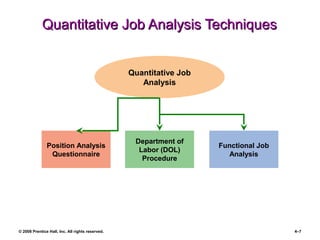
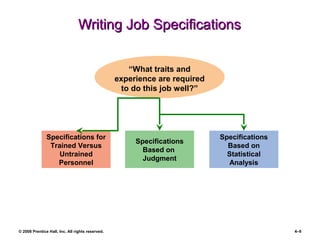
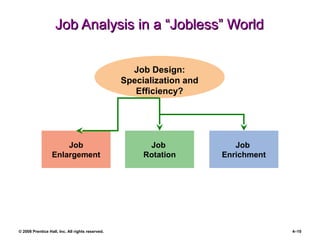
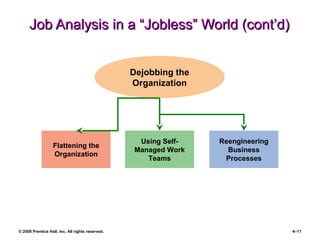
The document is a PowerPoint presentation focused on job analysis within human resource management, outlining its importance, methods of collection, and writing job descriptions and specifications. Key methods discussed include interviews, questionnaires, and observational techniques, along with their advantages and disadvantages. It also touches upon job analysis in a modern context, including concepts like job enlargement and dejobbing.