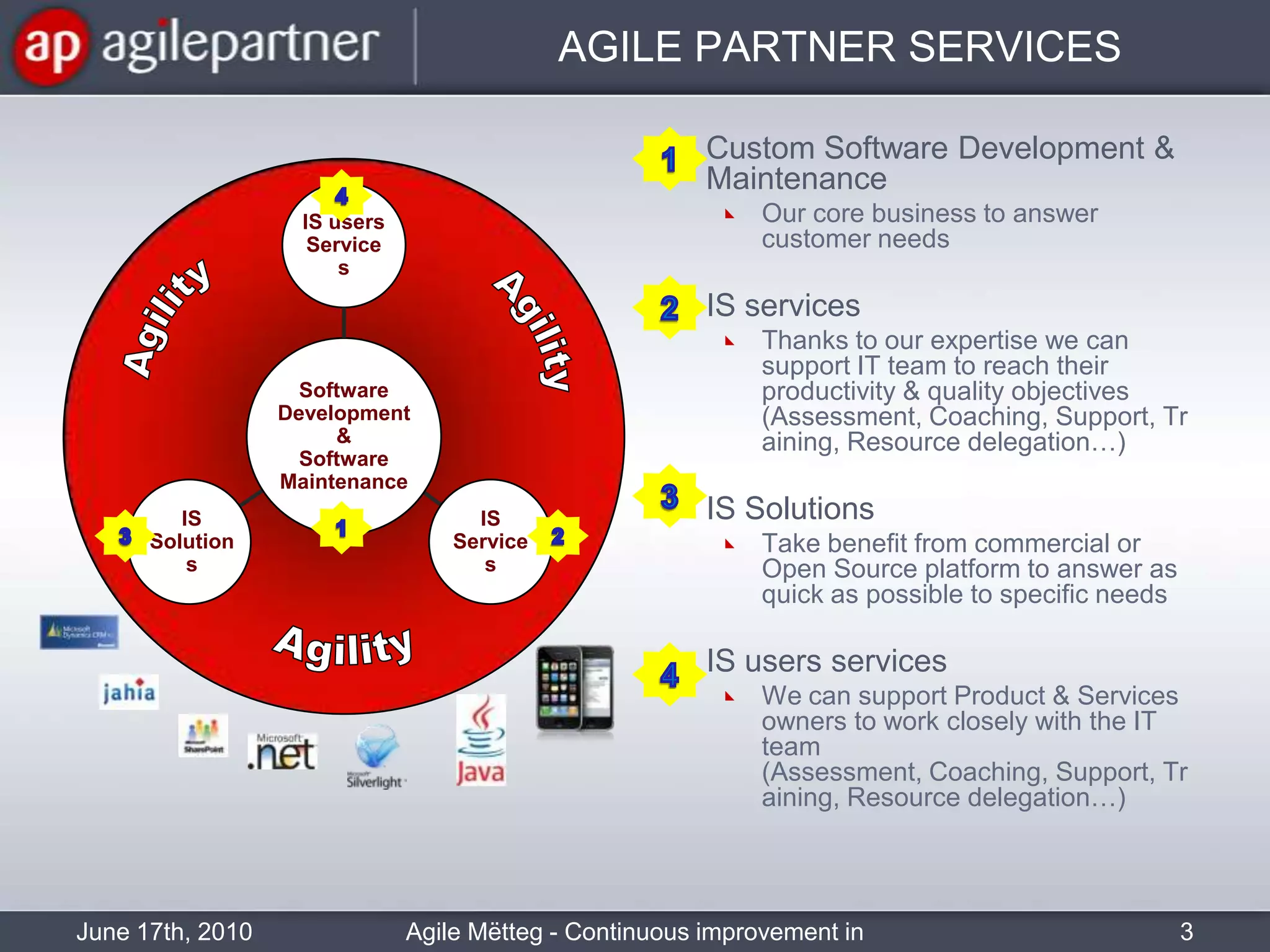
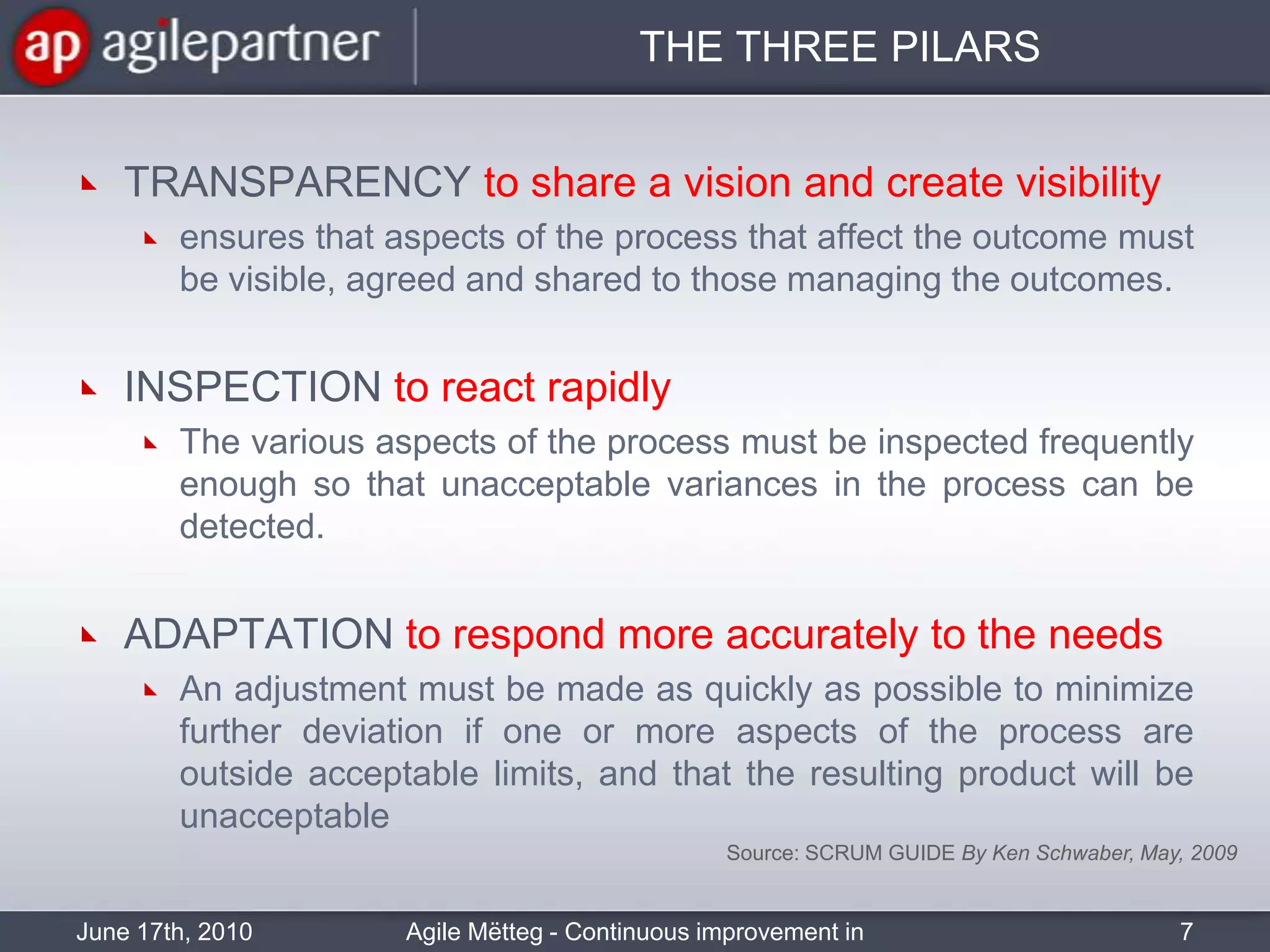
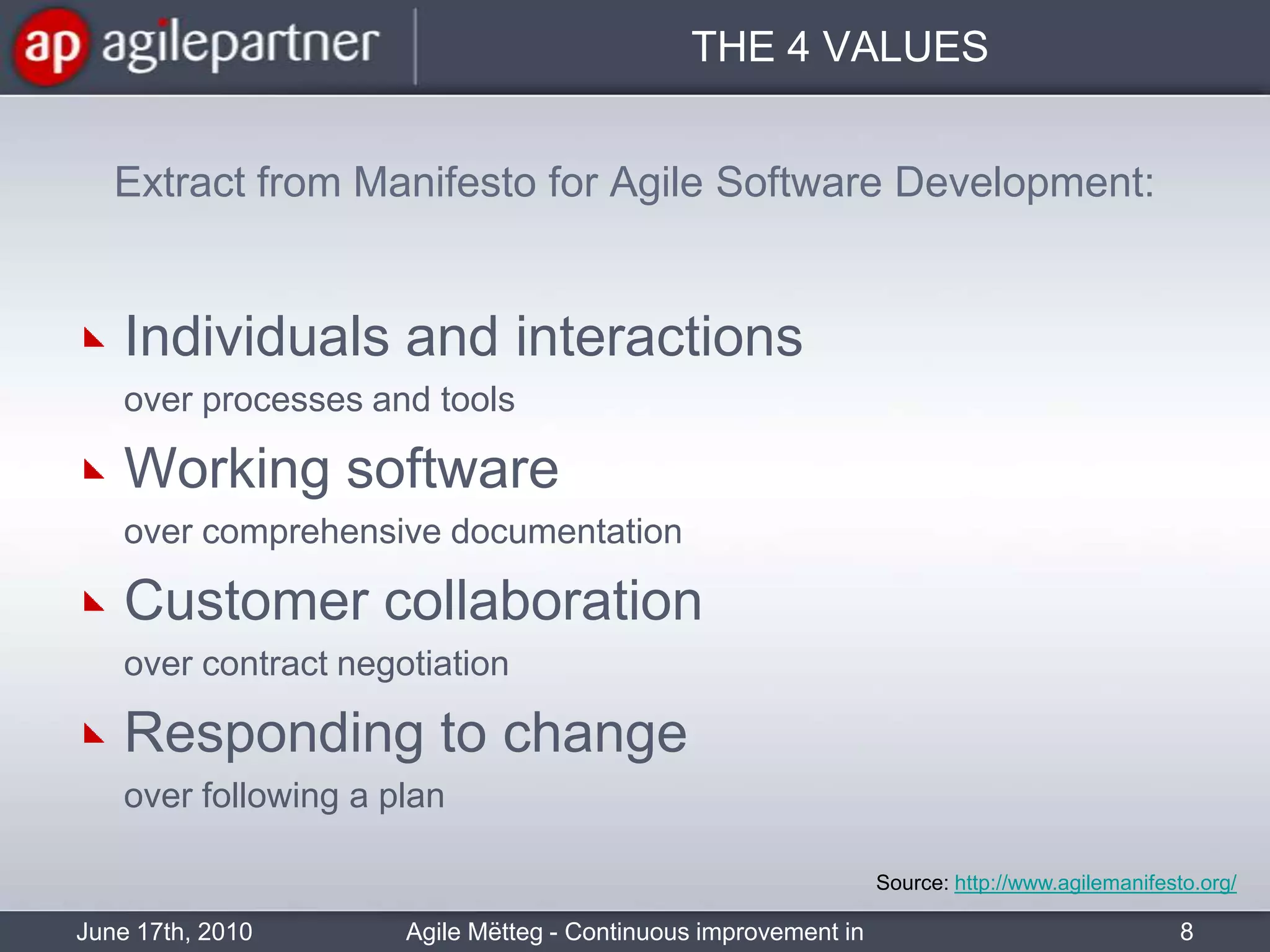
