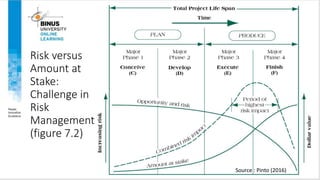
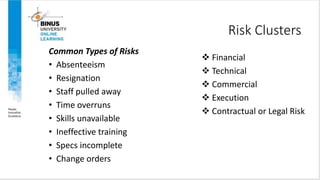
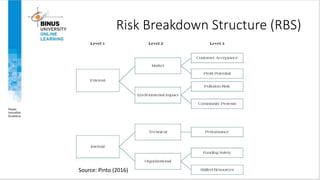
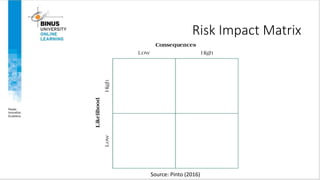
This document discusses project risk management. It defines project risk and outlines the four key stages of risk management: identification, analysis, mitigation strategies, and control/documentation. It describes five common sources of project risk and four approaches to risk identification. The document also explains the Project Risk Analysis and Management (PRAM) process, which includes nine phases to assess risk over the project life cycle.