More Related Content
Similar to MauraLavelle_VurfPoster
Similar to MauraLavelle_VurfPoster (20)
MauraLavelle_VurfPoster
- 1. RESEARCH POSTER PRESENTATION DESIGN © 2015
www.PosterPresentations.com
Figure 6: A graph showing the average total deaths across
five times and five concentrations. About 50% of the death
in each group occurred within the first 24 hours and the
remaining death occurred between 96 hours and 120 hours.
END POINTS
• Range finding experiments: mortality, hatching, and malformations were observed every 24 hours until 120 hours post fertilization.
• Full early life stage test: additional endpoints will be broken into three categories as shown in Figure 8.
• Hydraulic fracturing, commonly referred to as fracking, is a method of
extracting natural gas out of shale deposits from deep underground.
• The fracking process requires the use of a fluid to be injected into the
earth at high pressures to crack shale deposits in order to release gas.
• While companies are not required to reveal the exact makeup of their
fracking fluid, some of the chemicals known to be used in the fracking
process are proven to be harmful to humans, animals, and ecosystems.
• Although the individual effects of some of the chemicals on human
health and the environment are known, little research has been done
studying the fracking fluid as a whole.
Figure 1: A breakdown of the components found within a typical fracking fluid
(FracFocus.com)
• Zebrafish are an ideal system to use to study the possible effects of
fracking fluid on a wide range of organisms.
• There is a high degree of similarity between zebrafish and mammals in
terms of mechanisms of development and physiology.
• Additionally, the embryonic development occurs outside of the mother
making the embryos completely visible to study.
Figure 2: Stages of zebrafish embryo development ranging from its zygote period until its
hatching period (Kimmel et al. 1995).
BACKGROUND
HYPOTHESIS AND OBJECTIVES
Figure 4: Layout of how treatments were set up in the 24 well-plates in each experiment. Each number represents a different treatment (1 is the most concentrated and
5 is the least concentrated) and the C represents the control. Five treatments (dilutions: 1/20, 1/50, 1/100, 1/200, and 1/500) were made fresh for each experiment and
a control of 1 x E3 medium was also used. Each 24 well plate contained two treatments with 12 embryos per treatment (1 per well) and 1mL of solution in each well.
After exposure, the 24 well plates were placed in a dehumidifying container which was placed in an incubation chamber to prevent evaporation.
METHODS AND MATERIALS FUTURE DIRECTIONS
• Creation of a cumulative concentration-response curve to obtain
concrete LC50 and EC50 values.
• Conduct a full early life stage test using LC50 and EC50 values while
expanding on range finding endpoints as shown below in Figure 8.
• Test individual chemicals commonly found in fracking fluids both
independently and in various mixtures.
• Boric Acid (crosslinking agent), Naphthalene (carrier fluid
for active surfactants), and Ethylbenzene (component of
crude oil)
• Potential for investigation of effects on gene expression.
REFERENCES
Ball, J.S., Stedman, D.B., Hillegass, J.M., Zhang, C.X., Panzica-Kelly, J.,
Coburn, A., Enright, B.P., Tornesi, B., Amouzadeh, H.R., Hetheridge, M.,
et al. (2014). Fishing for Teratogens: A Consortium Effort for a
Harmonized Zebrafish Developmental Toxicology Assay. Toxicological
Sciences 139, 210–219.
Brannen, K.C., Panzica-Kelly, J.M., Danberry, T.L., and Augustine-Rauch,
K.A. (2010). Development of a zebrafish embryo teratogenicity assay and
quantitative prediction model. Birth Defects Research Part B:
Developmental and Reproductive Toxicology 89, 66–77.
Hagenaars, A., Vergauwen, L., De Coen, W., and Knapen, D. (2011).
Structure–activity relationship assessment of four perfluorinated chemicals
using a prolonged zebrafish early life stage test. Chemosphere 82, 764–
772.
Kimmel, C.B., Ballard, W.W., Kimmel, S.R., Ullmann, B., and Schilling,
T.F. (1995). Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish.
