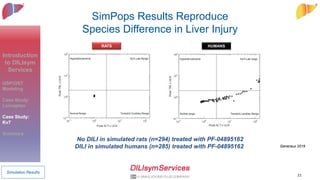
Dilisym Services Inc. develops and applies Quantitative Systems Pharmacology (QSP) and Quantitative Systems Toxicology (QST) modeling to support drug development, focusing on predicting drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and integrating various biological data. The document details case studies on lixivaptan, a vasopressin receptor antagonist, and pf-04895162, an epilepsy drug, demonstrating the utility of their modeling in assessing liver safety signals in different species. Dilisym's modeling capabilities aim to enhance drug safety and efficacy, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.