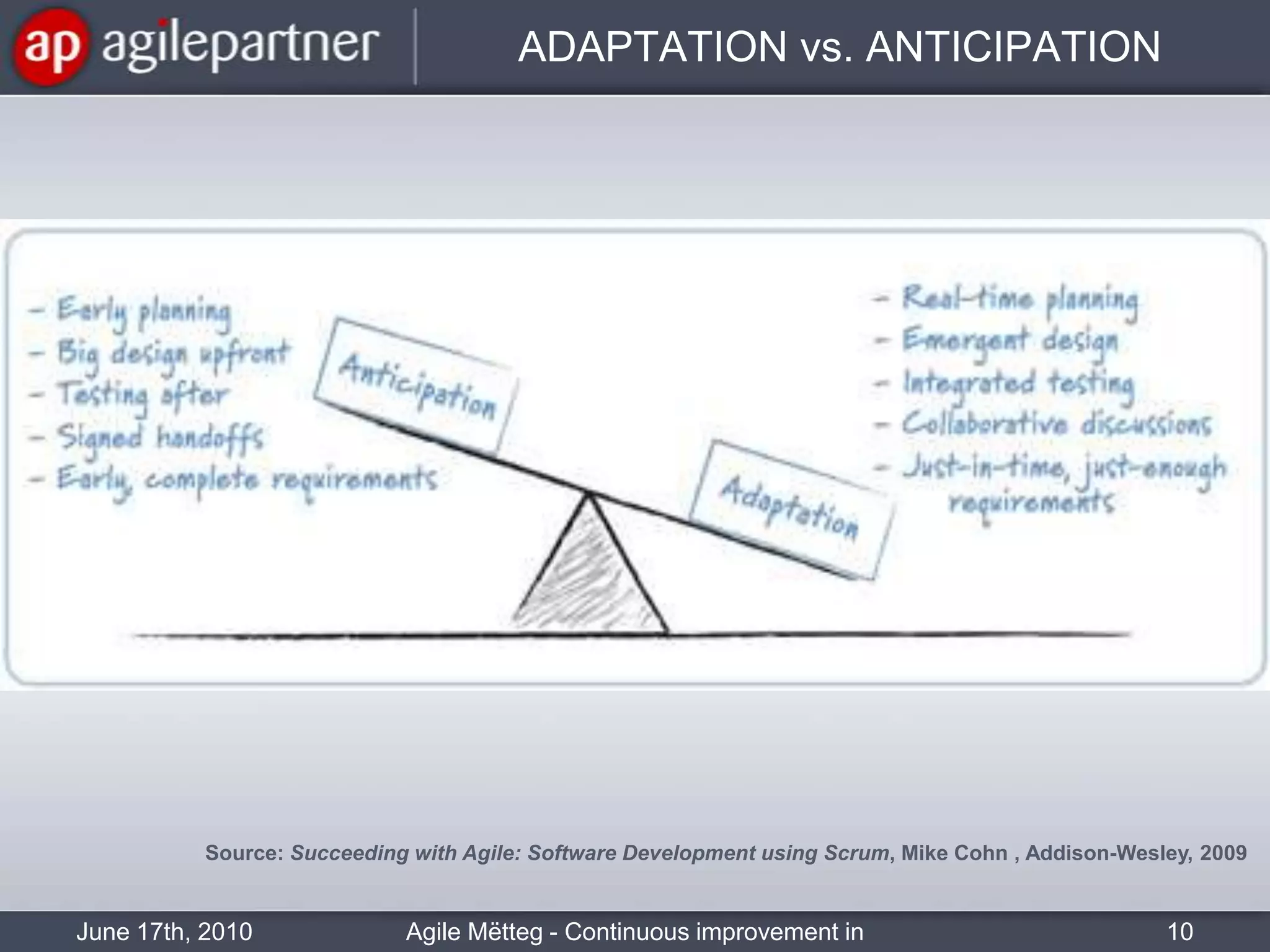
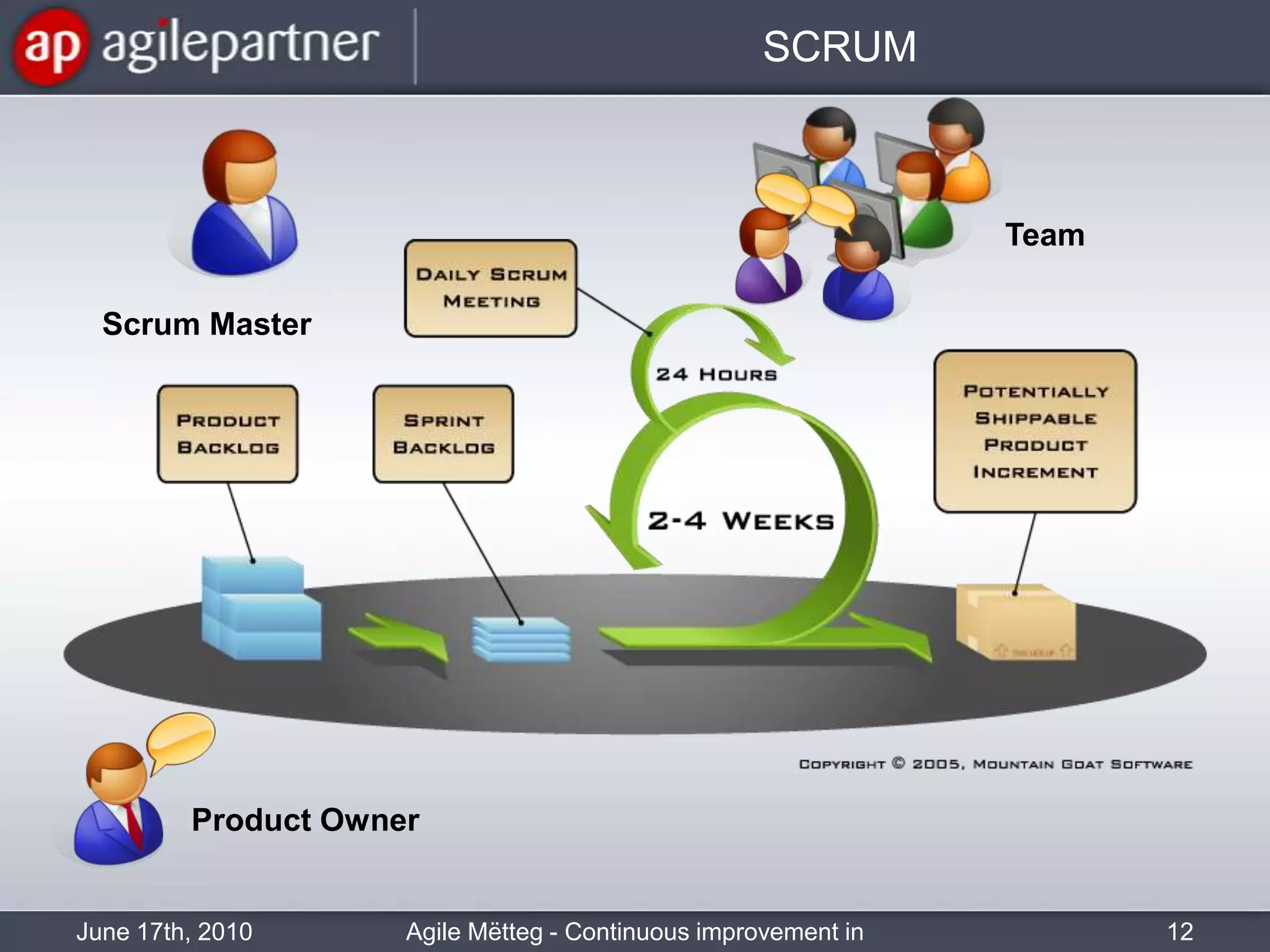
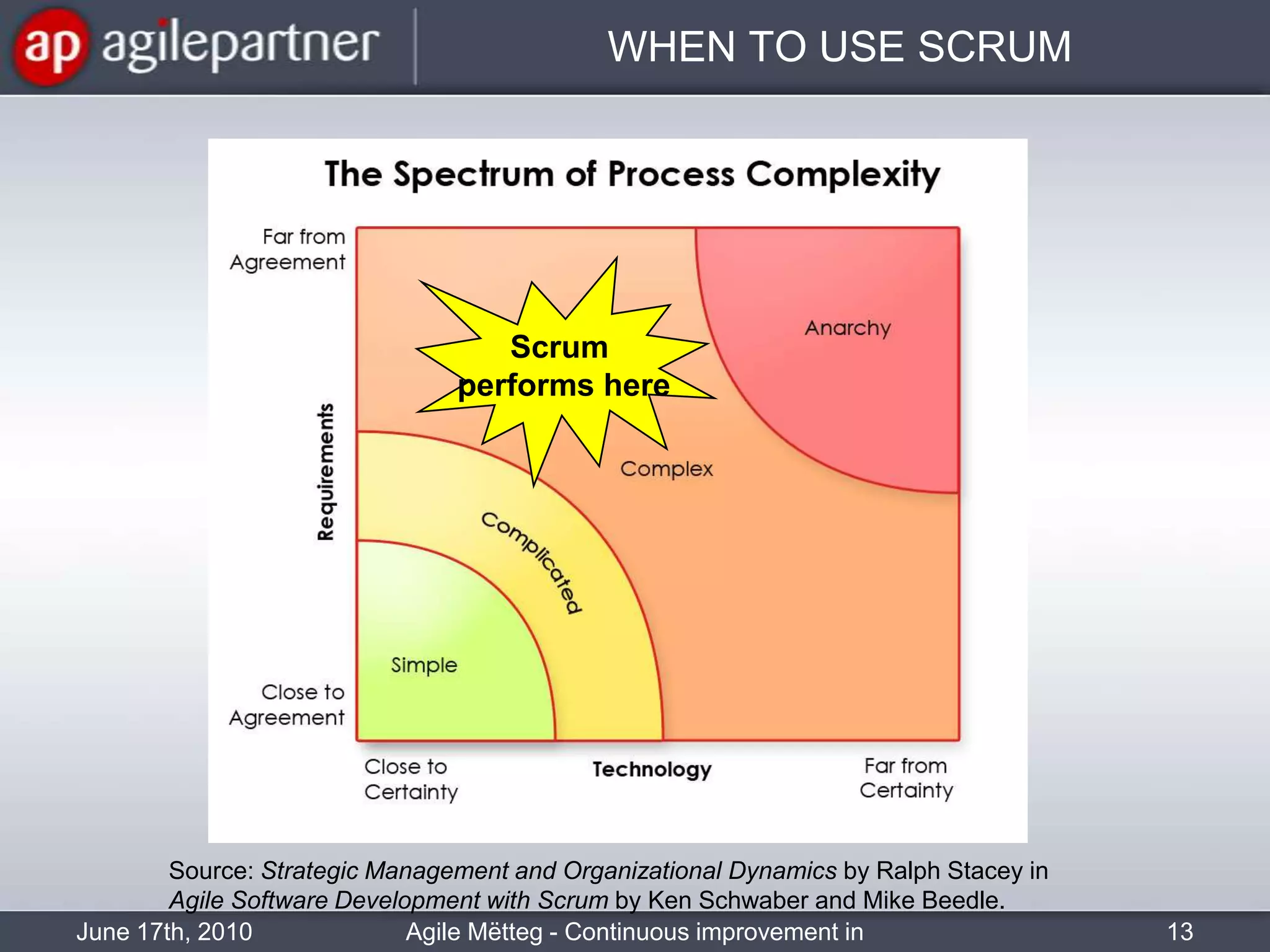
