Lesson-4-Meiosis-and-Human-Life-Cycle.pptx
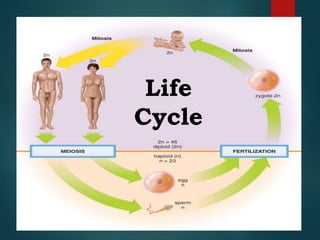
- 1. Life Cycle
- 6. Spermatogenesis is the production of sperm cell (spermatozoon/spermatozoa) in males males by the process of meiosis which is haploid. Oogenesis is the production of egg cell (ovum/ova) in females via meiosis which is haploid.
- 7. Human Life Cycle… Does human life cycle involves both mitosis and meiosis? How can you explain?
- 8. Human Life Cycle The human life cycle involves both mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis (equational division) occurs during development and after birth as part of growth and tissue repair Meiosis (reductional division) occurs during sexual reproduction and the number of chromosomes are reduced from diploid to haploid
- 9. Remember! Due to meiosis, two individuals can create off-spring that are genetically different not only from themselves but also from their siblings. Meiosis is a special type of nuclear division that results in 4 gamete cells. • Spermatogenesis in males • Oogenesis in females
- 10. Fertilization - Zygote The fertilization of an egg by a sperm gives rise to a zygote (a diploid) The zygote contains 2 sets of chromosomes – 1 set from father (n) and 1 set from mother (n) In humans, 1 set of chromosomes is equal to 23 pairs thus the diploid zygote contains 46 chromosomes.
- 11. Homologous Chromosomes The 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 altogether) are called the diploid (2n) number Homologous chromosomes (homologues) are members of a chromosome pair. Alternate versions of a gene for a particular trait are called alleles. The larger chromosome is the X and the smaller is the Y chromosome
- 12. Concept of Homologous Chromosomes Of the 23 pairs, 22 pairs are called autosomes while the remaining 1 pair is called sex chromosomes . Sex Chromosomes carry genes responsible for the sex/gender of the individual which is different from male and females Autosomes/Body Chromosomes in each pair are the same in males and females. Males contain XY sex chromosomes. Females contains XX sex chromosomes.
- 14. Karyogram Karyogram is the arrangement of the 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes from the biggest to smallest. Karyotyping is the process of preparing a karyogram.
- 15. Sexual Reproduction: Meiosis Meiosis serves 2 functions: 1.Reducing the chromosome number 2.Shuffling the chromosomes and genes to produce genetically different gametes
- 16. Meiosis
- 17. Meiosis is the process by which replicated chromosomes undergo two nuclear divisions to produce four haploid cells, also called meiocytes (sperms and eggs). Meiosis uses similar mechanisms as those employed during mitosis to accomplish the separation and redistribution of chromosomes. However, several features, namely, the pairing and genetic recombination between homologous chromosomes, are unique to meiosis.
- 18. The steps leading up to meiosis are similar to those of mitosis – the centrioles and chromosomes are replicated. The amount of DNA in the cell has doubled, and the ploidy of the cell remains the same as before, at 2n.
- 19. Meiosis 1
- 20. Meiosis I proceeds directly to meiosis II without going through interphase. Meiosis I is unique in that genetic diversity is generated through crossing over and random positioning of homologous chromosomes (bivalent chromosomes).
- 21. Prophase 1 During prophase I, chromosomal condensation allows chromosomes to be viewed under the microscope. In late prophase I, homologous chromosomes (also called bivalent chromosomes, or bivalents) pair laterally, or side-by-side. At this time they are said to be in synapsis. During synapsis/crossovers – cross- connections that form from breakage and rejoining between sister chromatids – can occur between the paired bivalents, leading to genetic recombination (exchange of genetic material) between the strands involved.
- 22. The point where a crossover occurs is called a chiasma (plural chiasmata). Note: The bivalents have two chromosomes and four chromatids, with one chromosome originating from each parent.
- 23. Metaphase 1 In metaphase I, each pair of bivalents (two chromosomes, four chromatids total) align on the metaphase plate. This is different from metaphase in mitosis, where all chromosomes align single file on the metaphase plate. The position of each chromosome in the bivalents is random - either parental homolog can appear on each side. This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother's or father's homolog for each chromosome
- 24. In a diploid cell with 2 pairs of chromosomes, there are 4 ways to arrange the chromosomes during metaphase I.
- 25. Anaphase 1 In anaphase I, homologous chromosomes separate. Homologous chromosomes, each containing two chromatids, move to separate poles. Unlike in mitosis, the centromeres do not split and sister chromatids remain paired in anaphase I.
- 26. Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis In telophase I, the homologs of each bivalent arrive at opposite poles of the cell, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes. Cytokines is then divides the cell into two daughter cells. Each of the two daughter cells is now haploid (n), with half the number of chromosomes per nucleus as in meiosis I.
- 27. Meiosis 2:
- 28. Chromosomal replication does not occur between meiosis I and meiosis II; meiosis I proceeds directly to meiosis II without going through interphase.
- 29. Prophase II Prophase II is the first stage, after Telophase I, in the second meiotic division cycle. In this stage, the chromosomes, in both daughter cells produced in meiosis I, migrate to the of the cell. Prophase II ends when the chromosomes are aligned along the middle of the cell along a single plane.
- 30. Metaphase II In metaphase II, in each of the two daughter cells produced by the first meiotic division (which are known as secondary germ cells), the spindle again draws the chromosomes to the metaphase plate. This time, unlike metaphase I, the two kinetochores of each centromere bind to spindle fibers from opposite poles (as in mitotic metaphase). This results in separation of the sister chromatids of each chromosome during the next phase of meiosis, anaphase II.
- 31. Anaphase II During anaphase II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move toward opposite poles. As the chromosomes are dragged along by the spindle apparatus, their arms can be seen dragging along behind so that the chromosomes form V- shapes. The poles themselves move further apart as cytokinesis begins and the cell lengthens .
- 32. Telophase II During telophase II, the chromosomes reach opposite poles, cytokinesis occurs, the two cells produced by meiosis I divide to form four haploid daughter cells, and nuclear envelopes When telophase II is over, the two cells are entirely separated and their nuclear membranes are fully formed. Meiosis is then complete.
- 33. Meiosis Compared to Mitosis Meiosis requires 2 nuclear divisions mitosis requires only 1 nuclear division Meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells (half the chromosome number of the parent cell) Mitosis produces 2 diploid daughter cells (same as the parent cell) Meiosis produces 4 daughter cells that are genetically different to each other and to the parent cell Mitosis produces 2 daughter cells that are genetically similar to each other and to the parent cell
Editor's Notes
- Sperm and egg: one chromosome derived from each homologous pair of chromosomes Spermatogenesis: occurs in the testes and sperm is produced Oogenesis is the production of eggs in the ovaries Both of these processes have a reduction of chromosome number (haploid cells)…the combination of the sperm and egg give rise to a zygote ( a diploid) The zygote undergoes mitosis and differentiation of cells to become a fetus IMPORTANT: Meiosis is important because if it did not halve the chromosome number, the gametes would contain the same number of chromosomes as the body cells, and the number of chromosomes would double with each generation MEIOSIS KEEPS THE CHROMOSOME NUMBER CONSTANT IN EACH GENERATION!