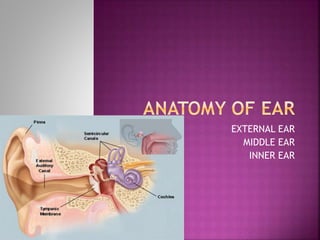
Anatomy of ear
- 2. PINNA/ EAC/ TM
- 3. Yellow elastic cartilage covered with skin Except Lobule (fat) and Incisura terminalis (endaural incision) Lateral surface – folds and hollows Helix/ anti helix Tragus/ anti tragus Crus of helix Scaphoid fossa Triangular fossa Cavum concha Cymba concha
- 4. Cartilage provides shape to auricle Skin of lateral side adherent to cartilage with minimal subcutaneous tissue – FROST BITE Cartilage extends medially to form EAC Epithelium – stratified squamous, hair follicles, sebaceous glands Medial surface/ cranial More sc tissue Skin loosely attached to cartilage – sebaceous cyst/ abscess USED AS GRAFT IN RHINOPLASTY (CONCHAL) AND TYMPANOPLASTY (TRAGUS/ CONCHA/ FAT LOBULE
- 5. Pinna connected to surrounding structures by ligaments and muscles Ligaments – extrinsic/ intrinsic Muscles – Extrinsic – ant, post and sup auricularis Intrinsic – tragicus, anti tragicus, helicus major, minor Facial N Blood supply ECA branches – post auricular artery, superficial temporal and occipital Venous drainage - EJV, common facial vein
- 6. Nerve supply of pinna Lateral surface Ant sup part, tragus, crus of helix – Auriculo temporal nerve (V3) Lat concha, anti helix – facial nerve (VII) Concha – arnold’s nerve (X) Post part of lateral surface, lower part, lobule – greater auricular nerve (C2,C3) Medial surface Upper 1/3 rd – lesser occipital nerve (C2) Lower 2/3 rd – greater auricular nerve (C2,C3)
- 8. Only Cul – de – sac in the body lined by skin Extends from concha to TM S shaped, 24 mm, 8 mm (outer 1/3rd) cartilaginous, 16 mm (inner 2/3rd ) bony Infants – cartilage part remains collapsed as bony part not developed Cartilage part - Directed backwards, upwards, medially, bony part – forwards, downwards, medially Isthmus – narrowest part medial to junction, 5 mm from TM – FB impaction Bony part formed by temporal bone (tympanic and squamous part)
- 10. Carilage and bony part attached by fibrous tissue Skin – cartilaginous part – thick (both epidermis and dermis), firmly adherent to cartilage, contains hair follicles, ceruminous, pilosebaceous glands Bony – skin thin, only epidermis no dermis, no glands, hair follicles 4 walls – roof, floor, anterior and posterior Floor and anterior wall are longer Ant wall proximal to TM joint, near TM forms a blind pouch called Anterior Recess (FB, discharge, debris)
- 11. Bony canal – Anterio inferior area deficient – Foramen of Huschke (till 4 years age) – parotid infection Floor/ ant wall cartilage part – deficiencies – Fissures of Santorini (two in number) – infection from parotid and mastoid Relations Ant – TM joint, Parotid Post – Mastoid, Facial N Sup – Middle cranial fossa Inf – Parotid Medial – TM (oblique) Lateral - Concha
- 12. Epithelial migration – self cleansing mechanism – medial to lateral Lymphatic drainage Pre auricular LN (ant wall) Post auricular LN (post wall) Retro auricular/ Infra auricular LN (floor and lobule) Nerve Supply Anterio superior part – Auriculo temporal nerve (V3) Posterio inferior part – Arnold’s nerve (X) – cough reflex
- 14. Thin, semi transparent, pearly white, lying obliquely medial to EAC, 55 degree to floor Forms lateral wall of middle ear Separates external and middle ear Vertical diameter 9-10mm, AP diameter 8-9 mm, thickness 0.1-0.15 mm Parts Pars tensa – pearly white, below malleolar folds Contains 3 layers – outer epithelial continous with skin of EAC, Middle fibrous contains inner circular, outer radial and parabolic fibres and inner mucosal continous with middle ear mucosa