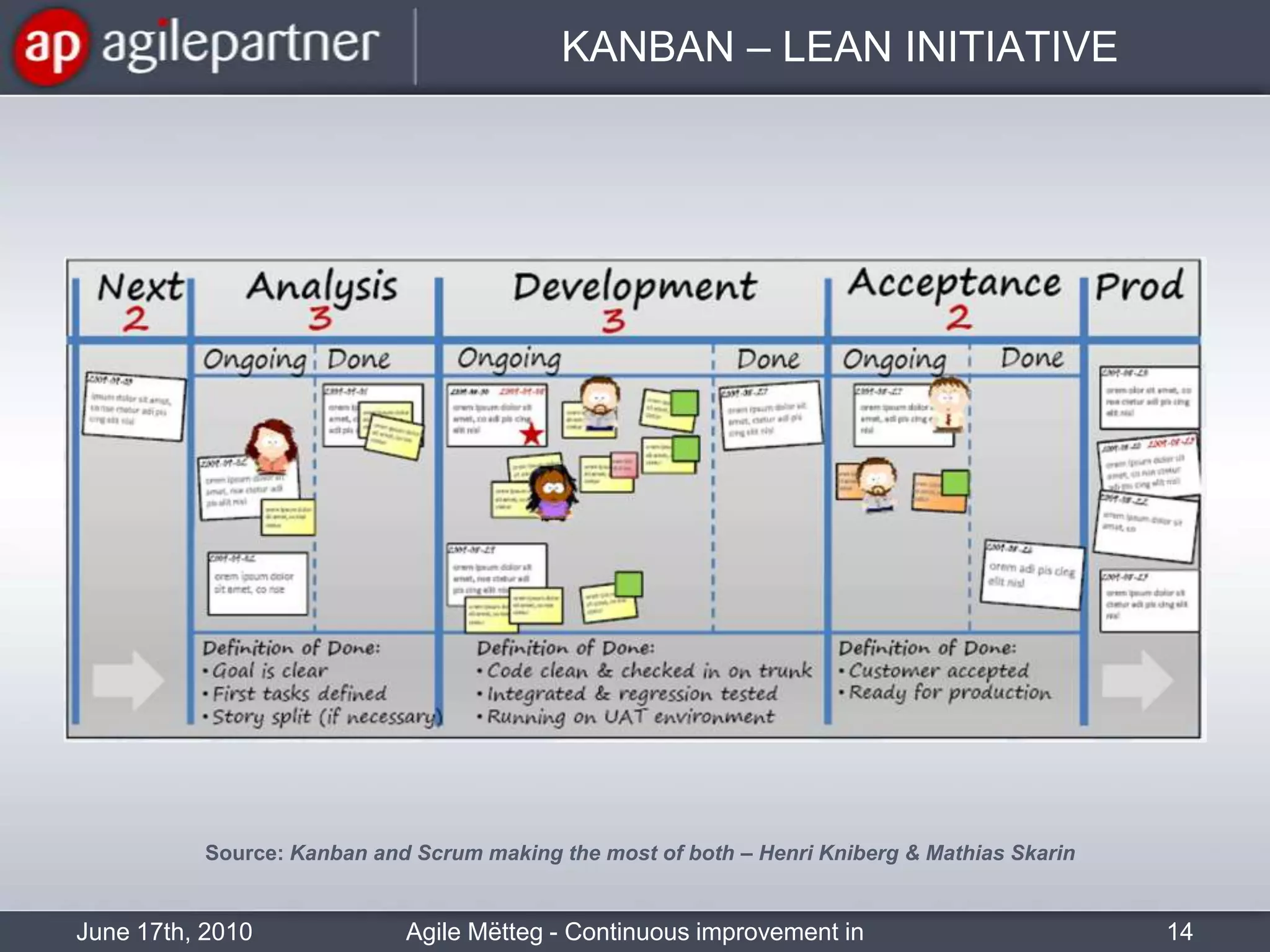
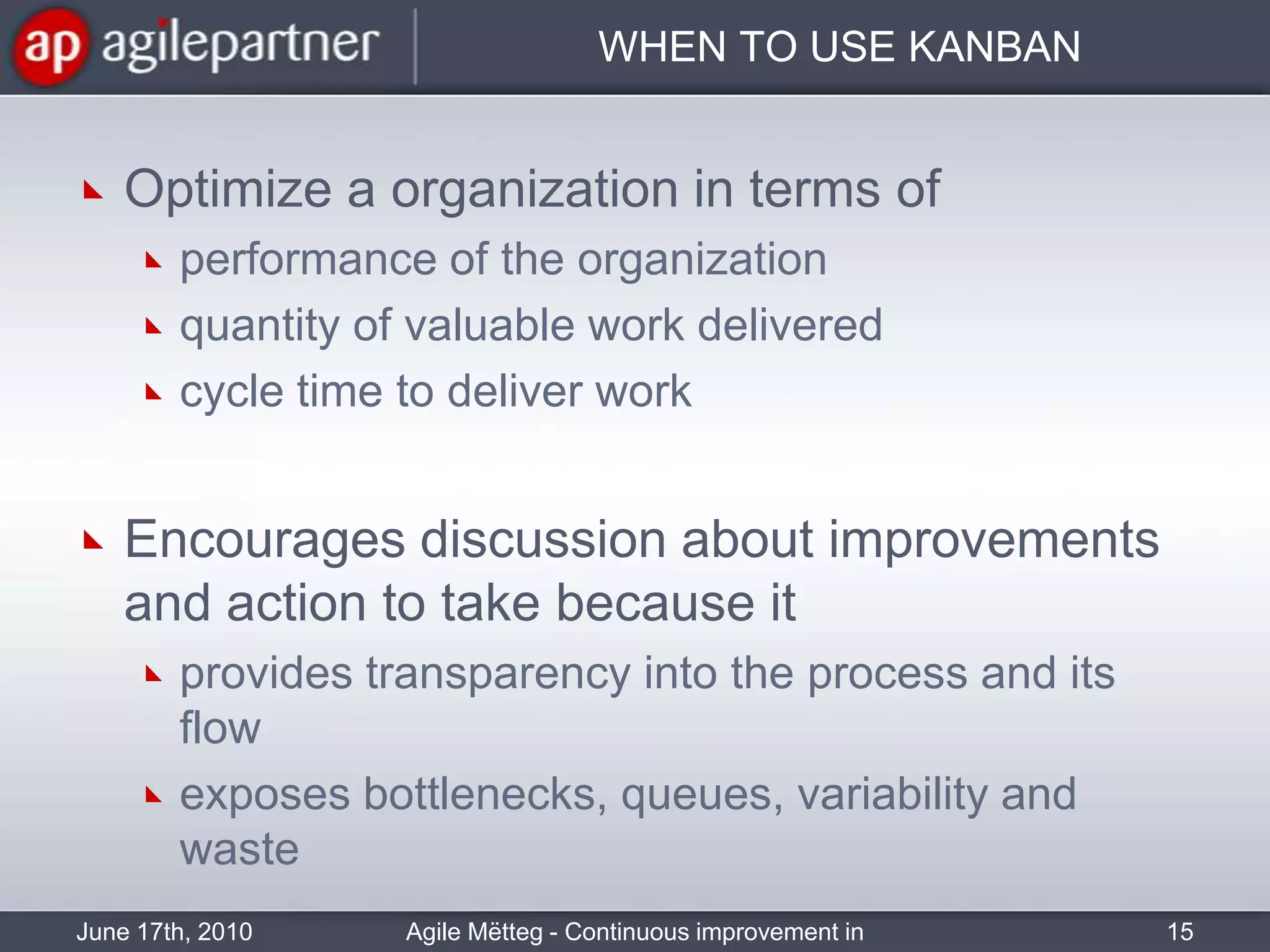
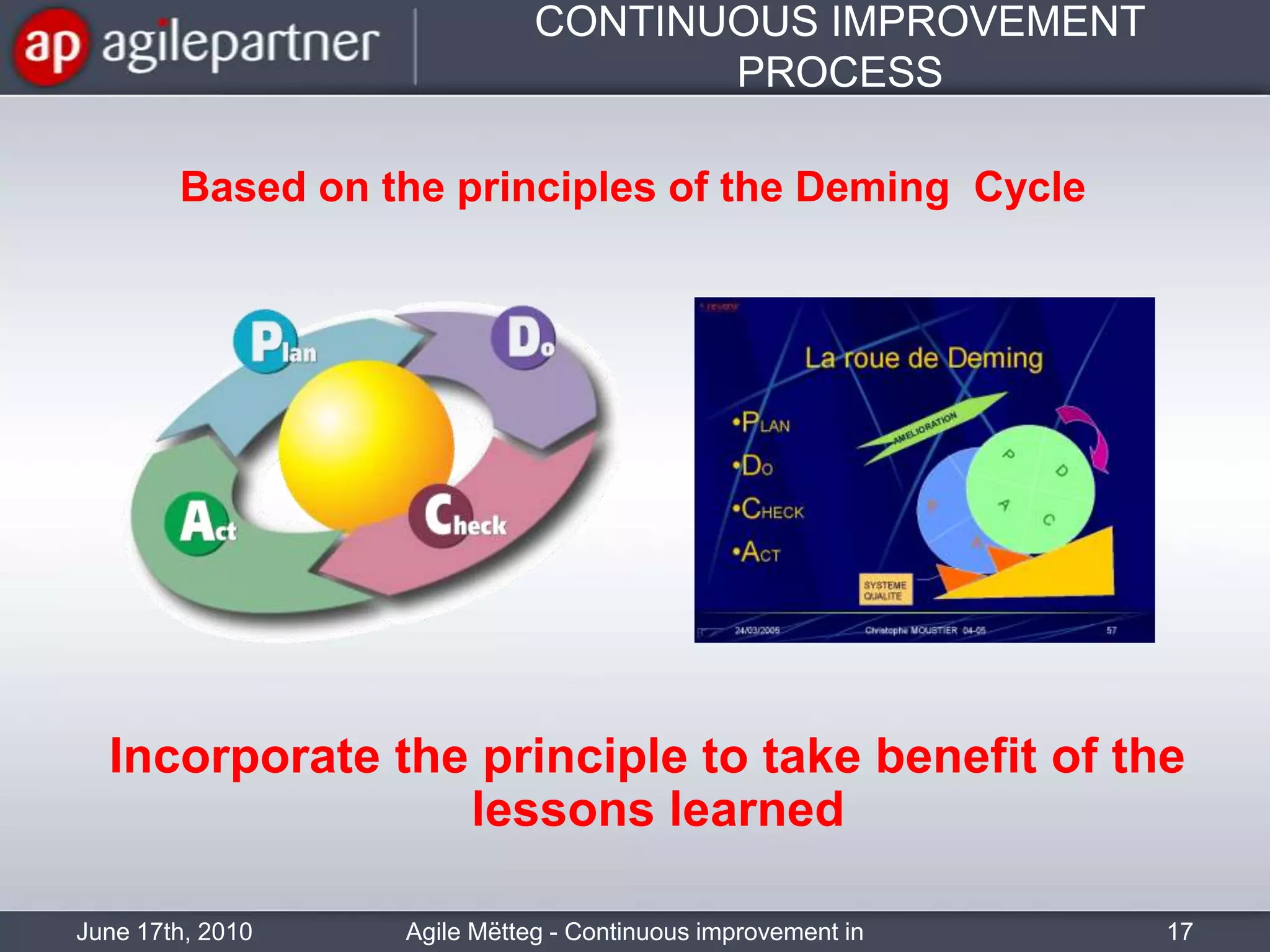
