gene transfer techniques
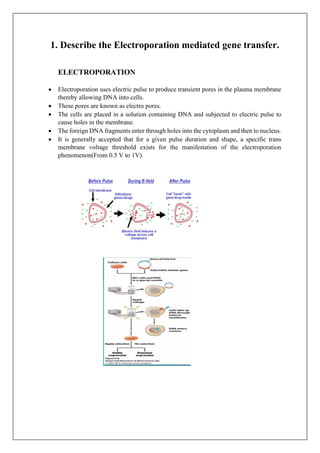
- 1. 1. Describe the Electroporation mediated gene transfer. ELECTROPORATION • Electroporation uses electric pulse to produce transient pores in the plasma membrane thereby allowing DNA into cells. • These pores are known as electro pores. • The cells are placed in a solution containing DNA and subjected to electric pulse to cause holes in the membrane. • The foreign DNA fragments enter through holes into the cytoplasm and then to nucleus. • It is generally accepted that for a given pulse duration and shape, a specific trans membrane voltage threshold exists for the manifestation of the electroporation phenomenon(From 0.5 V to 1V).
- 2. ADVANTAGES • Method is fast • Less costly • Applied for a number of cells • Simultaneously a large number of cells can be treated • High percentage of stable transformant can be produced 2. Describe the particle bombarded medicated gene transfer. BIOLISTIC OR MICRO-PROJECTILE • Prof Sanford and colleagues at Cornell University (USA) developed the original bombardment concept in 1987 and coined the term “biolistic” (short for “biological ballistics”) for both the process and the device. • Also termed as particle bombardment, particle gun, micro projectile bombardment and particle acceleration. • It employs high-velocity micro projectiles to deliver substances into cells and tissues. • Biolistic or particle bombardment is a physical method that uses accelerated micro- projectile to deliver DNA or other molecules into intact cells and tissues. • The gene gun is the device that literally fires the DNA into target cells. • The DNA to be transformed into the cells is coated onto microscopic beads made of either gold or tungsten. • The coated beads are then attached to the end of the plastic bullet and loaded into the firing chamber of the gene gun. • An explosive force fires the bullet with DNA coated beads towards the target cells that lie just beyond the end of the barrel. • Some of the beads pass through the cell wall into the cytoplasm of the target cells.
- 3. USES • This method is commonly employed for genetic transformation of plants and many organisms. • This method is applicable for the plants having less regeneration capacity and those which fail to show sufficient response to Agrobacterium– mediated gene transfer in rice, corn wheat, chickpea, sorghum and pigeon-pea. LIMITATIONS • Shallow penetration of particles. • Can cause the cell damage. • The inability to deliver the DNA systematically. • The tissue to incorporate the DNA may not be able to regenerate. • The equipment itself is very expensive. 3. Describe the Microinjection method of gene transfer. MICRO INJECTION • DNA microinjection was first proposed by Dr. Marshall A. Barber in the early of nineteenth century. • This method is widely used for gene transfection in mammals. • Micro injection is the process of transferring the desirable DNA into the living cell, through the use of glass pipette. • Glass pipette is usually of 0.5 to 5 micro meters, easily penetrate into cell membrane and nuclear envelope. • The desired gene is delivered into subcellular compartment and needle is removed.
- 4. ADVANTAGES • No requirement of a marker gene. • Introduction of the target gene directly into a single cell. • Easy identification of transformed cells upon injection of dye along with the DNA. • No requirement of selection of the transformed cells using antibiotic resistance or herbicide resistance markers. • It can be used for creating transgenic organisms, particularly mammals. LIMITATIONS • Costly • Skilled personal required • More useful for animal cells 4. Describe the calcium phosphate co precipitation CALCIUM PHOSPHATE CO PRECIPITATION • It is also called as Calcium phosphate mediated DNA transfer • Involves the formation of a fine DNA /Calcium phosphate co precipitate which first settles on the cells and then internalized by endocytosis • The process of transfection involves the mixing of isolated DNA with solution of calcium chloride and potassium phosphate of calcium phosphate to be formed • Cells are then incubated with precipitated DNA.A fraction of cells will take up the Calcium phosphate DNA precipitate by endocytosis. • Transfection efficiencies using Calcium phosphate can be quite low, in the range of 1- 2%.
- 5. 5. Describe the liposome mediated dna transfer • A Liposome is a spherical shaped vesicle that is composed of one or more phospholipid bilayers which closely resembles that structure of cells act as delivery agents for exogenous materials including transgender • 3 types of lipids: •Anionic (Negatively charged) •Neutral •Cationic (Positively charged) • Cationic lipids Liposomes are able to interact with the negatively charged cell membrane more easily than unchanged Liposome. The fusion between cationic Liposome and the cell surface resulting in the delivery of the DNA directly across the plasma membrane.