- 15. Peripheral part thickened and made of fibrocartilaginous ring called annulus tympanicus Deepest part in middle – umbo attached to handle of malleus Can be divided into 4 quadrants – ant sup, ant inf, post sup and post inf Ant inf part illuminated when light reflected on TM – light reflex (cone of light) Pars flaccida/ Shrapnell’s membrane Pinkish triangular area fits in notch of rivinus above malleolar folds, no middle fibrous layer – thin No annulus tympanicus Short/lateral process of malleus
- 18. Blood supply Outer (lateral surface) – Manubrial artery, Maxillary artery – deep auricular branch Inner (Medial surface – Maxillary artery – anterior tympanic branch, stylomastoid artery – posterior tympanic branch, ascending pharyngeal artery – inferior tympanic branch, middle meningeal artery Venous drainage Outer surface – EJV Inner surface – Transverse sinus, venous plexus around ET
- 19. Nerve Supply Outer surface – Auriculo temporal nerve supplies the anterior ½ Arnold’s nerve – posterior 1/2 Inner surface – Tympanic plexus – Jacobson’s N (IX)
- 20. MIDDLE EAR CLEFT Tympanic cavity along with Eustachian tube, aditus ad antrum, mastoid antrum and mastoid air cells Filled with air
- 21. Pharyngo tympanic tube Connects Tympanic cavity to Nasopharynx Equals/maintains pressure in tympanic cavity 36 mm long 2 parts – upper 1/3rd bony – tympanic part(12 mm) Lower 2/3rd cartilage – nasopharyngeal part ( 24 mm) The two parts meet at isthmus (narrowest part) – 160 degree angle at junction Nasopharyngeal part – closed at rest/collapsed , opens on yawning, present behind the post end of inferior turbinate, narrowest at this end Torus tubaris, Fossa of rosenmuller
- 22. Ostmann’s pad of fat – fibrofatty tissue in relation to nasopharyngeal part, keeps ET closed, protects from nasopharyngeal reflux and secretions Tubal tonsils – hypertrophy causes ET obstruction Infants ET wider, shorter, more horizontal Tubal cartilage is flaccid Less ostmann’s fat Length 13-18 mm, bony part longer than 1/3rd – milk can enter during feed – head up position
- 23. Muscles – Tensor palati (V3), Levator palati, Salpingopharyngeus (Pharyngeal plexus) Epithelium – pseudostratified ciliated columnar Nerve supply – Tympanic plexus Blood supply – ascending pharyngeal artery, middle meningeal artery, artery of pterygoid canal Venous drainage – Pterygoid plexus Functions Ventilation of middle ear cleft, equalises middle ear pressure with atmospheric pressure Prevents reflux of nasopharyngeal secretions into middle ear Drainage of middle ear secretions
- 25. Biconcave irregular space in petrous part of temporal bone filled with air Vertical diameter and AP diameter – 15 mm Transverse diameter – 6 mm at upper part, 2mm at center and 4 mm at lower part Six sided – roof, floor, ant wall, post wall, medial wall, lateral wall Three parts – epitympanum, mesotympanum, hypotympanum Three ossicles (tiny bones) – malleus, incus, stapes Two muscles – tensor tympani, stapedius
- 27. Epitympanum – attic – above malleolar folds of TM, medial to pars flaccida Contains head of malleus, body and short process of incus, incudo malleolar joint Connects with mastoid antrum via aditus – posteriorly Connects with mesotympanum via isthmus tympanic anticus and posticus Lined by pavement epithelium (cuboidal) Mesotympanum – medial to pars tensa Anterior mesotympanum – connects with nasopharynx via ET – respiratory epithelium Protympanum – around ET Hypotympanum – below level of TM, resp epithel
- 28. Ventilatory anatomy Nasopharynx ---air-- ET ------ Anterior mesotympanum ----Isthmus tympanic anticus ---- Anterior epitympanum ----- 1 Posterior epitympanum ----- Isthmus tympanic posticus ----- Posterior Mesotympanum ----- Hypotympanum 2 Posterior epitympanum - Aditus -- Mastoid antrum and air cells ----Posterior wall ---- Hypotympanum
