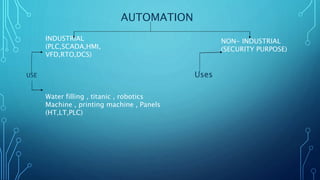
This document summarizes a seminar presentation about programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It introduces PLCs, describing their history and role in industrial automation. The presentation discusses the physical structure of PLCs, including their rack or chassis, power supply module, central processing unit, input/output modules, and communication interfaces. It also outlines the main types of PLCs and provides examples of their applications in water filling, manufacturing machinery, and other industrial processes. Finally, the document compares PLCs to SCADA systems.