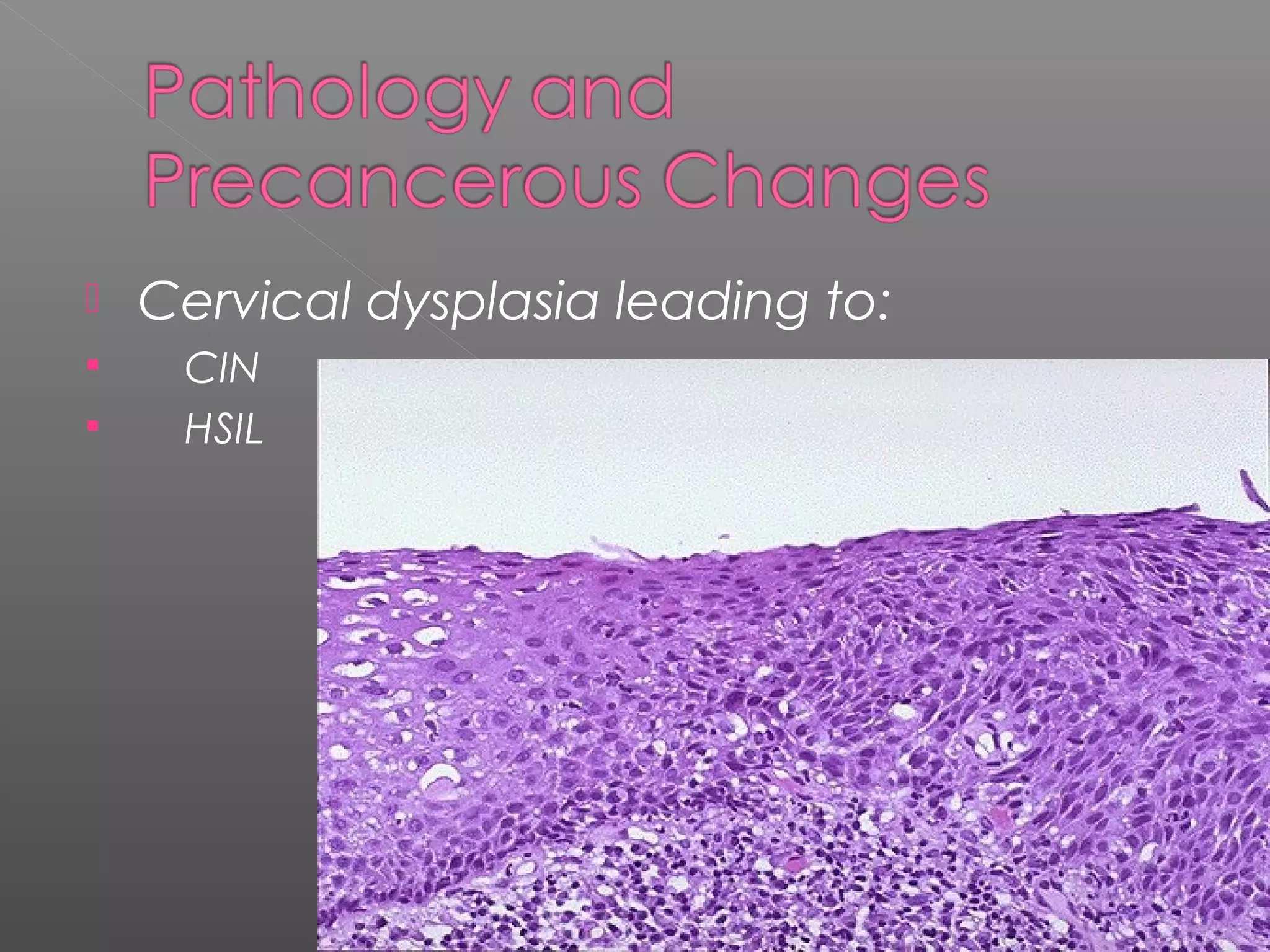
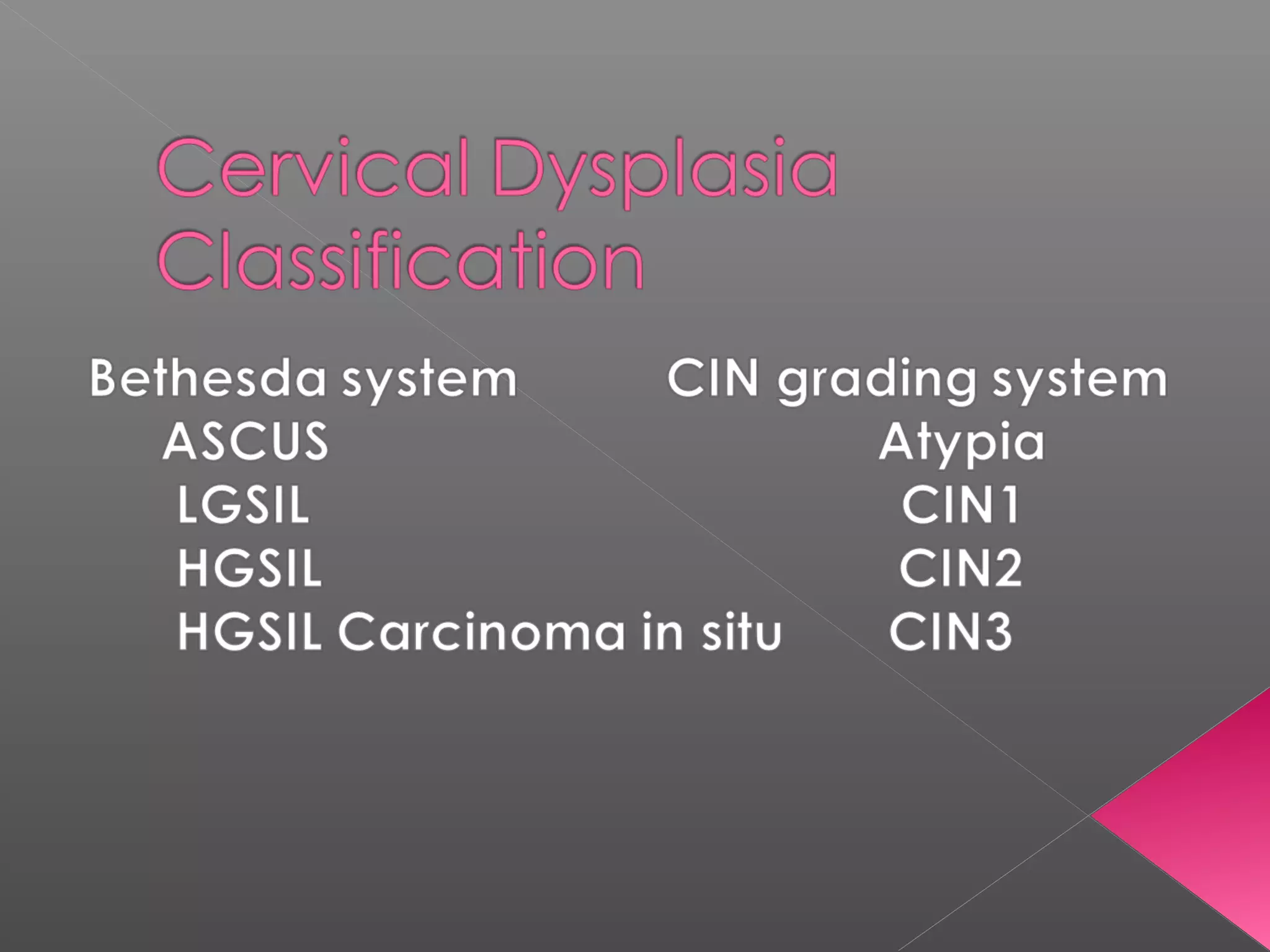
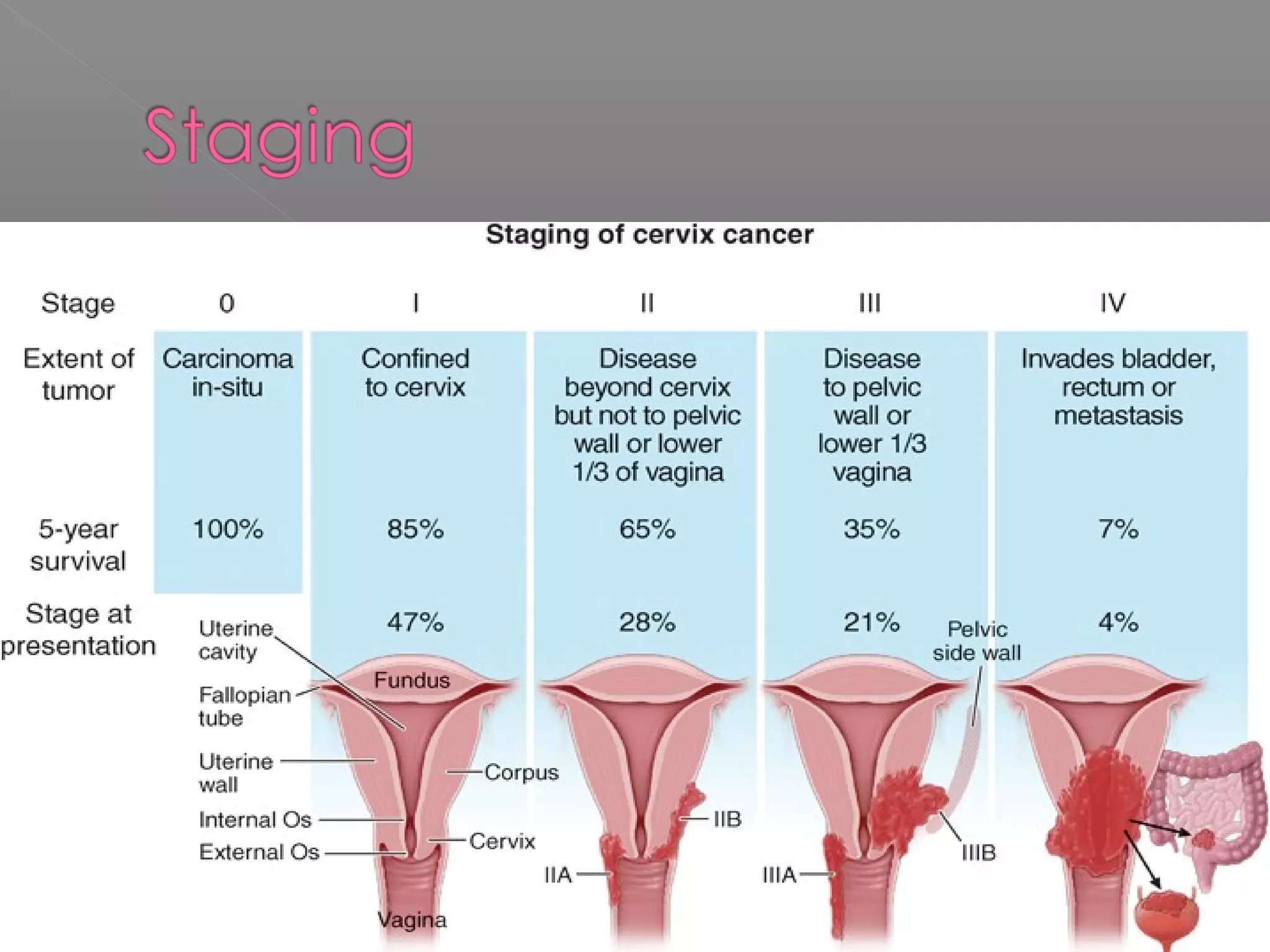
This document discusses cervical cancer. It begins by defining cervical cancer and noting that it is a common cause of death in developing countries. It occurs most often in younger women of childbearing age. Risk factors include HPV infection, multiple sexual partners, smoking, early sexual activity, and poor hygiene. Symptoms can include abnormal bleeding or discharge. Screening involves Pap smears and biopsies, while treatment options are cone biopsies, hysterectomies, radiation, and chemotherapy. The document provides details on the histological classification and diagnostic evaluation of cervical cancer.