- 29. Walls Roof – tegmen wall separates from middle cranial fossa, thin plate of bone – tegmen tympani Floor – Thin plate of bone separates from IJV bulb located in jugular fossa, can be deficient Lateral wall TM – separates from external ear Scutum or outer attic wall – made up of squamous part of temporal bone, upper part of lateral wall
- 30. Medial wall/labyrinthine wall Separates middle ear from inner ear Promontory – bony round bulge of medial wall by basal turn (coil) of cochlea, most prominent part Tympanic plexus lies on promontory Bony lateral semicircular canal – post sup to promontory, above oval window Fenestra vestibuli (oval window) – between middle ear and scala vestibuli of cochlea, post sup to promontory, foot plate of stapes is placed in the window, fixed by annular ligament Size 3.25*1.75 mm Ponticulus and Subiculum – bony ridges in medial wall
- 31. Fenestra cochlea (round window) – post inf to promontory, separates middle ear from scala tympani of cochlea, closed ny secondary membrane, size 1.5*1.3mm Processus cochleariformis – hook like projection ant to oval window, tendon of tensor tympani related to it, genu of facial nerve lies here – denotes the start of horizontal part of facial nerve Facial nerve – lies in bony fallopian canal below oval window – horizontal part of facial nerve
- 33. Anterior wall Separate middle ear cavity from ICA Thin plate of bone Openings Upper – canal for tensor tympani muscle Lower – ET Canal for chorda tympani nerve – canal of Huguier Opening of carotid canal – glasserian fissure Anterior malleolar ligament Anterior tympanic artery
- 34. Posterior wall/ Mastoid wall Opening of aditus – upper part Pyramidal eminence/ processus pyramidalis – triangular bony projection, stapedius muscle tendon related to it Vertical portion of facial nerve – courses along post wall to exit in stylomastoid foramen Facial recess – suprapyramidal recess – direct assess can be made through it via post tympanotomy approach via mastoid without disturbing the post meatal wall Collection of air cells lying lateral to facial nerve Bounded by chorda tympani n, pyramid, post wall, fossa incudis
- 36. Sinus tympani/ infra pyramidal recess Medial to pyramid Mc location for cholesteatoma persistance even after surgery Separated from facial recess by pyramid Fossa incudis – contains short process of incus Opening for exit of chorda tympani nerve present in post wall
- 37. Relations of middle ear cleft Laterally – External ear Medially – Inner ear Anteriorly – ICA Floor – jugular bulb Roof – tegmen plate Posteriorly – lateral sinus Nerves related to middle ear cleft V, VI CN – close to apex of petrous pyramid VII CN – horizontal part (medial wall), vertical part (posterior wall)
- 38. OSSICLES 3 tiny bones, conduct sound energy from TM to oval window Malleus (Hammer) Largest and lateral most ossicle 8-9 mm long, 23-25 mg weight Contains head, neck, handle, lateral process Head lies in epitympanum Lateral process – knob like pojectionon outer surface of TM providing attachment to anterior and posterior malleolar folds, projects laterally from neck of malleus
- 40. Incus (Anvil) 25-30 mg Contains body, short process and long process Body – lies in epitympanum, articulates with head of malleus Short process – projects into epitympanum Long process – projects downwards behind handle of malleus, articulates with head of stapes via lenticular process and forms incudo stapedial joint
- 41. Stapes (Stirrup) Smallest ossicle 3.5 mm Contains head, neck, foot plate, ant crura and post crura Foot plate attached to oval window by annular ligament ALL OSSICLES ARE SUPPLIED BY ANTERIOR, INFERIOR AND POSTERIOR TYMPANIC ARTERIES