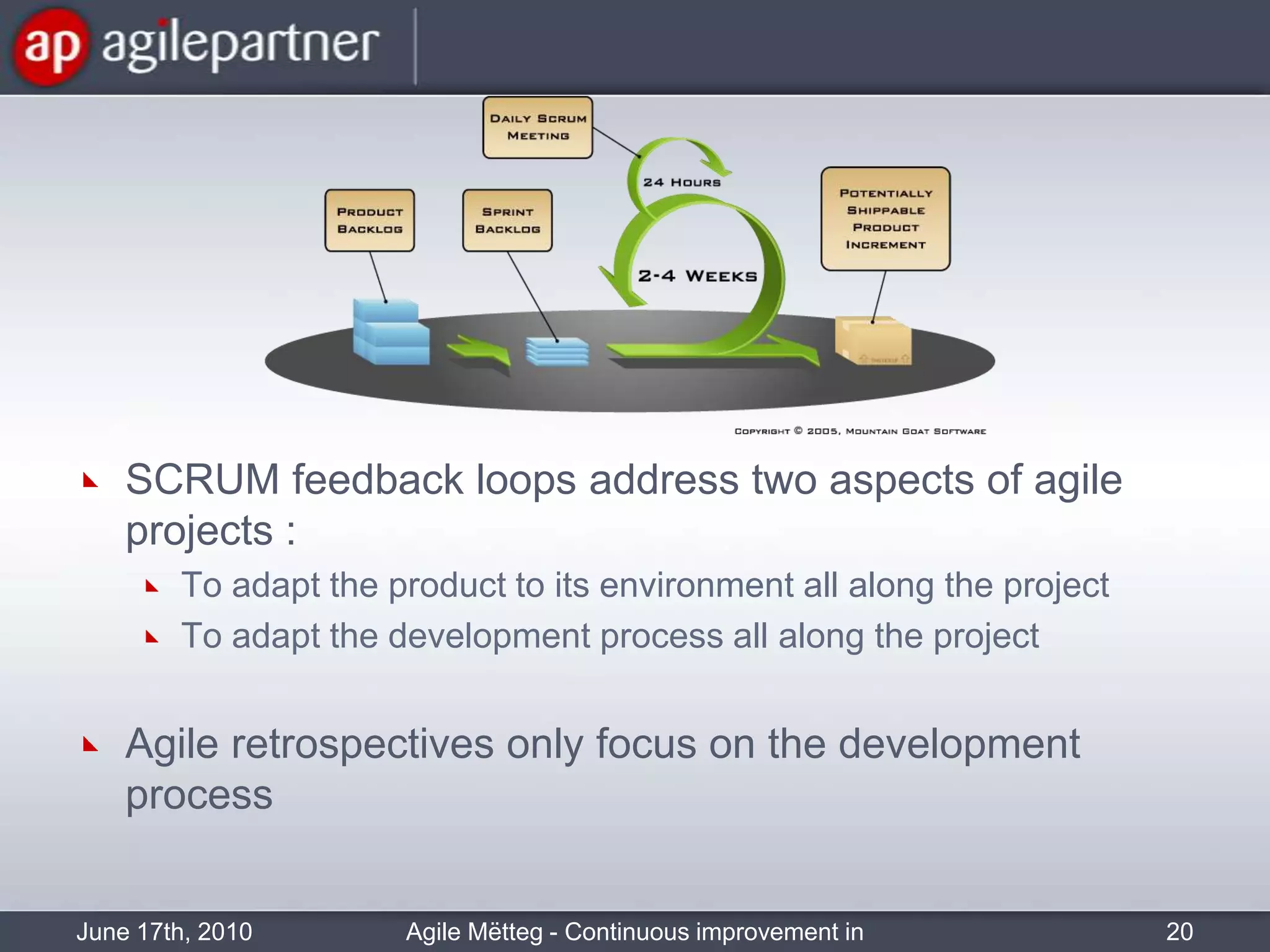
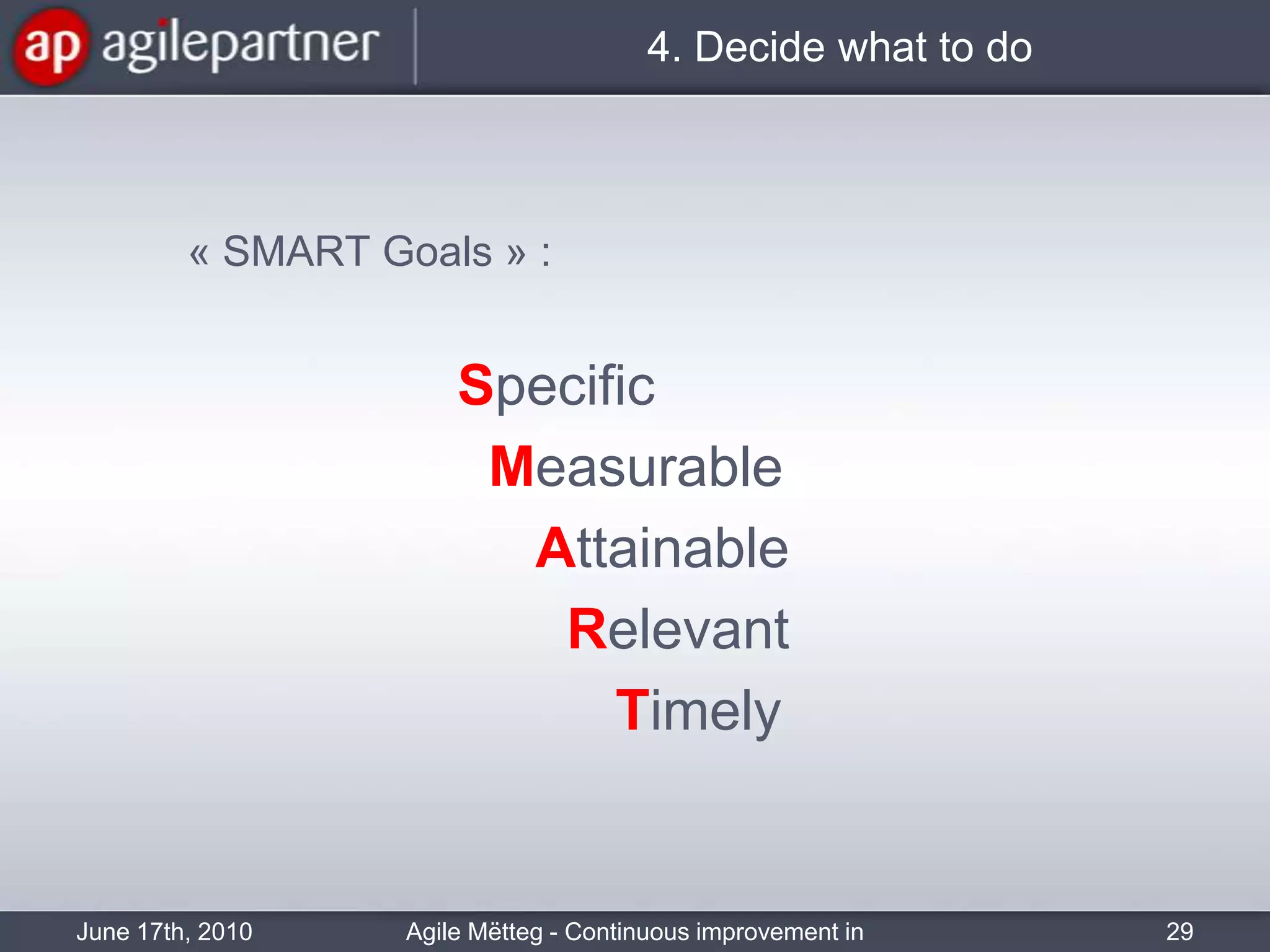
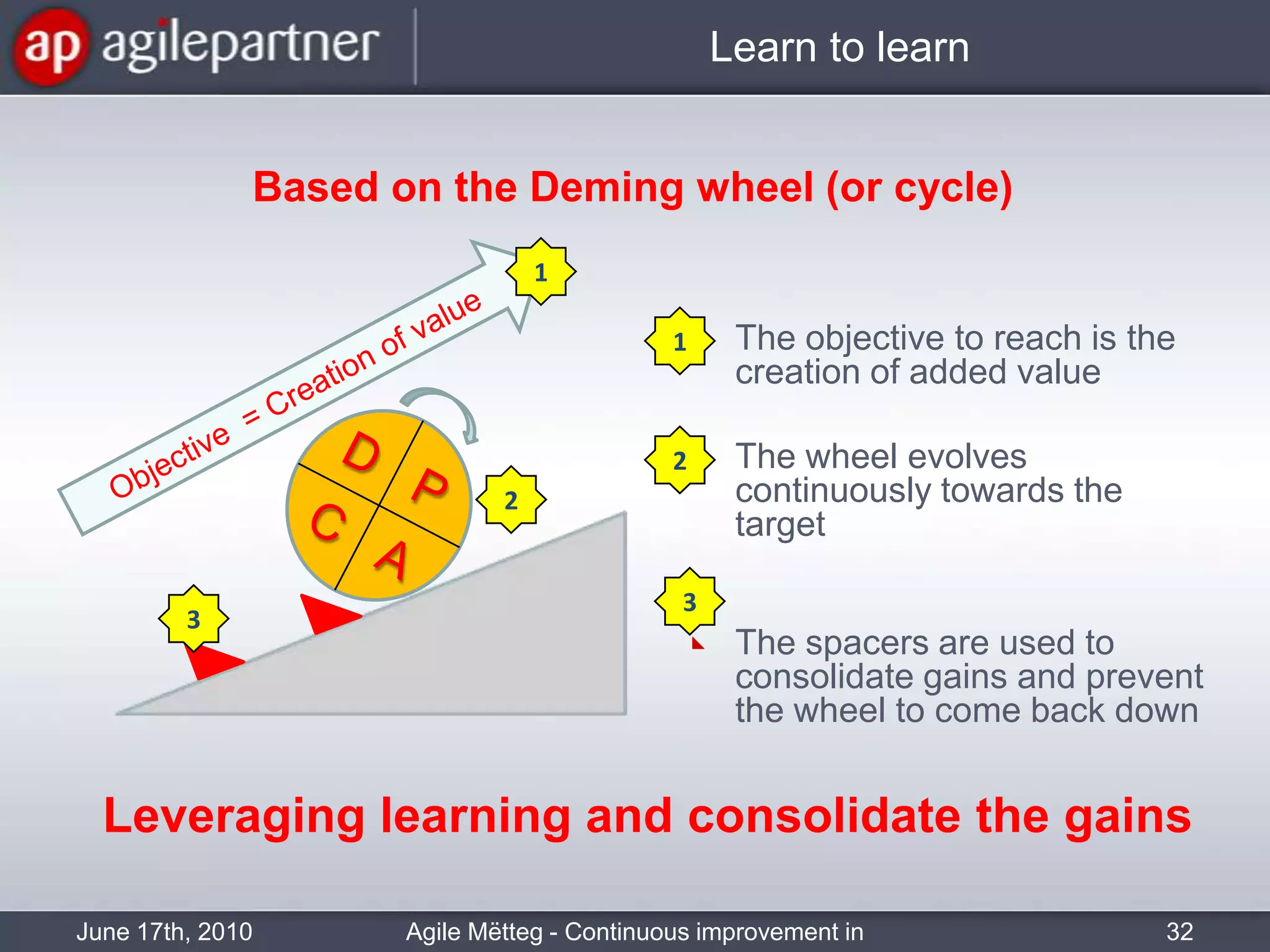
