Automotive Brake System.ppt
- 4. Introduction The modern automotive brake system has been refined for over 100 years and has become extremely dependable and efficient. Automotive brakes are the most important safety devices for automobiles. Braking is the mechanism in the motor vehicle which is used to slowing down and stopping the vehicle to rest in the shortest possible distance. While operating the braking system the K.E of moving vehicle is converted in to HEAT ENERGY.
- 5. Brakes have the following functions: It is used to stop the vehicle. It is used to control the speed where and when required. It is used to control the vehicle while descending along the slope. To park the vehicle and held it in stationary position without the presence of Driver. Functions of Brakes
- 6. It should work efficiently irrespective of road condition and quality. The retardation must be uniform throughout its application. The pedal effort must be within the convenient capacity of the driver. It must be reliable and should not be effected by heat water and dust. It should be in minimum weight. Requirements of Automobile Brakes:
- 7. It should have long life. It should be easy to maintain and adjust. Noise and vibrations are to be minimum. There should be provision for secondary brake or parking brake. Requirements of Automobile Brakes:
- 8. For practical measure for braking efficiency that of the minimum distance in which it can be brought in to rest after the brake is applied. The stopping distance depends upon ◙ Grip between the tire and road surface. ◙ Tire tread condition. ◙ Tire inflation. ◙ Nature of road surface. The stopping distance is calculated by d=kv2 Where d = stopping distance in kilometers, k = Constant depending upon the road and tire inflation. v = velocity of the vehicle per hour. Stopping distance and Braking efficiency
- 9. The value of k is 1/25 for 4 wheel braking system. 1/12 for 2 wheel braking system. The braking efficiency is calculated by the equation: η = v2/3d where v = velocity of the vehicle d = stopping distance. Stopping distance and Braking efficiency
- 10. Condition of Brake Braking efficiency in % 1. Perfect 90% 2. Excellent 77% 3. Good 70% 4. Fair 60% 5. Poor 50% 6. Bad 37% 7. Very bad 30% Below Fair is very danger. Stopping distance and Braking efficiency
- 11. The following are the classifications of Brakes: 1. By Method of Power. a. Mechanical brakes. b. Hydraulic brakes c. Vacuum brakes. d. Air brakes. e. Electrical brakes. f. Magnetic brakes. g. Air assisted hydraulic brakes. 2. By Method of Application. a. Service or foot brakes. b. Parking or hand brakes. Classification of Brakes:
- 12. 3. By Method of Operation. a. Manual b. Servo c. Power operation 4. By method of Braking Contact. a. Internal Expanding Brakes b. External Contracting Brakes. 5. By Method of Applying Brake force. a. Single Acting Brakes. b. Double Acting Brakes. Classification of Brakes:
- 13. Service brakes. Operated by foot pedal. Most automotive service brakes are hydraulic type. Some vehicles use air or pneumatic brakes. Service brakes used in cars are of two types: Drum brake. Disc brake Parking brakes. Operated by hand lever which hold the veh stationary when applied. By Method of application
- 14. Drum Brakes (Internal Expanding or External Contracting). Types of Mechanical Brakes Disc Brakes (Single or Two caliper).
- 15. The drum brake has a metal drum that encloses the brake assembly at each wheel - the drum is attached to the wheel. Two curved brake shoes are pushed outward by wheel cylinder pistons which hold the drum by friction force. Brake shoes are made of metal and faced with friction material called brake lining which is riveted or cemented to the shoes. Drum Brakes
- 16. The lining is made of heat resistant materials like fiber glass or a semi-metallic material. Drum Brakes
- 17. Drum Brakes The main components of drum brakes are Brake drum Back plate Brake shoes Brake Liners. Retaining Springs Cam Brake Linkages
- 18. When the pedal is pressed the fluid pr pushes the shoes outwards through linkages, there by coming in frictional contact with the rotating drum. As soon as the brake pedal is released the retaining springs help the brake shoes to brought back and release the brakes. How a Drum Brakes Works
- 19. It has a metal disc or rotor instead of a drum and the braking is achieved by lined shoes or pads that are forced against a rotating disc. The pads are held in a caliper that straddles the disc. The caliper has one or more pistons which are activated by fluid pressure from the master cylinder. Disc brakes
- 20. Disc brakes
- 21. There are three types of disc brakes: Fixed-caliper disc brake. ◙ It has pistons on both sides of the disc, sometimes one on each side and sometimes two. ◙ The caliper is rigidly attached to the steering knuckle. Floating-caliper disc brake. ◙ It has one piston on the inboard side of the disc. ◙ The caliper moves or floats on rubber bushings on one or two steel guide pins. Types of Disc brake
- 22. Types of Disc brake
- 23. Sliding-caliper disc brake. Similar to the floating- caliper disc brake, except that the caliper moves slightly on machined surfaces on the steering knuckle adapter or anchor plate. Types of Disc brake