- 42. MUSCLES OF MIDDLE EAR Tensor tympani Tenses the TM, decreases the movement of ossicles so dampens loud sound before it enters inner ear Muscle for malleus, 1st arch muscle, supplied by mandibular nerve (V3), inserted into neck of malleus Stapedius Dampens loud sound Muscle for stapes, 2nd arch muscle, supplied by nerve to stapedius (VII), inserted into neck of stapes
- 44. NERVES OF MIDDLE EAR Chorda tympani Branch of facial nerve, enters tympanic cavity from posterior wall --- runs forwards medial to malleus and lateral to incus, runs on medial surface of TM ---escapes through anterior wall Carries taste fibres from ant 2/3rd of tongue Carries p.s secretomotor fibres to submaxillary and sublingual salivary glands
- 45. Tympanic plexus Lies on promontory Innervates the medial surface of TM, mastoid air cells, tympanic cavity, bony ET Carries secretomotor fibres to parotid gland Formed by - Jacobson’s nerve (IX) – sensory supply Plexus around ICA Motor supply – tensor tympani (V3), Stapedius (VII) Mastoid antrum – Meningeal branch of mandibular nerve (V3)
- 46. Blood supply ECA – maxillary artery, stylomastoid artery, ascending pharyngeal artery and middle meningeal artery ICA – carotico tympanic artery Venous drainage Ptreygoid venous plexus, sup petrosal sinus, sigmoid sinus Lymphatic drainage Pre auricular ln, retropharyngeal ln, upper deep cervical ln
- 47. Greek word “resemblance to breast” Air containing space in petrous part of temporal bone 9mm height, 14 mm width, 7 mm depth Not at birth, develop at 1 yr age, adult size at puberty (Facial N directly exposed) Aditus ad antrum Short canal connecting epitympanum to mastoid antrum Facial nerve, short process of incus lie on floor
- 48. Mastoid antrum Largest air cell of mastoid bone Ant – Aditus ad antrum Post inf- communicates with mastoid air cells Medially – post scc Lateral wall – cortex of mastoid bone, 1.5 cm thick Roof – Tegmen antrum, separates from middle cranial fossa Floor – formed by mastoid bone
- 49. Antrum lies 15 mm deep Clinically palpable at Cymba concha Mac Ewen’s triangle/ Suprameatal triangle Bony surface landmark of antrum Spine of henle lies in the triangle Bounded by Temporal line of suprameatal crest – linea temporalis – ridge extends from zygomatic process Post sup meatal wall Line connecting the two tangent to post margin of EAC
- 51. Mastoid air cells Types of mastoid - Cellular – well pneumatized – numerous large air cells – honey comb appearance - 80% - Sclerotic – acellular – absent air cells – due to ET blockage – 20% - Mixed – diploeic – small and less numerous air cells – narrow spaces Pneumatization begins in 1st year of life and is completed by 4-6 years of age
- 53. Classification of mastoid air cells A) Peripheral – dural, sinodural, perisinus, tip, retrofacial B) Central – periantral C) Accessory – peritubal, styloid, zygomatic, squamous, occipital Korner’s septum Persistant petrosquamous suture line/ bony plate between petrous and squamus part of temporal bone which separates squamous cells and petrosal cells Causes difficulty in locating the antrum and deeper cells
- 56. Articulates with 5 cranial bones – parietal, sphenoid, occipital, zygomatic, mandibular Forms base and lateral side of skull Pyramidal shaped Parts – squamous, petrous, tympanic and mastoid Petrous part separates middle and posterior cranial fossa Contents Bony part of external, middle eear including ossicles, inner ear Bony covering for sigmoid sinus and jugular bulb
- 57. Fallopian canal containing facial nerve Osseous canal containing ICA