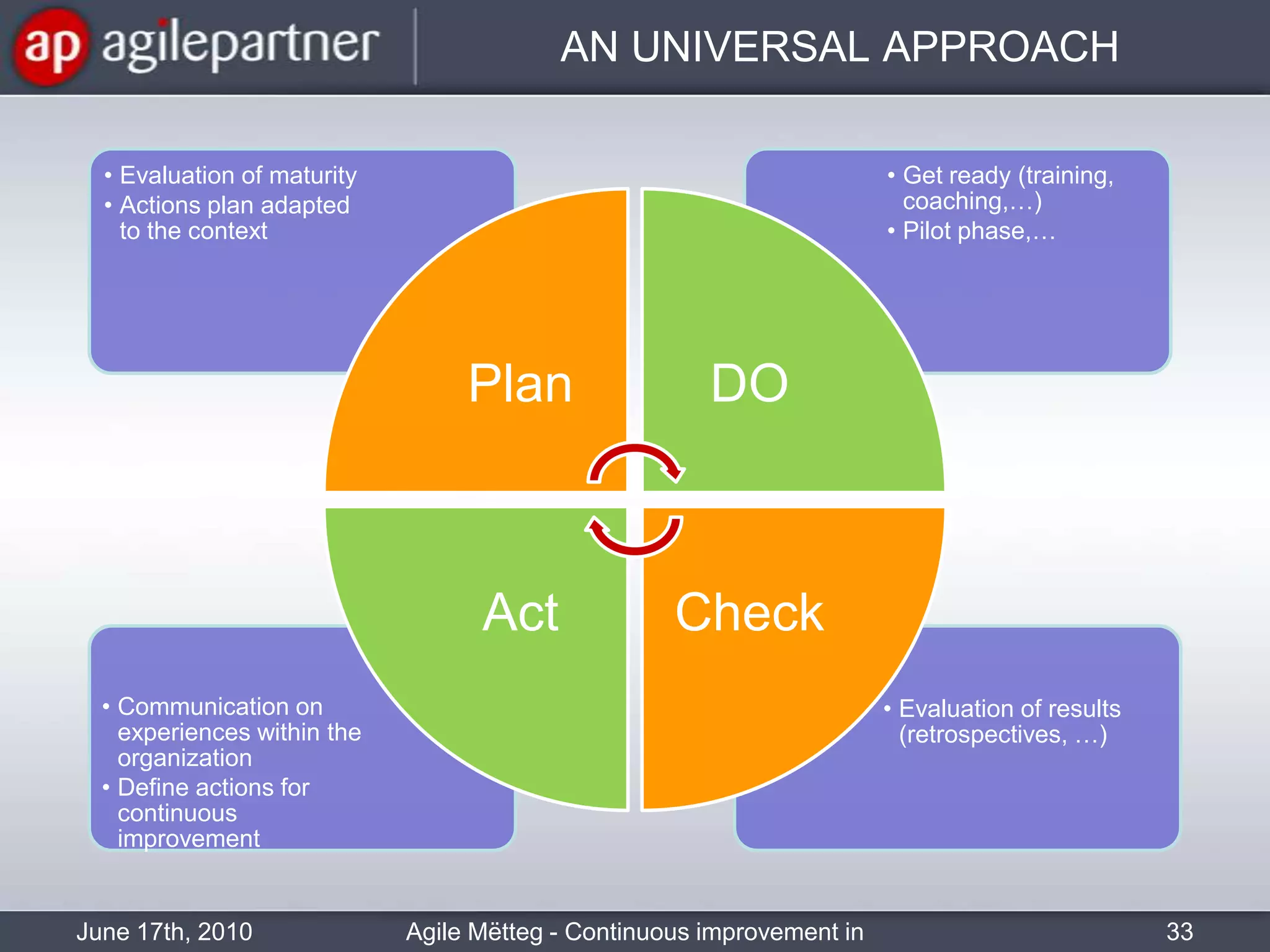
This document summarizes a seminar about continuous improvement in agile practices. The seminar introduced agile values and principles like transparency, inspection and adaptation. It covered techniques for continuous improvement like retrospectives and emphasized learning from experiences to constantly improve. Attendees participated in a retrospective exercise to discuss what went well and possibilities for future seminars to become more effective.