Pathogenesis of cell injury By Rohit Kumar Trivedi
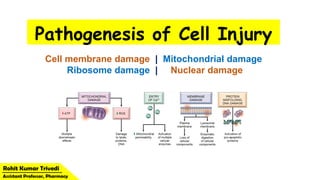
- 1. Pathogenesis of Cell Injury. Cell membrane damage | Mitochondrial damage Ribosome damage | Nuclear damage
- 2. https://youtu.be/DqPU9iz-Dl8 Video Lecture Link Click or Paste above given link to your internet browser
- 3. Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. What is Pathogenesis…??
- 4. ▪ Cell injury (Cell Damage) is defined as the functional and morphologic effects of a variety of stresses on the cell from various etiologic agents which result in change in its internal and external environment. Cell Injury Normal Cell Adaptation Reversible Cell Injury Irreversible Cell Injury (Cell Death) Stress Mild Stress Persistent
- 5. • Mitochondria are critical players in cell injury and cell death by all pathways. • They supply life-sustaining energy by producing ATP. • Mitochondria can be damaged by 1. Increase in cytosolic Ca2+ 2. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) developed due to abnormal oxidative phosphorylation 3. Oxygen deprivation • And so they are sensitive to virtually all types of injurious stimuli, including hypoxia and toxins. In addition, mutations in mitochondrial genes are the cause of some inherited diseases Mitochondrial Damage
- 6. There are three major consequences of mitochondrial damage: 1. Mitochondrial damage often results in the formation of a high-conductance channel in the mitochondrial membrane, called the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. The opening of this conductance channel leads to the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, resulting in failure of oxidative phosphorylation and progressive depletion of ATP, culminating in necrosis of the cell. 2. Abnormal oxidative phosphorylation also leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species, which have many deleterious effects. 3. The mitochondria sequester (store) between their outer and inner membranes several proteins that are capable of activating apoptotic pathways; these include cytochrome-c and proteins that indirectly activate apoptosis- inducing enzymes called caspases. Increased permeability of the outer mitochondrial membrane may result in leakage of these proteins into the cytosol and death by apoptosis. Mitochondrial Damage (cont..)
- 7. Depletion of ATP ▪ Reduction in ATP levels is fundamental cause of necrotic cell death. ▪ ATP depletion and decreased ATP synthesis are frequently associated with both hypoxic and chemical (toxic) injury. ▪ ATP is produced in two ways: 1. The major pathway in mammalian cells is oxidative phosphorylation of adenosine diphosphate (ADP). 2. The second is the glycolytic pathway, which can generate ATP in the absence of oxygen using glucose derived either from body fluids or from the hydrolysis of glycogen. ▪ The major causes of ATP depletion are reduced supply of oxygen and nutrients, mitochondrial damage, and the actions of some toxins (e.g., cyanide).
- 8. ▪ High-energy phosphate in the form of ATP is required for virtually all synthetic and degradative processes within the cell. These include membrane transport, protein synthesis, lipogenesis, and the deacylation-reacylation reactions necessary for phospholipid turnover. ▪ Depletion of ATP to 5% to 10% of normal levels has widespread effects on many critical cellular systems ▪ The activity of the plasma membrane energy dependent sodium pump (Na+, K+-ATPase) is reduced. Cellular energy metabolism is altered: ▪ If the supply of oxygen to cells is reduced, as in ischemia, oxidative phosphorylation ceases, resulting in a decrease in cellular ATP and associated increase in adenosine monophosphate. ▪ These changes stimulate phosphofructokinase and phosphorylase activities, leading to an increased rate of anaerobic glycolysis, which is designed to maintain the cell’s energy sources by generating ATP through metabolism of glucose derived from glycogen. ▪ As a consequence glycogen stores are rapidly depleted. Anaerobic glycolysis results in the accumulation of lactic acid and inorganic phosphates from the hydrolysis of phosphate esters. ▪ This reduces the intracellular pH, resulting in decreased activity of many cellular enzymes. Depletion of ATP (cont..)
- 9. ▪ Failure of the Ca2+ pump leads to influx of Ca2+, with damaging effects on numerous cellular components. ▪ With prolonged or worsening depletion of ATP, structural disruption of the protein synthetic apparatus occurs, manifested as detachment of ribosomes from the rough ER and dissociation of polysomes, with a consequent reduction in protein synthesis. ▪ In cells deprived of oxygen or glucose, proteins may become misfolded, and accumulation of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) triggers a cellular reaction called the unfolded protein response that may culminate in cell injury and even death. ▪ Ultimately, there is irreversible damage to mitochondrial and lysosomal membranes, and the cell undergoes necrosis. Depletion of ATP (cont..)