- 58. Mixed nerve – sensory, motor, secretomotor fibers From pons to parotid Sensory – nerve of wrisberg (nervus intermedius) – solitary tract nucleus in medulla – carries taste sensation from ant 2/3rd of tongue (afferent fibers) / general sensation from skin of concha, EAC, TM Secretomotor – sup salivary nucleus in pons – secretomotor to lacrimal, submandibular, sublingual, nasal and palate glands (efferent fibers) Motor – motor facial nucleus in pons – supplies muscles of facial expression
- 59. Parts Supranuclear Infranuclear SUPRANUCLEAR/ INTRACRANIAL (15-17 mm) Motor fibers from Pons nucleus – hook around VI CN nucleus – travel through CP angle along with sensory fibers and VI and VIII CN – leave brain stem at ponto medullary junction Upper part of nucleus – innervate forehead muscles – receive fibers from both cerebral cortex (tracts both crossed and uncrossed) Lower part of nucleus – innervate lower face – receives fibers from opposite cerebral cortex ( crossed fibers)
- 61. Infranuclear Intratemporal Extratemporal INTRATEMPORAL IAM – stylomastoid foramen Parts Intrameatal Labyrintine Tympanic Mastoid
- 62. Intrameatal part Within IAC 8-10mm Passes along with VIII CN and internal auditory artery At fundus of IAC – sensory and motor fibers combine and enter fallopian canal Labyrinthine part From fundus of IAC – geniculate ganglion 3-5mm Narrowest part at entry of labyrinthine part (0.6 mm) Geniculate ganglion – 1st genu – here facial nerve takes a posterior turn Intrameatal part and labyrinthine part together form the petrous portion of facial nerve
- 64. Tympanic part Enters middle ear at geniculate ganglion (processus cochleariformis) Geniculate ganglion – oval window Horizontal part 10-12 mm At oval window (pyramid) nerve turns inferiorly – 2nd genu Mastoid part Vertical part 10-14 mm Oval window – stylomastoid foramen Intracranial – from nucleus to stylomastoid foramen
- 65. Extratemporal/ Extracranial From stylomastoid foramen to parotid Crosses the styloid process and divided into terminal branches in face BRANCHES Greater superficial petrosal nerve – arises at geniculate ganglion – carries secretomotor fibers to lacrimal glands and glands of nasal mucosa and palate, also brings taste fibers from hard and soft palate – 1st branch Nerve to stapedius – arises at 2nd genu( pyramidal eminence)- carries motor fibers to stapedius muscle
- 67. Chorda tympani – arises from middle of mastoid segment near stylomastoid foramen – carries secretomotor fibers to submandibular and sublingual gands. Also brings taste fibers from anterior 2/3rd of tongue Muscular branches after exiting stylomastoid foramen Posterior auricular nerve – supplies muscles of pinna, occipital belly of occipito frontalis muscle Digastric branch – to post belly of digastric Stylohyoid branch – to stylohyoid muscle
- 68. Terminal branches After crossing styloid process Upper temporofacial branch Temporal branch – supplies muscles of auricle, upper orbicularis oculi, frontalis, procerus – raises the eyebrow Zygomatic branch – supplies lower orbicularis oculi – tight shutting of eyes Buccal branch – middle part of face, muscles of nose, upper orbicularis oris, buccinator – showing of teeth
- 70. Lower cervicofacial Mandibular branch – lower orbicularis oris, muscles of lips and chin – whistling Cervical branch – supplies platysma – contraction of platysma BLOOD SUPPLY At CP angle – Ant inf cerebellar artery IAC – labyrinthine artery Geniculate ganglion – sup petrosal artery Tympanic and mastoid segment – stylomastoid artery
- 71. Communications IAC – VIII CN Geniculate ganglion – X CN (auricular branch) Outside stylomastoid foramen – IX, X, greater auricular nerve (C2,C3), Auriculotemporal nerve (V3) Lesser occipital nerve (C2) Neck – cervical cutaneus nerve
- 72. In petrous part of temporal bone b/w middle ear and IAC Parts Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth Perilymph – fluid b/w bony and membranous Endolymph – fills membranous labyrinth Has organs of both hearing and equilibrium
