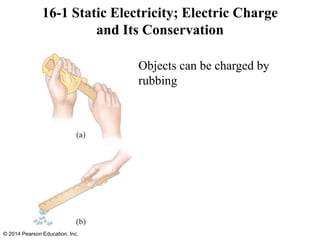
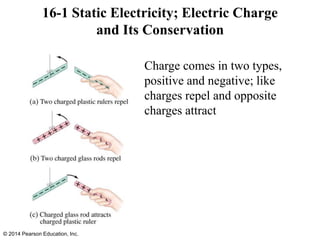
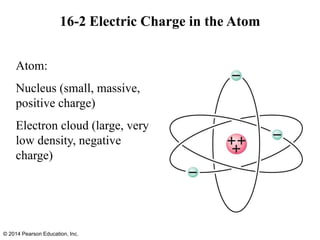
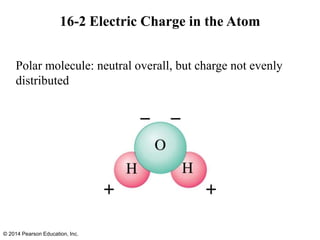
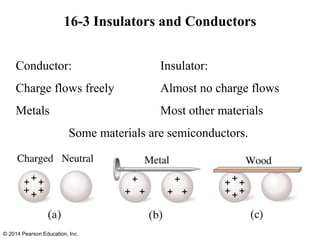
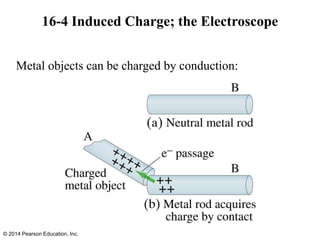
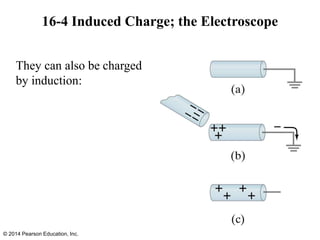
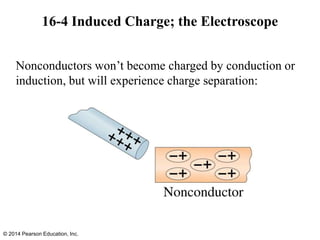
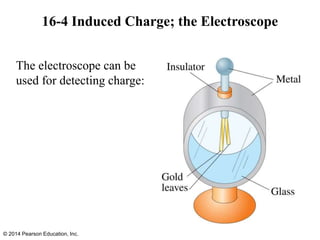
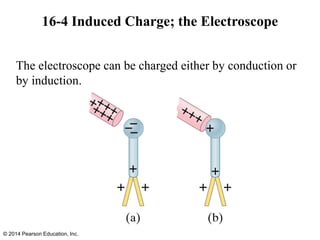
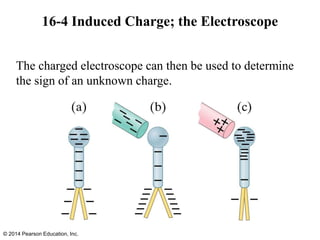
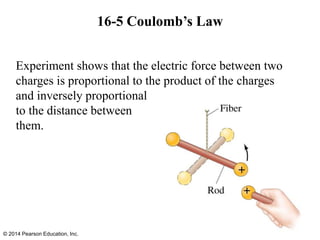
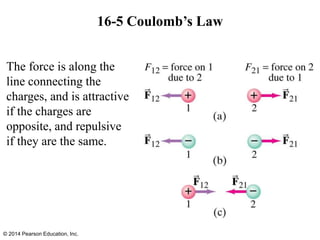
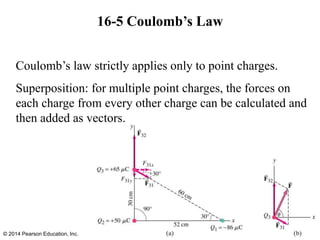
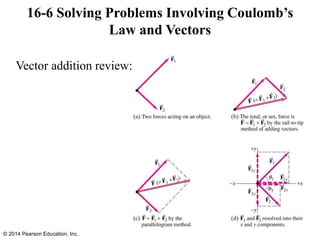
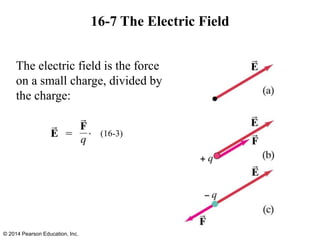
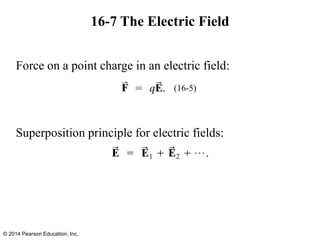
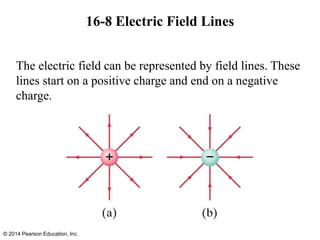
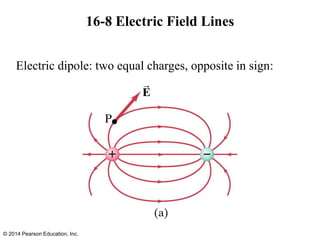
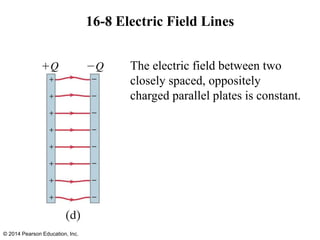
