The document summarizes a presentation on thought and thought disorders. It defines thought, describes different types of thinking (fantasy, imaginative, rational), and characteristics of healthy thinking. It then discusses thought disorders, formal thought disorders, and specific disorders like flight of ideas, poverty of speech, circumstantiality, and loose associations. Research on thought disorders in schizophrenia is mentioned, focusing on structural brain abnormalities and biomarkers.


![THOUGHT
Thought - what we think
Language of the mind[propositional thought - hear in
the mind, imaginal thought – see in the mind]
Goal oriented flow of ideas and associations that leads
to reality oriented conclusion.
An idea or opinion produced by thinking or occurring
suddenly in the mind](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-3-2048.jpg)
![TYPES OF THINKING
Fantasy [ autistic or dereistic]
Imaginative
Rational or conceptual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-4-2048.jpg)











![THOUGHT DISORDERS
Any disturbance of thinking that affects language ,
communication and thought content
Disturbances of thoughts : change in nature of
individual thoughts i.e. disorder of content of
thoughts [ obsession& compulsions, delusions and
overvalued idea]
Disturbances of thinking process: change in speed or
form of relationships between thoughts, individual
thoughts are unremarkable in nature[ formal thought
disorders]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-16-2048.jpg)

![Formal thought disorders
Disruption of normal flow of thought
Disturbances in organization and expression of thoughts
BLEULER – formal thought disorders are core feature of
schizophrenia.
Syndrome with different symptoms resulting in thought ,
language and communication problems .
FTD – abnormality in amount and form of speech
Amount: poverty and pressure of speech
Form : disconnection symptoms[distractible speech, loss of
goal, loose associations, illogicality and incoherence]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-18-2048.jpg)




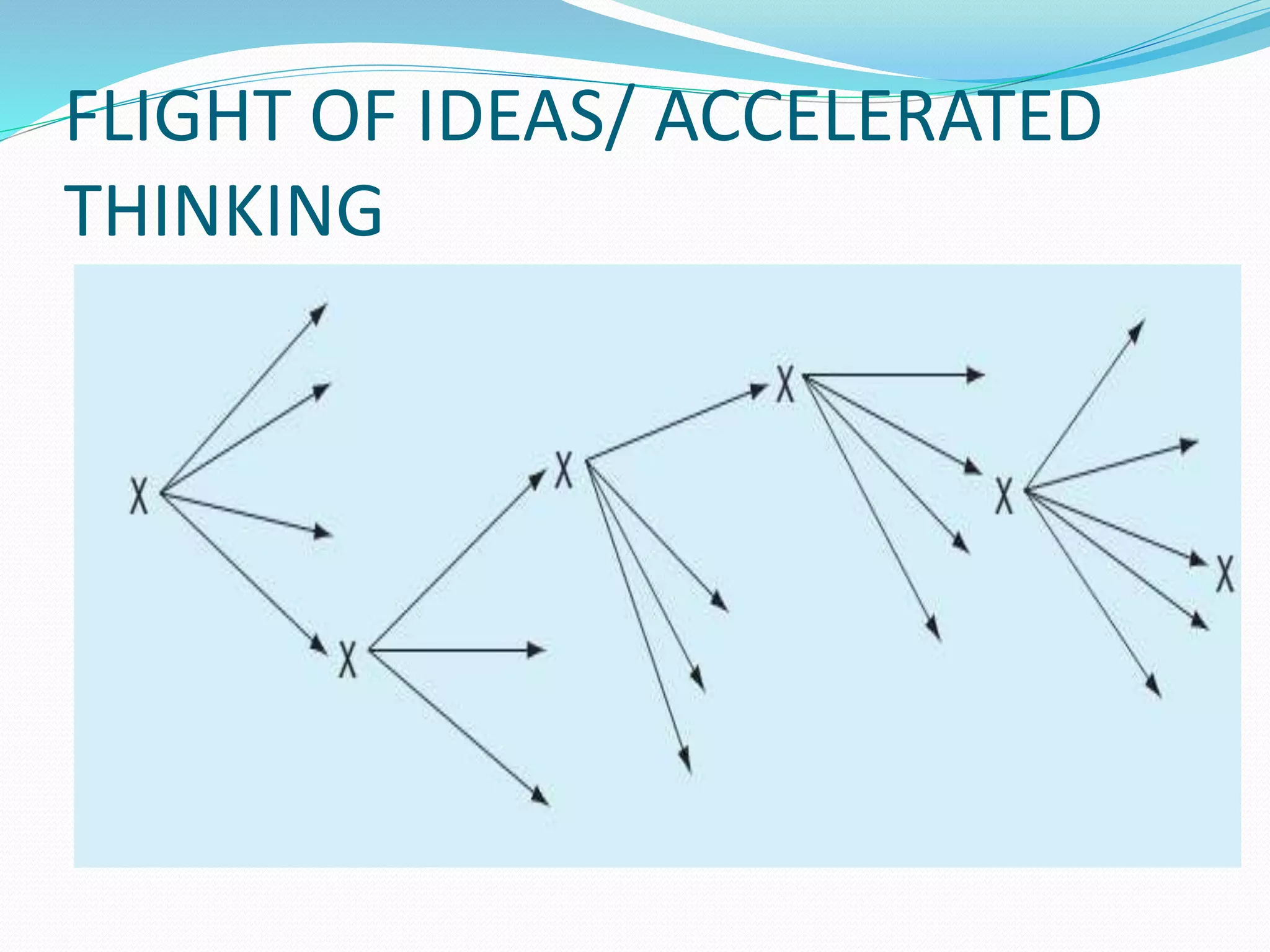
![FLIGHT OF IDEAS
Acceleration of flow of thinking
Rapid succession of thoughts
No general direction of thinking
Logical connection present
Easy distractibility [ external stimulus & internal
superficial associations]
Associations – chance factors or verbal
Verbal – clang , puns and rhymes
Clang – a 2nd word with sound similar to 1st
Puns – a 2nd meaning of first word
Typical of mania
Also in schizophrenia, organic brain disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-23-2048.jpg)