- 74. 3 parts Bony Vestibule Bony Semicircular canals (SCC) Bony Cochlea Bony Vestibule Ovoid central part of bony labyrinth 5mm X 3mm Lateral wall – related to middle ear, has bean shaped opening – fenestra vestibuli (oval window) closed by foot plate of stapes and surrounded by annular ligament
- 75. Medial wall – related to IAC Anteriorly or front ½ - marked depression called Spherical recess (lodges the saccule) Posteriorly or behind – another depression called Elliptical recess (lodges the utricle) Below elliptical recess – diverticulum called Vestibular aqueduct – through it passes the endolymphatic duct Spherical and Elliptical recess are separated by Vestibular crest – splits inferiorly to enclose Cochlear recess (for cochlear nerve filaments) Post part of vestibule – 5 openings of SCC Anteriorly – lies cochlea
- 77. Medial wall is perforated by minute holes called Macula cribrosa – for passage of vestibular nerve
- 78. BONY SEMICIRCULAR CANALS Posterior part of bony labyrinth 3 canals – superior(anterior), posterior (vertical), lateral (horizontal) Each canal 2/3rd of a circle Diameter 0.8 mm Lie at right angle to each other Contain membranous semicircular ducts Contain 2 ends – ampullated (dilated) and non ampullated. Both open into vestibule Ampulla contains sensory epithelium
- 80. Superior or anterior SCC Length 15-20 mm Ampullated ends opens into lateral part of vestibule Non ampullated end fuses with non ampullated end of posterior scc to form a common opening called crus commune – opens into medial part of vestibule ( so total 5 openings into vestibule) Forms arcuate eminence on petrous part of temporal bone Posterior or vertical SCC 18-22 mm Ampullated end (lower end) – opens into lower part of vestibule Non ampullated (upper end) – forms crus commune
- 81. Lateral/horizontal SCC Forms a round bulge into aditus and antrum of middle ear Length 12-15 mm Ampullated/anterior end – opens into upper part of vestibule Non ampullated/ posterior end – opens into lower part of vestibule (below opening of crus commune) Solid angle – angle formed by all 3 SCC
- 82. BONY COCHLEA Anterior part of labyrinth Coiled tube like a snail 30-35 mm long, 5 mm from base to apex, 9 mm across its base Has 2 3/4 turns around a conical central pyramid of bone called Modiolus (has perforations for cochlear nerve) Basal turn of cochlea – promontory in medial wall of middle ear Within it lies membranous cochlea Osseous spiral lamina – thin plate of bone projects into modiolus, divides cochlea into 3 compartments (longitudinal channels)
- 83. Scala Vestibuli – above – communicates with middle ear through oval window, closed by foot plate of stapes Scala Tympani – below – communicates with middle ear through round window, closed by secondary tympanic membrane Both of these communicate with each other at apex of cochlea through helicotrema Filled with perilymph Scale Media – Cochlear duct – in between – part of membranous cochlea
- 86. Membranous vestibular labyrinth Membranous semicircular ducts Membranous cochlear duct Contains endolymph Lies within bony labyrinth floating on perilymph Membranous Vestibule Contains Saccule Utricle Endolymphatic duct and sac
- 88. Saccule – globular in shape Lies in anterio inferior part, occupies spherical recess Connected to cochlear duct by membranous ductus reuniens Connected to utricle by utriculo saccular duct which forms endolymphatic duct and ends up in endolymphatic sac Utricle – oblong and irregular in shspe Lies in posterio sup part, occupies elliptical recess Connected to 3 semi circular ducts by 5 openings Bigger than saccule