- 6. 6. Describe diethyl-amino-ethyl-dextran (deae) co-precipitation • DNA can be transferred with the help of DEAE Dextran also • If DEAE-Dextran-treatment is coupled with Dimethyl sulphoxide shock, then up to 80% transformed cell can express the transformed gene • DEAE- dextran mediated transfection is more sensitive than calcium phosphate co precipitation
- 7. 7. Describe ADENO VIRUS mediated gene transfer. • Adenoviruses are non-enveloped DNA viruses, linear genome and ds DNA molecule of about 36kb. • Genome regions: distinguished into early (E) and late (L) transcription regions. • Adenoviral vectors have a wide range of action and are able to deliver nucleic acids to both dividing and non-dividing cells. STRUCTURE OF ADENOVIRUS
- 8. MECHANISM OF ADENOVIRUS MEDIATED GENE TRANSFER 8. Describe RETROVIRUS mediated gene transfer. • Retroviruses are a class of enveloped viruses that contain 2 copies of single strand sense (+) RNA genome that replicates via double stranded DNA intermediate. • Viral genome is 7-10kb in size, containing at least three genes: gag, pol, env • The gag gene encodes a viral structural protein, pol encodes the reverse Transcriptase and integrase and the env gene encodes viral envelope proteins. STRUCTURE OF RETROVIRUS
- 9. CONSTRUCTION OF RETROVIRAL VECTORS 9. Describe agrobacterium mediated gene transfer/ describe the structure of Ti plasmid and TDNA structure. AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENE TRANSFER • Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil borne gram negative bacterium. • It invades many dicot plants when they are injured at the soil level and causes crown gall disease. • The ability to cause crown gall disease is associated with the presence of the Ti (tumour inducing) plasmid within the bacterial cell. • Ti plasmid can be used to transport new genes into plant cells. • There are two species of agrobacterium - Agrobacterium tumefaciens that induces crown gall disease. - Agrobacterium rhizogene that induces hairy root disease. • It is a phyto-pathogen it is mainly treated as the nature’s most effective plant genetic engineer
- 10. Ti - PLASMIDS • A remarkable feature of the Ti plasmid is that, after infection, part of the molecule is integrated into the plant chromosomal DNA. • This segment, called the T-DNA, is between 15 and 30 kb in size, depending on the strain. • T-DNA contains eight or so genes that are expressed in the plant cell and are responsible for the cancerous properties of the transformed cells. • These gene also direct synthesis of unusual compounds, called opines, that the bacteria use as nutrient. • The vir (virulence) region of the Ti - plasmid contains the genes required for the T - DNA transfer process. • The genes in this region encode the DNA processing enzymes required for excision, transfer and integration of the T - DNA segment. • The T - DNA region of any Ti plasmid is defined by the presence of the right and the left border sequences. • These border sequences are 24 bp imperfect repeats. • Any DNA between the borders will be transferred into the genome of the plant. • Ti plasmid consists of • T-DNA region- this region has the genes for the biosynthesis of Auxin (aux),Cytokinin(cyt), opine(ocs) . • T DNA borders - A set of 24kb sequence present on both right and left border. • Virulence region- the gene responsible for the transfer of T-DNA into the host plant are located outside T-DNA and the region is referred to as vir or virulence region. vir gene codes for proteins involved in T-DNA transfer. • Opine metabolism region -Codes for proteins involved in the uptake and metabolism of opines. • Ori region - origin of DNA replication which permits the Ti plasmid to the stably maintained agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- 11. STRUCTURE OF Ti - PLASMID Ti - PLASMID MEDIATED TRANSFER OF GENE INTO A PLANT • The Ti - plasmid has an innate ability to transmit bacterial DNA into plant cells. • The gene of a donor organism can be introduced into the Ti plasmid at the T - DNA region. • This plasmid now becomes a recombinant plasmid. • By Agrobacterium infection, the donor genes can transferred from the recombinant Ti plasmid and integrated into the genotype of the host plant. T-DNA TRANSFER AND INTEGRATION: The process of T-DNA transfer and its integration into the host plant genome 1. Signal induction to Agrobacterium: The wounded plant cells release certain chemicals- phenolic compounds and sugars which are recognized as signals by Agrobacterium. The signals induced result in a sequence of biochemical events in Agrobacterium that ultimately helps in the transfer of T-DNA of Ti- plasmid. 2. Attachment of Agrobacterium to plant cells: The Agrobacterium attaches to plant cells through polysaccharides, particularly cellulose fibres produced by the bacterium. 3. Production of virulence proteins: As the signal induction occurs in the Agrobacterium cells attached to plant cells, a series of events take place that result in the production of virulence proteins. To start with, signal induction by Phenolic stimulates vir A which in turn activates (by phosphorylation) vir C. This induces expression of virulence genes of Ti plasmid to produce the corresponding virulence proteins (D1, D2, E2, B, etc.). Certain sugars (e.g. glucose, galactose, xylose ) that induce virulence genes have been identified. 4. Production of T-DNA strand: The right and left borders of T-DNA are recognized by vir D1/vir D2 proteins. These proteins are involved in the production of single-stranded T-DNA, its protection and export to plant cells. The ss T-DNA gets attached to vir D2. 5. Transfer of T-DNA out of Agrobacterium:
- 12. The ss T-DNA-vir D2 complex in association with vir G is exported from the bacterial cell. Vir B products form the transport apparatus. 6. Transfer of T-DNA into plant cells and integration: The T-DNA-vir D2 complex crosses the plant plasma membrane. In the plant cells, T- DNA gets covered with vir E2. This covering protects the T-DNA from degradation by nucleases; vir D2 and vir E2 interact with a variety of plant proteins which influences T- DNA transport and integration. The T-DNA-vir D2-vir E2-plant protein complex enters the nucleus through nuclear pore complex. Within the nucleus, the T-DNA gets integrated into the plant chromosome through a process referred to illegitimate recombination.
- 13. ADVANTAGES OF AGROBACTERIUM MEDIATED GENE TRANSFER 1. Simple and comparatively less expensive 2. High transformation efficiency 3. Transgenic crops obtained have better fertility percentage 4. Protocols for both di-cotyledons and monocotyledon are available 5. Relatively large length DNA segment can be transferred