Final features of 8086_microprocessor
•Download as PPT, PDF•
0 likes•693 views
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Difference between 8085 and 8086 microprocessor Architecture

Difference between 8085 and 8086 microprocessor Architecture
Final features of 8086_microprocessor
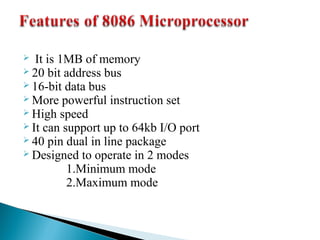
- 1. It is 1MB of memory 20 bit address bus 16-bit data bus More powerful instruction set High speed It can support up to 64kb I/O port 40 pin dual in line package Designed to operate in 2 modes 1.Minimum mode 2.Maximum mode