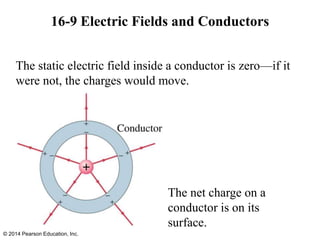
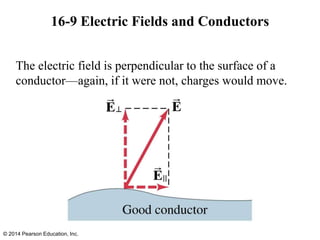
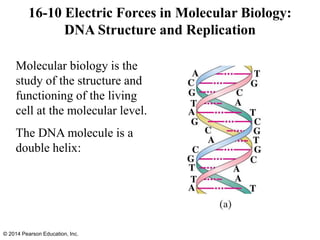
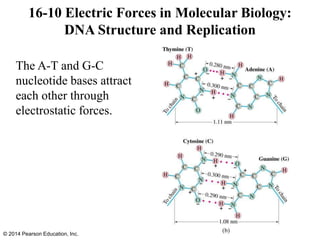
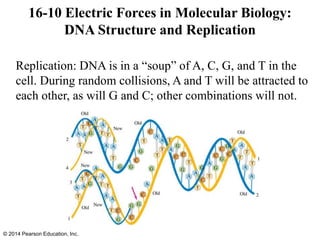
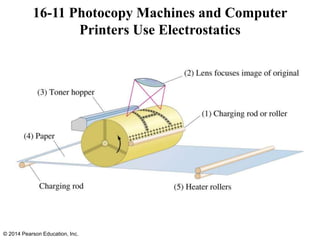
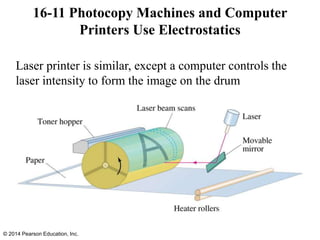
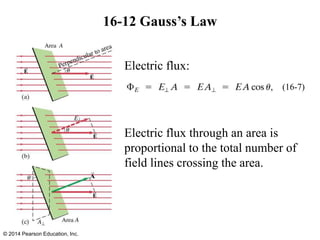
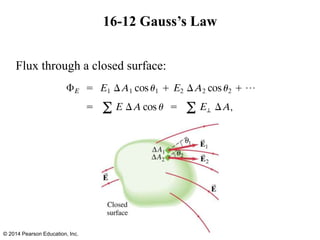
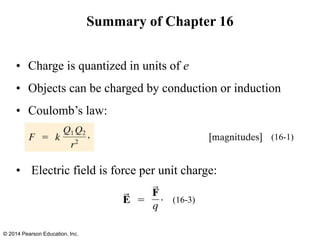
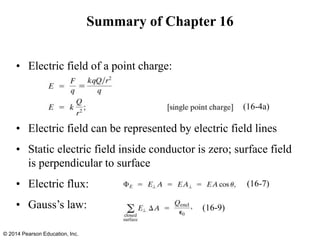
The document is a chapter from a physics textbook about electric charge and electric fields. It covers topics such as electric charge, Coulomb's law, electric fields, electric field lines, conductors, Gauss's law, and applications like photocopiers and DNA structure. Diagrams and equations are included to illustrate key concepts and formulas.