Developmental Dynamics 203, 253–310.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS AND CONTACT
I would like to thank Dr. DiBenedetto for her guidance and support with
this project along with the Center for Undergraduate Research and
Fellowships for funding this project.
Maura Lavelle: mlavell6@villanova.edu
Dr. Angela DiBenedetto angela.dibenedetto@villanova.edu
Fracking fluid will have adverse effects on zebrafish embryogenesis.
1. Investigate embryo toxicity and teratogenicity of fracking fluid at
different concentrations.
2. Evaluate the effects of known components of fracking fluids on
zebrafish development, both independently and in combination.
3. Calculate LC50, EC50, and teratogenic index values.
LC50 values are regression estimates of the concentration at which 50% mortality occurs.
EC50 values are regression estimates of the concentration at which 50% of the embryos
showed an effect (mortality or malformation).
Teratogenic index (TI) is equivalent to LC50/ EC50.
Lavelle MM, DiBenedetto AJ, Department of Biology, Villanova University, Villanova PA
The Toxicological Effects of Fracking Fluid on the Developing Zebrafish Embryo
Figure 8: Full early life stage test toxicological endpoints for the lethal, sub lethal,
and teratogenic effects of chemicals, adapted from A. Hagenaars et al. (2011)
Endpoints 8 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108 120
Lethal
Death
Lack of hatching
Lack of somites
Sub lethal
Hatching
Spontaneous movement
Pericardial oedema
Yolk sac oedema
Heart rate*
Teratogenic
Malformation of the head
Malformation of the tail
Length*
Fracking
Exposure
Experiments
Range Finding Experiment
Salt Solution
Exposure
Experiments
Statistical Analysis to Obtain
LC50 and EC50
Full Early Life Stage Test
Figure 3: Simple layout of the experimental design for the overall project. Salinity testing and pH testing of the fracking fluid dilutions were completed prior to any
exposures. Salt exposures were completed to determine the effects of salinity alone so that effects of the chemical composition of the fracking fluid could be isolated.
Range finding experiments were carried out in order to locate preliminary LC50 and EC50 values from a broad range of chemical concentrations. Data were compiled
and various statistical analyses were run to explore significance of results and hone in on a more narrow range of concentrations to use in full early life stage tests.
Results were not included in statistical analysis if there was more than 10% death in the control.
pH testing
Salinity testing
24 hours 48 hours 72 hours 96 hours 120 hours
Figure 5: Photographs of the deaths of five zebrafish at different stages. Each fish was
exposed to the same concentration (1/20 fracking fluid dilution) but died at different times.
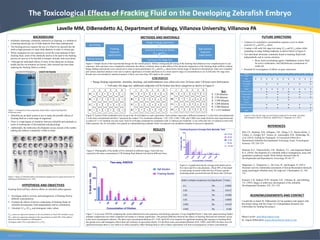
Figure 7: A two-way ANOVA comparing the results obtained from salt exposures and fracking exposures. Using GraphPad Prism 7, data were analyzed using Sidak’s
multiple comparisons test which compared cell means to evaluate significance. The greatest difference between the effects of fracking fluid and salt solutions occurs
in the more concentrated solutions. The three most concentrated dilutions (0.1, 0.05, and 0.02) were found to be significant meaning that exposure to fracking fluid
has greater toxic and teratogenic effects than salt solutions of equivalent salinity. For the three least concentrated dilutions (0.01, 0.005, and 0.002) the data were not
significant because there is very little to no effect caused by either fracking fluid or salt so future experiments will look at teratogenicity in these concentrations.
Key:
1: 1/20 dilution
2: 1/50 dilution
3: 1/100 dilution
4: 1/200 dilution
5: 1/500 dilution
C:1 x E3 medium
Sidak's multiple comparisons test Significant? P Value
0.1 Yes 0.0001
0.05 Yes 0.0117
0.02 Yes 0.0383
0.01 No 0.9859
0.005 No 0.4129
0.002 No 0.566
RESULTS