- 10. ▪ Cytosolic free calcium is normally maintained at very low concentrations (~0.1 µmol) compared with extracellular levels of 1.3 mmol. ▪ Most intracellular calcium is sequestered (stored) in mitochondria and the ER. ▪ Ischemia and certain toxins cause an increase in cytosolic calcium concentration, initially because of release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores, and later due to increased influx across the plasma membrane. Increased intracellular Ca2+ causes cell injury by several mechanisms: 1. The accumulation of Ca2+ in mitochondria results in opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and failure of ATP generation. 2. Increased cytosolic Ca2+ activates a number of enzymes with potentially deleterious effects on cells. These enzymes include: ▪ Phospholipases (which cause membrane damage), ▪ Proteases (which break down both membrane and cytoskeletal proteins), ▪ Endonucleases (which are responsible for DNA and chromatin fragmentation), ▪ ATPases (thereby hastening ATP depletion). 3. Increased intracellular Ca2+ levels also result in the induction of apoptosis, by direct activation of caspases and by increasing mitochondrial permeability. Influx of Calcium and Loss of Calcium Homeostasis
- 11. ▪ Cell injury induced by free radicals, particularly Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), is an important mechanism of cell damage in many pathologic conditions. ▪ Free radicals are chemical species that have a single unpaired electron in an outer orbit. ▪ Unpaired electrons are highly reactive and “attack” & modify adjacent molecules, such as : • Proteins, • Lipids • Carbohydrates • Nucleic acids—many of which are key components of cell membranes and nuclei. • ROS are produced normally in cells during mitochondrial respiration and energy generation, but they are degraded and removed by cellular defense systems. • Increased production or decreased scavenging of ROS may lead to an excess of these free radicals, a condition called oxidative stress. • ROS are also produced in large amounts by activated leukocytes, particularly neutrophils and macrophages, during inflammatory reactions aimed at destroying microbes and cleaning up dead cells and other unwanted substances Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress)
- 12. Generation of Free Radicals: ▪ The reduction-oxidation reactions that occur during normal metabolic processes. ▪ Absorption of radiant energy (e.g., ultraviolet light, x-rays). ▪ Rapid bursts of ROS are produced in activated leukocytes during inflammation. ▪ Enzymatic metabolism of exogenous chemicals or drugs can generate free radicals that are not ROS but have similar effects. ▪ Transition metals such as iron and copper donate or accept free electrons during intracellular reactions and catalyze free radical formation Removal of Free Radicals: It include the following: ▪ Antioxidants: Examples are the lipid-soluble vitamins E and A as well as ascorbic acid and glutathione in the cytosol. ▪ Binding of free iron and copper to storage and transport proteins transferrin, ferritin, lactoferrin, and ceruloplasmin), which prevents these metals from participating in reactions that generate ROS. ▪ Free radical-scavenging systems (Enzymes) 1. Catalase 2. Superoxidase dismutases (SODs) 3. Glutathione peroxidase Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) cont..
- 13. Pathologic Effects of Free Radicals: 1. Lipid peroxidation in membranes (oxidative degradation of lipids) 2. Oxidative modification of proteins 3. Lesions in DNA. Accumulation of Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals (Oxidative Stress) cont..
- 14. • Early loss of selective membrane permeability, leading ultimately to overt membrane damage, is a consistent feature of most forms of cell injury (except apoptosis). Mechanisms of Membrane Damage: • Reactive oxygen species. • Decreased phospholipid synthesis • Increased phospholipid breakdown • Cytoskeletal abnormalities Cell Membrane Damage
- 15. ▪ Cells have mechanisms that repair damage to DNA, but if DNA damage is too severe to be corrected (e.g., after exposure to DNA damaging drugs, radiation, or oxidative stress), the cell initiates a suicide program that results in death by apoptosis. ▪ Activation of endonuclease and ROS leads to DNA damage. Nuclear Damage
- 16. Practice Questions ▪ What do you mean by pathogenesis? Discuss. ▪ How is ATP produced in our body? ▪ What is ATP depletion? Explain in detail. ▪ Discuss the mechanism of cell death due to ATP depletion. ▪ Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. Why? ▪ Discuss the role of mitochondrial damage in the pathogenesis of cell death. ▪ Discuss the mechanism of cell injury caused due to increases intracellular Ca2+ ions. ▪ What do you mean by ROS? Discuss. ▪ Discuss the generation and removal of free radicals from the cell. ▪ What are the pathologic effects of free radicals? ▪ What do you mean by nuclear damage? Discuss its role in cell injury and cell death.
- 17. Rohit Kumar Trivedi Assistant Professor, Pharmacy
