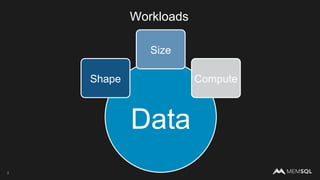
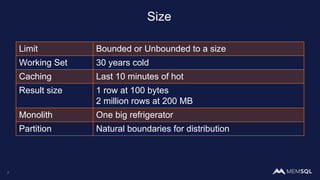
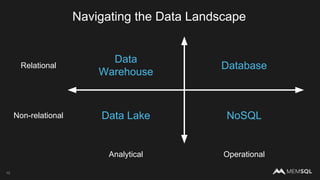
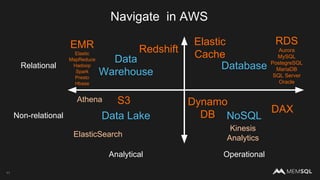
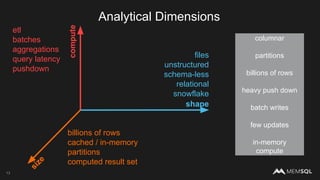
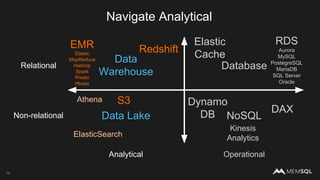
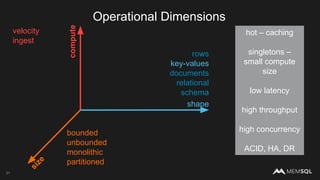
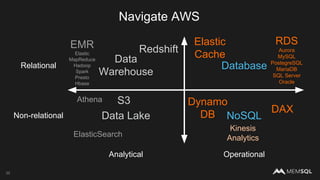
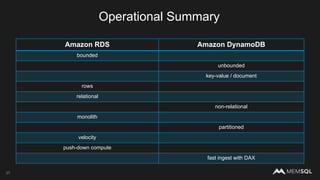
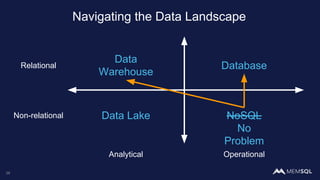
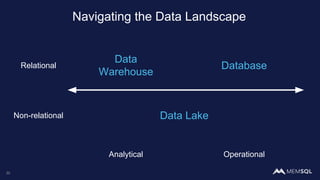
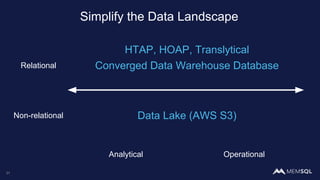
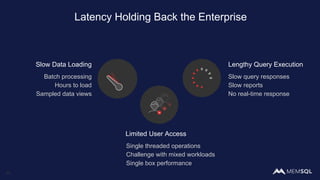
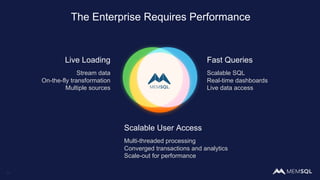
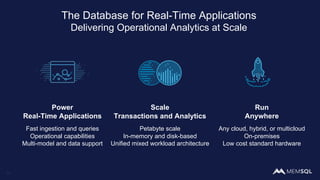
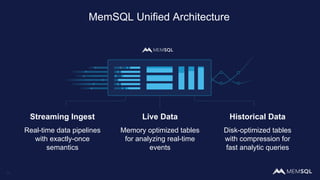
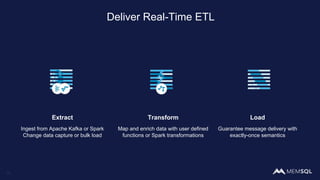
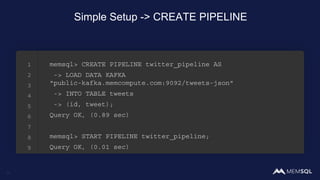
The document discusses the architecture of data within the AWS ecosystem, highlighting the integration of MemSQL for various database needs including operational, analytical, and real-time applications. It outlines the benefits of different AWS services such as DynamoDB, RDS, Redshift, and S3, emphasizing their capabilities and use cases in handling data effectively. Additionally, it touches on modern data processing challenges and solutions for scaling and efficient query performance in the cloud environment.