![INHIBITION OR SLOWING OF
THINKING
Thought process slowed down
Few thoughts [ ideas and mental images]
Lack of concentration, loss of clarity and difficulty in
making decisions
Defective attention- poor registration
Loss of memory and cognitive deficits [ Difficult to
differentiate from dementia]
Depression and manic stupor
Depression – anxious preoccupations and increased
distractibility due to anxiety.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-28-2048.jpg)


![CIRCUMSTANTIAL THINKING
Non linear thought pattern
Thinking proceeds slowly with unnecessary and trivial
details but finally the goal is reached.
Goal of thinking not lost completely
Proceeds in intricate and convoluted path
In OCD – excess detail is introduced anxiously to avoid any
omissions
Learning disabilities and temporal lobe epilepsy[
Geschwind syndrome-interictal changes in personality
progressing over time. Includes hypergraphia,
hyperreligiosity, atypical sexuality, circumstantiality and
intensified mental life]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-31-2048.jpg)







![DERAILMENT
Characterized by discourse consisting of sequence of
unrelated or remotely related ideas.
Slippage of ideas further and further away from point
of discussion.
Euphoria , hysteria and schizophrenia
Entgleisen[ derailment]- Schneider
Asyndesis- Cameron
Knight’s move thinking- Peter McKellar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-39-2048.jpg)


![INCOHERNCE[ WORD SALAD]
Pattern of speech that is incomprehensible
confused or unintelligible mixture of seemingly
random words and phrases
Set of words or phrases used together without any
arbitrary connection or grammatical rules
Schizophasia- speech confusion or word salad
occurs in schizophrenia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-42-2048.jpg)





![OVER INCLUSIVENESS
Ideas that are remotely linked to the concept become
incorporated within it in the patients thinking
Inability to preserve conceptual boundaries [Cameron]
Schizophrenia
Example: what are the essentials of room? Wall ,
doors, chairs and window](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-48-2048.jpg)






![DELUSIONS OF CONTROL OF
THOUGHT
Patient ascribes his own internal thought process to
outside influences – passivity
Thoughts as foreign or alien, not emanating from
himself and not within his control
Unable to discriminate between himself and outside
world
Passivity of thought, thought withdrawal, thought
broadcasting and thought insertion[ first rank
symptoms of schizophrenia]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-55-2048.jpg)

![RESEARCHES
FTD- lack of hemispheric asymmetry in language
areas
FTD: Structural abnormalities in left STG, left planum
temporale and orbito frontal cortex
FTD ; schizophrenia trait marker
Eotaxin – ECDC [ endogenous cognitive deteriorating
chemokine] is increased in patients with FTD’s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalthoughtdisorders-200414102502/75/Formal-thought-disorders-57-2048.jpg)