- 89. Macula Vestibular receptor organ Neuroepithelial organ of saccule and utricle For static balance, responds to gravitational changes and linear acceleration and deceleration Composed of hair cells (saccule – 18000, utricle – 33000) and supporting cells Hair cells – type I – centre part (flask shaped) type II – peripheral part (cylindrical shaped) Also contains a gelatinous mass composed of muco ps and calcium carbonate secreted by supporting cells – otolith/ statoconia/ otoconia
- 91. Semicircular ducts Within scc Ampullated end contains neuroepithelium called cristae (saddle shaped) Contains hair cells and supporting cells Gelatinous mass is called cupula Hair cells contain one large kinocilium and 65-110 small steriocilia Responds to angular acceleration and deceleration Organ for kinetic balance
- 92. MEMBRANOUS COCHLEA/ COCHLEAR DUCT/ SCALA MEDIA Occupies mid portion of cochlear canal Connected to saccule through ductus reuniens Anterior most part Triangular shape Boundaries Floor – Basilar Membrane – supports Organ of Corti Roof – Reissner’s Membrana – separates it from Scala Vestibuli Lateral wall – Stria Vascularis – secretes endolymph, contains vascular epithelium, maintains ionic composition and electronic potential of endolymph
- 93. Organ of Corti Neuroepithelium situated on the basilar membrane Sensory organ of hearing Spread like a ribbon along entire length of basilar membrane Contains 2 rows of rods of inner and outer hair cells Inner hairs cells – one row – 3500, flask shaped Outer hair cells – 3-4 rows – 12000, cylindrical Hair cells are receptor cells of hearing, convert sound energy -> electrical energy
- 94. Terminal fibres of cochlear nerve are in contact with hair cells Hair cells are separated by supporting cells and dieter cells Tectorial Membrane – overlies organ of corti, contain gelatinous material Sheering force between organ of corti and tectorial membrane – cxause hair cell stimulation Organ of corti contains cortilymph( resembles perilymph) No blood supply. Depends on stria vascularis for oxygen
- 97. Inner ear fluids Perilymph – fills the space between bony and membranous labyrinth, resembles ECF and CSF, plasma Rich in sodium ions, proteins, glucose CSF reach labyrinth via cochlear aqueduct Endolymph – fills membranous labyrinth, resembles ICF Rich in potassium ions Secreted and absorbed by stria vascularis and endolymphatic sac
- 98. ENDOLYMPHATIC DUCT AND SAC Ducts from utricle and saccule form utriculo saccular duct -> this continues as endolymphatic duct (passes through vestibular aqueduct) -> terminal part dilated to form endolymphatic sac Regulates pressure of membranous labyrinth Role in reabsorption and regulation of endolymph
- 100. ARTERIAL SUPPLY Basilar artery -> Ant inf cerebellar artery -> Internal Auditory Artery 3 branches Ant vestibular artery – supplies utricle, superior and lateral scc Vestibulo cochlear artery – 1. posterior vestibular artery – supplies saccule, post scc 2. cochlear branch – supplies cochlea (10%) Main cochlear artery – supplies cochlea (90%)
- 102. VENOUS DRAINAGE Internal auditory vein, vein of cochlear aqueduct, vein of vestibular aqueduct -> labyrinthine vein -> inferior petrosal sinus, sigmoid sinus, lateral venous sinus
- 103. Lined by dura Length – 1 cm In petrous part of temporal bone Medial end – related to inner ear Lateral end – has numerous apertures for - VII CN - VIII CN - Internal auditory artery - Internal auditory vein
- 105. In IAC – divides into Anerior – Cochlear N Posterior – Vestibular N COCHLEAR NERVE Fibres of cochlear nerve from IAC reach the modiolus to form spiral ganglion Bipolar cells of spiral ganglion of cochlear nerve innervate the hair cells of organ of corti (95% IHC, 5% OHC) to form the auditory pathway