- 24. The discs are made of gray cast Iron. It consists of rotating disc and two friction pads which are actuated by the four hydraulic wheel pistons contain in two halves of an assembly is called a caliper. The caliper assembly is secured to the steering knuckle in a front wheel brakes. The road wheel is fashioned to the outer surface of the disc. The friction pads rides freely on each side of the discs. They are in position being the hydraulic systems. Construction Disc brakes
- 25. When the brakes is applied hydraulic pressure is supply to the fluid inlet tube, due to which the wheel cylinder piston force the friction pads against the rotating disc. In the released piston, the spring hold the piston pads so that they maintain contact with disc surface. Disc brakes
- 26. Hydraulic brakes make used of hydraulic pr to force brake shoes out words against the brake drum based on PASCAL’S LAW. The main components of the service braking systems is a. Master Cylinder. b. Wheel Cylinder. Hydraulic brakes
- 27. When the driver release the brake pedal, the piston in the master cylinder returns back to its original position due to the return spring pressure. Thus the pistons in the wheel cylinder come back in its original inward position. Thus the brakes are released. When the brake pedal is pressed the piston is forced in to the master cylinder, the hydraulic pr is applied equally to all wheel cylinders. The pistons in the wheel cylinders pushed outwards against the brake drum. Hydraulic brakes
- 28. Master Cylinder The Master Cylinder is the heart of the hydraulic brake system. It consists of two main chambers. The fluid reservoir which contains the fluid to supply to the brake system, and the compression chamber in which the piston operates. The reservoir supplies fluid to the brake system through two ports.
- 29. The larger port is called the filler or intake part and is connected to the hollow portion of the piston between the primary and secondary cups which act as piston seals. The smaller port is called the relief, bypass or compensating port which connects the reservoir directly with the cylinder and lines when the piston is in the released position. Master Cylinder
- 30. When the pedal is pushed down, the piston pushed toward the closed end of the MC and sends the fluid from the front pr chamber to the front wheel brakes. Fluid from the rear chamber is sent to the rear wheel brakes. All four brakes then operate to slow or stop the veh. Master Cylinder If there are two pistons in the master cylinder - known as the dual braking system. Dual braking system adds to the vehicle safety.
- 31. Wheel Cylinder It consists of two pistons which can move in opposite directions by the fluid pr and a spring in between. It is rigidly mounted on the brake shield or backing plate. Wheel cylinders are larger than the master cylinders and again, the front-wheel cylinders are larger than the rear-wheel cylinders.
- 32. When the brakes are applied the brake fluid enters the cylinder from a brake line connection inlet between the two pistons. It causes to force out the two pistons in opposite directions. This motion is transmitted to the brake shoe. Directly or through links force them against the brake drum, thus applying the brake. Wheel Cylinder
- 33. Parking brakes Parking brakes are mechanically operated brakes generally applied to the rear wheels to hold the vehicle stationary when it is parked. The two types of parking brakes are: ◙ Integral ◙ Independent
- 34. If both disc and drum brakes are used in a car, the front one is generally the disc brake. Disc brake provides more braking force than the drum brake During hard braking, more vehicle weight transfers to the front wheels A proportioning valve is used in the brake line with front- disc and rear-drum brakes If same braking force is applied to both front wheels and rear wheels, the rear wheels become locked and try to skid. Imp Point to be Note
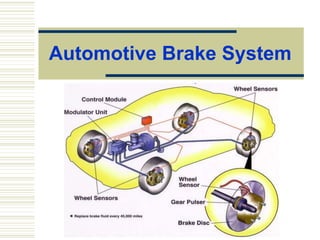
- 35. When the wheel skids, kinetic friction results and when the wheel still rotates the friction is static. Static friction is generally more than the kinetic friction, i.e. static friction gives better braking force. Anti-lock braking system (ABS) An ABS is designed to modulate braking pr to attain the peak coefficient of kinetic friction between the tire and the road, and thereby prevents wheel lockup & skidding. An ABS, under hard braking conditions, is designed to reduce stopping distances under most conditions, while maintaining vehicle stability and steer ability.
- 36. Basically, there are sensors at each of the four wheels. These sensors watch the rotation of the wheels. When any one of the wheels stops rotating due to too much brake application, the sensors tell the computer, which then releases some of the brake line pr that you have applied - allowing the wheel to turn again. Then, just as fast as it released the pr, the computer allows the pr to be applied again - which stops the rotation of the wheel again. Then it releases it again. And so on. With most ABS, this releasing and re-application - or pulsing - of the brake pr happens 20 or more times per second. ABS prevents you from ever locking up the brakes and skidding - no matter how hard you apply the brakes. Anti-lock braking system (ABS)
- 37. Wheel Speed Sensors (up to 4) Electronic Control Unit (ECU) A Brake Master Cylinder, with accompanying Hydraulic Modulator Unit and Solenoid Valves Vehicle’s Physical Brakes Typical ABS Components