Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Research Poster 2014
Similar to Research Poster 2014 (20)
PREVENTIVE AND CURATIVE IMPORTANCE OF THE BAROPODOMETRIC ANALYSIS FOR ERGONOM...

PREVENTIVE AND CURATIVE IMPORTANCE OF THE BAROPODOMETRIC ANALYSIS FOR ERGONOM...
The Effects of Heel Lift Height on Back Squat Performance

The Effects of Heel Lift Height on Back Squat Performance
EFFECT OF POSTURAL CONTROL BIOMECHANICAL GAIN ON PSYCHOPHYSICAL DETECTION THR...

EFFECT OF POSTURAL CONTROL BIOMECHANICAL GAIN ON PSYCHOPHYSICAL DETECTION THR...
Research Poster 2014
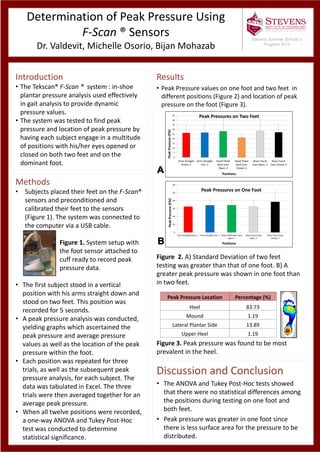
- 1. Determination of Peak Pressure Using F-Scan ® Sensors Dr. Valdevit, Michelle Osorio, Bijan Mohazab Introduction • The Tekscan® F-Scan ® system : in-shoe plantar pressure analysis used effectively in gait analysis to provide dynamic pressure values. • The system was tested to find peak pressure and location of peak pressure by having each subject engage in a multitude of positions with his/her eyes opened or closed on both two feet and on the dominant foot. Results • Peak Pressure values on one foot and two feet in different positions (Figure 2) and location of peak pressure on the foot (Figure 3). Figure 2. A) Standard Deviation of two feet testing was greater than that of one foot. B) A greater peak pressure was shown in one foot than in two feet. Figure 3. Peak pressure was found to be most prevalent in the heel. Methods • Subjects placed their feet on the F-Scan® sensors and preconditioned and calibrated their feet to the sensors (Figure 1). The system was connected to the computer via a USB cable. Figure 1. System setup with the foot sensor attached to cuff ready to record peak pressure data. • The first subject stood in a vertical position with his arms straight down and stood on two feet. This position was recorded for 5 seconds. • A peak pressure analysis was conducted, yielding graphs which ascertained the peak pressure and average pressure values as well as the location of the peak pressure within the foot. • Each position was repeated for three trials, as well as the subsequent peak pressure analysis, for each subject. The data was tabulated in Excel. The three trials were then averaged together for an average peak pressure. • When all twelve positions were recorded, a one-way ANOVA and Tukey Post-Hoc test was conducted to determine statistical significance. Discussion and Conclusion • The ANOVA and Tukey Post-Hoc tests showed that there were no statistical differences among the positions during testing on one foot and both feet. • Peak pressure was greater in one foot since there is less surface area for the pressure to be distributed. Stevens Summer Scholar’s Program 2014 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 Arms Straight Down, 2 Arms Straight Out, 2 Head Tilted Back Eyes Open, 2 Head Tilted Back Eyes Closed, 2 Nose Touch Eyes Open, 2 Nose Touch Eyes Closed, 2 PeakPressure(PSI) Positions Peak Pressures on Two Feet 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Arms Straight Down, 1 Arms Straight Out, 1 Head Tilted Back Eyes Open, 1 Nose Touch Eyes Open, 1 Nose Touch Eyes Closed, 1 PeakPressure(PSI) Positions Peak Pressures on One Foot Peak Pressure Location Percentage (%) Heel 83.73 Mound 1.19 Lateral Plantar Side 13.89 Upper Heel 1.19