- 106. Vibration of stapes footplate -> movement of inner ear fluids -> displaces basement membrane -> stimulates organ of corti 1st order neurons – spiral ganglion of cochlear nerve Gives 2 processes Peripheral process – innervates hair cells of organ of corti Central process – terminates in dorsal and ventral i/l cochlear nuclei (2nd order neurons) Terminate into lateral lemniscus on both sides (u/l and c/l)
- 107. Terminates into sup olivary nucleus (c/l or i/l) – 3rd order neurons Terminates into inf colliculus (c/l or i/l) – 4th order neurons Terminates into medial geniculate body of thalamus – 5th order neurons From here axons pass into auditory cortex in cerebrum Area of cortex associated with hearing – Brodmann’s area - 41
- 109. Emerges in post part of IAC where it forms scarpa’s ganglion containing bipolar cells of vestibular nerve which form the vestibular pathway Vestibular nerve divides into Superior vestibular nerve – innervates macula of utricle and anterior part of saccule and cristae of anterior and lateral semicircular ducts Inferior vestibular nerve – innervates macula of posterior part of saccule and cristae of posterior semicircular ducts
- 110. Scarpa’s ganglion form 1st order neurons Terminate into vestibular nuclei in floor of IVth ventricle which forms the 2nd order neurons Vestibular nuclei – superior (receives fibres from semicircular ducts), inferior, medial and lateral nuclei (receives fibres from utricle and saccule) Vestibular nuclei terminate into Oculomotor nuclei (3rd order neurons) Terminate into effector organs (ocular and postural)
- 111. Efferent from vestibular nuclei into ANS – responsible for nausea, vomiting, sweating Motor part of spinal cord – coordination movements of head, neck and body Cerebellum – maintain body balance External ocular muscles
- 113. Branchial apparatus (4th and 5th week) Consists of Branchial arches (pharyngeal) Clefts or groove on outer aspect Pouches on inner aspect Cervical and occipital myotomes
- 114. Development of sound conducting apparatus (External Ear and Middle Ear) and sound perceiving apparatus (Inner Ear) is from different structures and independent of each other EXTERNAL EAR AND MIDDLE EAR PINNA From six tubercles/hillocks of His around 1st branchial cleft 1st tubercle of His from 1st branchial arch leads to formation of tragus 2nd to 6th from 2nd branchial arch
- 115. Starts at 6th week of IUL completed at 20th week Defective fusion of 1st and 2nd arch – preauricular sinus Failure deveopment of tubercles – anotia Failed development of 4th tubercle – anti helix defect – bat ear deformity EAC Develops around 1st branchial cleft between 8th and 10th week of IUL
- 117. TYMPANIC MEMBRANE Develops from membrane separating 1st branchial cleft and 1st pharyngeal pouch From all 3 germinal layers Outer epithelial layer – from ectoderm Middle fibrous layer – from mesoderm Inner mucosal layer – from endoderm TYMPANO MASTOID CAVITY From tubotympanic recess (1st pharyngeal pouch) Eustachian tube – from proximal narrow part Middle ear – from distal dilated part
- 118. Ossicles Malleus and Incus – from mesoderm of 1st arch Stapes suprastructure – from 2nd arch Stapes footplate and annular ligament – from otic capsule
- 119. Starts in 3rd week of IUL and completed by 16th week Develops from otic capsule Thickening of ectoderm of hind brain -> Formation of Otic Placode -> Invaginates into otocyst (otic cyst or capsule) Differentiates to form Membranous labyrinth Mesoderm around otic capsule -> leads to formation of bony labyrinth Development of pars superior – utricle and SCC much earlier than pars inferior – saccule and cochlea