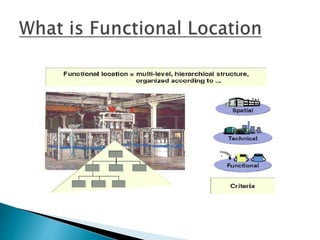
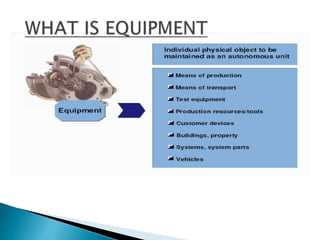
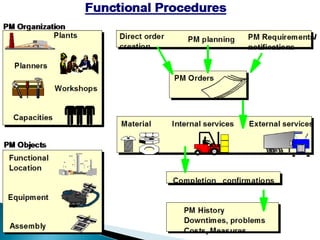
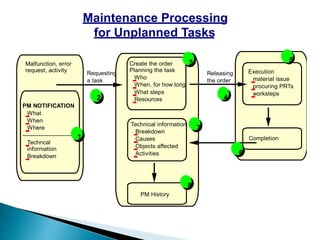
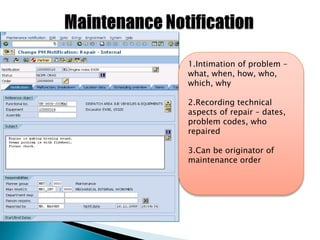
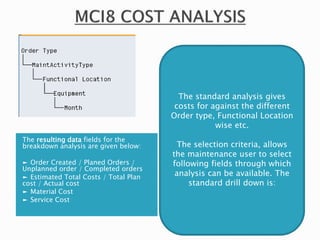
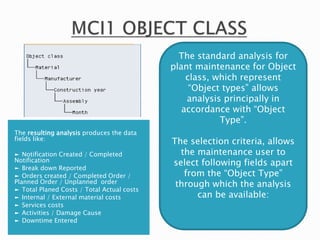
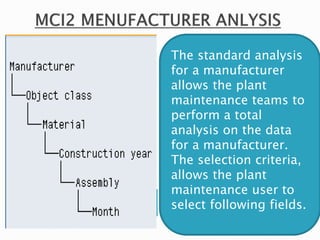
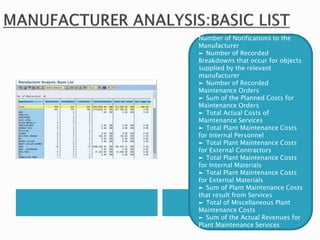
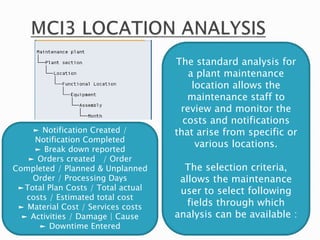
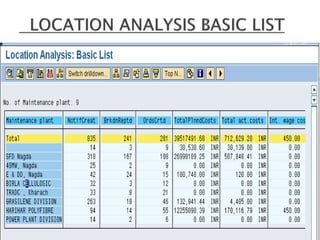
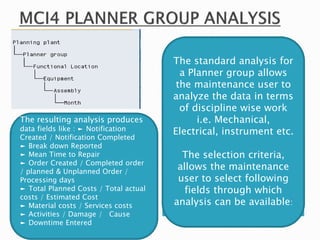
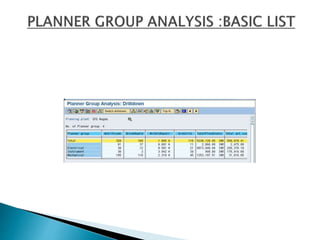
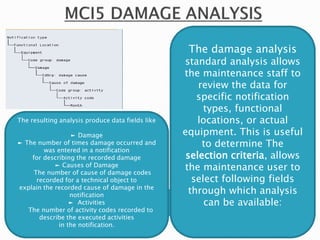
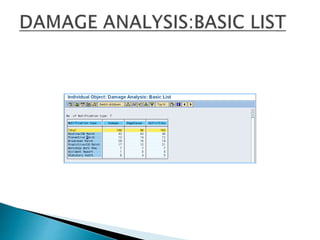
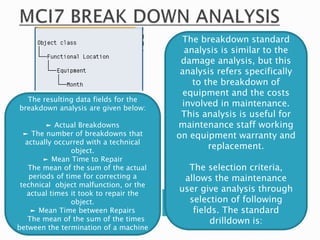
The document discusses the benefits of SAP's Plant Maintenance (PM) module. The PM module allows companies to: 1) plan and manage preventative maintenance to reduce breakdowns and increase equipment availability; 2) identify and rectify equipment problems whether from failure or deterioration; and 3) break maintenance down into different levels for both planning and performing tasks at either the individual equipment or functional location level. Overall, the PM module standardizes maintenance practices, integrates maintenance with other business functions, and provides structured cost and equipment history data for better resource control and cost management.